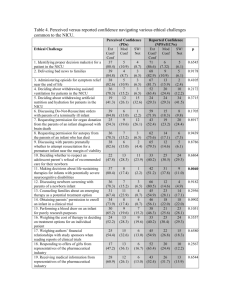
Newborn Initial Care Notes
1
Newborn Initial Care
Chapter 24: pp. 620, 783, 826- 827, 832, 958-962
First Hour after delivery of infant:
First Priority is Respirations –
Suction Mouth then Nose
Assess color
Signs of distress (see below)
Second Priority is Temperature-
Dry Infant Off, Stimulate, and get rid of wet towel
Continual temperature regulation to prevent heat loss
Wrap Infant
_______________________
________________________
Warm all Equipment
___________________________
Third Priority is Apgar Score-
at 1 and 5 minutes
Heart Rate – absent, above or below 100; count _____________ and add a zero
Respiratory Effort- absent, irregular or good
Reflex Irritability- absent, grimace or ____________________ when stimulated
Muscle Tone- flaccid, some flexion, active motion
Color- cyanotic, ____________________, pink
Good condition is _______________
4-7 needs stimulation
< 4 needs resuscitation
Fourth Priorities include-
Infant Security
Identification Bands: one to mother, one to significant other, two to newborn (one on wrist and one on ankle)
Apply bands snuggly with one finger between
Keep on until DC
Some have alarms on band
Staff must all wear Pink ID badges.
Instruct all mothers to _____________________________ to anyone who does not have this badge and to keep infant away from door
Umbilical cord cut and clamp
Weight and length
Fifth Priority is Attachment-
Dim lights
_________________________
_________________________
Breast feeding or initiate feeding
Alone time with infant
Newborn and GA Assessment within the two hours after delivery
Signs of Neonatal Distress (
Infants Needing Stabilization
)
Low Apgar
________or LGA infants
Increased respiratory rate or difficult respirations
Sternal, substernal, or intercostal retractions
_____________________________
______________________________
Excessive mucus
Facial grimacing
__________________ (central-skin, lips, tongue)
Temperature _________________ (hypothermia or hyperthermia)
Heart Rate- < 110 or > 160
Respirations - <30 or above 60
Jitteriness or glucose less than the 40mg
First Period of Reactivity
• Lasts _________________
• Awake
• Active
• Hungry
• Respirations rapid with transient signs of distress
• Heart rate ___________ and ________________________
• Bowel sounds absent
Risks for Cold Stress
Who is at risk?
• Premature
• _________
• Hypoxemia in labor or in-utero
• Intracranial hemorrhage
• CNS abnormality
2
• __________________________ (premature, LGA ,SGA, IUGR, mothers with GDM or HIP, males, respiratory distress, sepsis, anomalies, epidural anesthesia)
Prevention
• ____________________: Immediately dry infant at birth/after bathing.
• ____________________: Avoid placing infant on cold surface
• ____________________: Avoid cold drafts
• Radiation: Maintain warm environmental
• Unwrap only what is necessary
Signs of Cold Stress:
• Increased movement
• Increased respirations with episodes of ___________________________
• Decreased _____________________ or unstable
• Peripheral vasoconstriction
• Metabolic acidosis
• ________________________
• __________________________
• Hypoxia with decreased surfactant production and atelectasis
Thermoregulation: Don’t use the warmer read out for your assessment
97.2 to 97.6
• Temperature under _______________________
• Document both temps
• Skin to skin with hat on and warm blanket
• Breastfeed or radiant warmer (no blanket or hat on; use probe under warmer)
97.1 Or less
• Temperature under each arm
• Document both temps ___________________________
• Radiant warmer ________________________________
• Re-warm ___________________; about one degree per hour
• Check for hypoglycemia
Once temperature is achieved, wrap, recheck in __________________________ then hourly
Hypoglycemia: 0- 12 hours old
Who is at risk?
• Premature (< 37 weeks)
• LGA , SGA or IUGR
• Mothers with GDM, HIP, or Terbutaline
• Polycythemia (twins)
• _____________________
3
• ______________________
• Anomalies
• Males
• Epidural anesthesia
Prevention
• _________________________________- Assess newborn for risk factors
• Check blood glucose as appropriate for infants at risk (preterm, mother DM, etc.)
• Provide early, frequent feedings.
• _________________________
• Ensure no respiratory distress
Hypoglycemia Signs
• Glucose of < 40 mg/dl
• Lethargy or limp or hypotonia
• __________________________
• Irritable
• High-pitched cry
• Poor feeding or vomit or loss of swallow reflex
• Hypothermia or _______________________
• Cyanosis or pale
• _______________ or irregular breathing
• Seizures or exaggerated moro
Steps of Heel Stick
ID infant
Medial or lateral aspect of heel
Pre-warm heel
Flex foot
Clean with alcohol
Dry with gauze
Puncture heel
Wipe first drop
Apply blood to glucometer; fill the strip
Apply pressure to site
Algorithm for Birth to Four Hours of Life
Blood Sugar Testing
Normal BS (> 40 mg/dl glucose level)
Test in the presence of risk factors or symptomatic
Within the 30 minutes to one hour of life
Breastfeed if no symptoms
Monitor 24 hours if SGA, LGA, IDM
4
Symptomatic
Check immediately
< 40m
Serum level
Notify Neonatologist
Notify NICU
Feed
Recheck in one hour
> 40
Feed
Notify pediatrician
Asymptomatic with High Risk Factors
Initiate feeding within 30 to 60 minutes
Screen 30 minutes after feeding or within 2 hours of birth
>40
Recheck before the next three feeding or within 3 hours of last check
>30-39
Serum level
Feed
Recheck in one hour
If 30-39 again notify pediatrician and NICU STAT for venous serum level
Critical Value < 30 mg/dl or Symptomatic and < 40 mg/dl
Notify Neonatologist
Notify NICU STAT to determine if admitted to NICU
Venous serum level
Possible IV D10W 2 ml/kg
Feed
Recheck in one hour
Continues < 30, transfer to NICU
>30-39 or > 40 follow pathways above
Feeding
Skin to skin
Breast feed immediately (if not latching within 15 to 30 minutes, express mild and colostrum)
If continues to not eat, bottle feed 3-10 ml/kg by the first hour of life
5