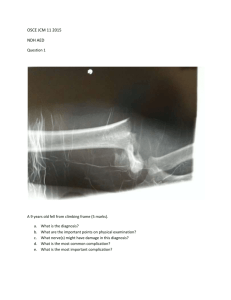
Lviv - 2015
advertisement

MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF UKRAINE Danylo Halytskyy Lviv National Medical University First Vice Rector of scientific and pedagogical work Professor. M.R. Hzhehotskyy ___________________________ "______" ______________2015 Year Department of Pediatric Surgery, Orthopedics and Traumatology Subjects "Pediatric Surgery" Supporting Department: Dnipropetrovsk State Medical Academy Syllabus of pediatric surgery for university students III – IV of level accreditation Specialty: 7.12010001 "Medicine" Approved at methodological meeting Protocol № __10___ "__12 __ '______ 06______ 2015. Head of Department prof. AY. Nakonechnyy ___________________________________ Approved by the Commission on the methodical of surgical disciplines Protocol № ___59____ "__19__" _____06_________ 2015. Committee Chairman Prof. V.P. Andryushchenko ____________________________________ Lviv - 2015 EXPLANATORY NOTE I. The work program of pediatric surgery are based on cross-cutting work program on the subject "Surgery" for higher educational institutions Ukraine III-IV accreditation levels and on the basis of the curriculum by order number 1226 of 04.24.2015 on-year for the specialty "Medicine" 7.12010001 , 7.12010002 "Pediatrics" 7.12010003 "Medical prophylaxis" towards training 1101 "Medicine". According to the curriculum in 2005 in the version of 2007 study of the course is conducted as a single discipline, ensuring the principle naskriznosti teaching. The purpose of studying pediatric surgery: learning theoretical and practical knowledge of the etiology, pathogenesis, typical and atypical clinical presentation, diagnostic methods, differential diagnosis, conservative and surgical treatment and rehabilitation of children with surgical pathology within the limits of appropriate preparation doctor general. The ultimate goals of discipline: • Identify common clinical syndromes and symptoms in the children's clinic of surgical diseases; • diagnose and provide medical care in emergency conditions in the clinic childhood diseases; • To interpret the general principles of treatment, rehabilitation and prevention of the most common surgical diseases and injuries in children; • To determine the prognosis for life, health and quality of life in common surgical diseases and injuries in children; • draw up a plan of survey and interpret the results of laboratory and instrumental methods of examination in children; • Demonstrate the ability to perform the necessary medical procedures; • Provide emergency medical assistance in urgent states in pediatric surgery; • Demonstrate the ability to conduct medical documentation; • To demonstrate the moral and ethical principles of medical specialist and principles of professional subordination in surgery. The program content I. Pediatric Surgery, bases transplantation. 1. Urgent Children's Surgery. 2. Neoplasms of tissues. II. Malformations in children the basics transplantation. A structured training plan for pediatric surgery "Medicine" The structure of the number of hours of study Year Type of control Credit ECTS total of classes CPC Lectures Practical classes I. Pediatric Surgery, bases transplantation. 1.Urhentna pediatric surgery. 2. Neoplasms of tissues. 1.5 45 6 28 11 5 differentiated credit Malformations in children the basics transplantation. 30 January - 18 June 12th test A structured training plan for pediatric surgery "Medical prophylaxis" The structure of the number of hours of study Year Type of control Credit ECTS total of classes CPC Lectures Practical classes I. Pediatric Surgery, bases transplantation. 1. Urgent Children's Surgery. 2. Neoplasms of tissues. 1.5 45 6 28 11 5 differentiated credit II.Vady development in children, bases transplantation. 30 January - 18 June 12th test A structured training plan for pediatric surgery "Pediatrics" The structure of the number of hours of study Year Type of control Credit ECTS total of classes CPC Lectures Practical classes I.Dytyacha surgery, transplantation bases. 1. Urgent Children's Surgery. 2. Neoplasms of tissues. 1.5 45 6 28 11 5 differentiated credit Malformations in children the basics transplantation. 4.5 135 0 90 45 6 test Media scope of the discipline Pediatric surgery, transplantation bases. 1. Urgent Children's Surgery. 2. Neoplasms of tissues. Specific goals: - Diagnose urgent states in pediatric surgery clinic and provide emergency medical care to the child; - Determine the tactics of a child suffering from major surgical disease; - Identify the different clinical manifestations and complications set a preliminary diagnosis of surgical diseases in children and herbs; - Learn to recognize the major clinical manifestations of soft tissue tumors. - Learn to differentiate from tumors depending on the type of tumor. - Learn to identify signs of malignant transformation of tumors and complications (bleeding, inflammation, nerve compression, vascular lesions and others.) Treatment guidelines to treat soft tissue tumors and their complications Theme 1. Acute appendicitis, peritonitis in children. Anatomical and physiological characteristics of the abdominal cavity in children. Acute appendicitis in children. The complicated forms of acute appendicitis, appendiceal abscess, peritonitis, infiltration. Primary peritonitis. Peritonitis newborns. Necrotizing enterocolitis. Causes, clinical classification. Surgical complications. Principles of surgical treatment. Features of NEC in infants with extremely low birth weight. Clinic. Rehabilitation after surgery. Theme 2. Acquired intestinal obstruction. Adhesive obstruction. Intussusception. Classification, pathogenesis, prevention of postoperative adhesive intestinal obstruction. Principles of treatment of adhesive intestinal obstruction. Etiology, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis of idiopathic intussusception in children. Differential diagnosis of infectious diseases. Indications for conservative and surgical treatment, prevention of complications. Short bowel syndrome. Principles intestinal transplantation. Theme 3. Congenital intestinal obstruction. Pyloric stenosis, pilorospazm. Hirschsprung's disease. Causes. Methods for early diagnosis and treatment. Esophageal atresia. Atresia anus. Pathogenesis, clinical manifestations pyloric stenosis, pilorospazmu, diagnostic methods, treatment methods. Congenital ahanhlioz intestine, forms, clinical signs, diagnostic methods and treatment. Theme 4. Urgent children's urology. Obstuktyvni defects and urinary tract disease, hydronephrosis, uretrohidronefroz, vesico-ureteric reflux, mehaureter, infravezkalna obstruction. Chronic lung disease, renal colic, calculous pyelonephritis. Etiopathogenesis, clinical features, differential diagnosis, treatment and prevention. Syndrome swollen scrotum, vulva injury, incarcerated inguinal hernia and tense hidrofunikulotsele, testicular torsion and spermatic cord, testicular torsion hidatyd, orchitis, orhopididymit. Etiopathogenesis, clinical features, differential diagnosis, treatment and prevention. Topic 5. Purulent septic diseases of bones and joints in children. Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis. Infectious diseases of soft tissues. Purulent diseases of lung, pleura and mediastinum. Surgical sepsis. Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis, osteomyelitis metaepifizarnyy newborns atypical forms of osteomyelitis (Brodie abscess, antibiotic osteomyelitis, sclerosing osteomyelitis Harry). Etiopathogenesis, classification, clinic, diagnostic features, principles of treatment, especially surgery in children of different age groups, prevention of complications. Clinical examination. Infectious diseases of soft tissues. Phlegmon newborns purulent mastitis, lymphadenitis, erysipelas. Purulent diseases of lung, pleura and mediastinum. The acute destructive pneumonia (ODS) vnutrishnolehenevi form. The acute destructive pneumonia (ODS) (pulmonary and pleural form): piotoraks, pneumoempyema, pneumothorax. Classification, etiopathogenesis, diagnosis, conservative, instrumental and surgical treatment. Complications and their prevention. Mediastinitis. Causes, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, conservative and surgical treatment, complications, prognosis. Surgical sepsis. Syndrome of systemic response to inflammation. Sepsis. Septic shock. The syndrome of multiple organ failure. Basics of antimicrobial therapy in children. 6. Subject multiple trauma in children: traumatic illness; traumatic shock. Syndrome mutual encumbrance types of traumatic injuries. The degree of severity of traumatic shock: diagnostic criteria for emergency aid. Closed trauma of the abdomen and pozaocherevynoho space: Injury hollow organs: the mechanism of injury, clinical manifestations, diagnostic algorithm, first aid. Principles of surgical treatment. Injury parenchymal organs: trauma pancreas, liver, spleen, kidneys, bladder, urethra. Pseudocyst pancreas, traumatic pancreatitis. Signs intraperitoneal bleeding. Indications for conservative and surgical treatment. Hemobiliya. Diagnosis, treatment principles. Injury to the chest and the chest cavity. Definition of basic concepts. Etiology. Pathogenesis. Classification. Clinic. Psychological characteristics of patients. Course. Complication. Methods, diagnosis, differential diagnosis. Surgical tactic. Principles of surgical treatment. Methods of surgery. Methods rehabilitation tracheobronchial tree. Puncture of the pleural cavity. Drainage of the pleural cavity. The effects of surgical treatment. Damage to the esophagus, guardianship and foreign bodies. Rehabilitation patients. Bleeding of the gastrointestinal tract in children. Portal hypertension. Clinical and differential diagnosis of gastrointestinal bleeding in children with gastroesophageal reflux, hemorrhagic gastritis, portal hypertension, gastric ulcer, 12 duodenal ulcer, Meckel diverticulitis, polyps and polyposis bowel disease (Peyts-Jeghers). Options for surgery, reconstruction and transplant organs - liver and intestine. Theme 7. Features of childhood cancer. Benign and malignant tumors of embryonal tumors: teratoma, teratoblastoma; nefroblastoma; neuroblastoma; leyo-, rhabdomyosarcoma. Bone tumors. Benign (hemangioma, hamartoma, hepatocellular adenoma) and malignant (hepatoblastoma, hepatocellular carcinoma) tumors of the liver. Peculiarities, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, likvannya outlook. Vascular abnormalities: vascular tumors (hemangiomas are rare tumors), vascular malformations (slow blood flow - capillary, venous, lymphatic, mixed, with rapid blood flow (arterio-venous). Etiology, pathogenesis, clinical, modern principles of classification and treatment. Clinical supervision . Clinic. Malformations in children the basics transplantation. For students in specialties "General Medicine", "Medical-prophylaxis" Theme 1. Malformations of the respiratory system. Organic, compression and functional stenosis. Vascular rings and loops. Diverticulum, cysts, tumors. Agenesis, aplasia, hypoplasia of the lungs. Congenital pulmonary cysts. Congenital emphysema. Pulmonary sequestration. Esophageal atresia. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: hernia own diaphragm; hiatal hernia, eventration (relaxation) of the diaphragm. Features prenatal diagnosis. Clinical manifestations. Complications and their prevention. Modern principles of diagnosis and treatment. 2. Subject defects which appear intestinal obstruction. Congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Duodenal intestinal obstruction (stenosis, atresia, the membrane of the duodenum, pancreas kiltsevydna). Anomalies rotation and fixation of the intestine. Physiological rotation of the intestine. Syndrome (triad) Lyedda; midgut volvulus. Complications rotational abnormalities and their prevention and treatment. Atresia and stenosis of small intestine and colon. Lines. Pre- and postnatal diagnosis. Treatment. Hirschsprung's disease. Etiology. Clinical manifestations. Diagnostics (anomanometriya, radiography, biopsy). Principles of surgical treatment. Complications and their prevention. Intestinal dyshanhlioz, hipohanhlioz and other intestinal dysmotility. Mekonialna intestinal obstruction. Etiology, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations. Conservative and operative treatment. Complications (gastrointestinal and pulmonary). Anorectal malformations. Anatomical classification, Herbal tactics weather. Malformations of the anterior abdominal wall. Omphalocele. GS. Prenatal diagnosis. Differential diagnosis. Emergency aid. Principles of surgery. Rare forms of defects of the anterior abdominal wall. Syndrome "plum stomach." Umbilical and inguinal hernia. Features of clinical manifestations. Complication. Principles of treatment in children. Features surgery in infants. Malformations of the liver and biliary tract. Biliary atresia. Etiology, pathophysiology. Clinical manifestations maozhlyvosti early diagnosis. The principles of operating treatment. Portoenteprostomiya (Kasai operation) and liver transplantation. Postoperative management of patients. Opportunities to improve treatment outcomes biliary atresia. Cysts of the liver and choledochus. Classification. Etiology, pathophysiology. Diagnosis. Surgical treatment. Complications forecast. Theme 3. Malformations of the musculoskeletal system. Methods of early diagnosis and early treatment of congenital torticollis, kosolaposti, ploskostopiya, hip dislocation. Diagnosis, conservative and surgical treatment of congenital deformities of limbs and shoulder girdle. Clinical supervision and rehabilitation of bone pathology. For students of the specialty "Pediatrics" 1. Subject defects manifested high intestinal obstruction. Congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Features of clinical course, modern diagnostic methods. Preoperative preparation, surgical treatment. Features laparoscopy with pyloric stenosis. The membrane, atresia stomach. Duodenal intestinal obstruction (stenosis, atresia, the membrane of the duodenum, pancreas kiltsevydna). Prenatal diagnosis, diagnostic algorithm in the newborn. Anomalies rotation and fixation of the intestine. Physiological rotation of the intestine. Features of clinical course. Radiological diagnosis of anomalies rotation and fixation of the intestine. Syndrome (triad) Lyedda; midgut volvulus. Complications rotational abnormalities and their prevention and treatment. 2. Subject defects manifested low intestinal obstruction. Atresia and stenosis of small intestine and colon. Lines. Pre- and postnatal diagnosis. Treatment. Hirschsprung's disease. Etiology. Clinical manifestations. Diagnostics (anomanometriya, radiography, biopsy). Principles of surgical treatment. Complications and their prevention. Intestinal dyshanhlioz, hipohanhlioz and other intestinal dysmotility. Mekonialna intestinal obstruction. Etiology, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations. Conservative and operative treatment. Complications (gastrointestinal and pulmonary). 3. Subject anorectal malformations. Anatomical classification is based on the therapeutic management and prognosis. Anorectal malformations in boys (perineal fistula, rektouretralna fistula, fistula rektomihurova, atresia without fistula, rectal atresia, combined defects). Anorectal malformations in girls (perineal fistula, vestibular fistula, persistent cloaca, atresia without fistula, rectal atresia, combined defects). Clinical manifestations and primary care. Posterior sagittal anaproktoplastyka. Colostomy. Complications, their prevention and treatment. Theme 4. Anomalies of the anterior abdominal wall. Omphalocele. GS. Prenatal diagnosis. Differential diagnosis. Emergency aid. Principles of surgery. Rare forms of defects of the anterior abdominal wall. Syndrome "plum stomach." Umbilical and inguinal hernia. Features of clinical manifestations. Complication. Principles of treatment in children. Features surgery in infants. Topic 5. Malformations of the liver and biliary tract. Etiology, pathophysiology. Clinical manifestations, the possibility of early diagnosis. The principles of operating treatment. Portoentnrostomiya (Kasai operation) and liver transplantation. Postoperative management of patients. Opportunities to improve treatment outcomes biliary atresia. Cysts of the liver and choledochus. Classification. Etiology, pathophysiology. Diagnosis. Surgical treatment. Complications forecast. Topic 6. Malformations of the lungs. Agenesis, aplasia, hypoplasia of the lungs. Congenital pulmonary cysts. Congenital emphysema. Bronchiectasis. Pulmonary sequestration. Embryology of the lungs. The main methods of diagnosing lung malformations. Treatment. Complications and their prevention. 7. Subject Malformations of the esophagus. Esophageal atresia. Prenatal diagnosis. Emergency newborn. Preoperative preparation. Surgical treatment based on the type of blemish. Prospects thoracoscopy. Gastrostomy. Methods esophagoplasty. Congenital stenosis. A- and halaziya cardia. Gastro-esophageal reflux. Causes. Clinical manifestations. Principles of diagnosis and treatment. Complication. Theme 8. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: hernia own diaphragm; hiatal hernia, eventration (relaxation) of the diaphragm. Embryology aperture, its connection with the development of lung and esophagus. Benefits of prenatal diagnosis. Features fetal surgery. Emergency newborn in the delivery room. Preoperative stabilization. Possibilities of correction of pulmonary hypertension. Surgical treatment. Postoperative complications, prognosis. Kovno and paraezofahealna hernia. Clinical course and surgery. Theme 9. Malformations of the kidneys. Anomalies of position and kidneys. Agenesis, hypoplasia, dysplasia kidneys. Cystic kidney disease, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease; autosomal recessive (infantile) polikistoznyrok; mulkistoz kidneys. Clinical manifestations, diagnosis, prognosis. Ectopic kidney (pelvic, lumbar, thoracic) fusion (horseshoe) kidney. Theme 10. Malformations of the urinary system. Mehaureter, hydronephrosis, uretrohidronefroz. Pathogenesis, pathophysiology of impaired patency pelvis-ureter segment. Complications and their prevention. Diagnosis. Forecast. Classification. Diagnosis. Practical exercises include: Methods of practical classes. This takes into account all types of work, provided the curriculum. The student must obtain an assessment of each topic. The maximum number of points that a student can collect for current educational activity at the study subjects is 200 points. 12 Congenital malformations of the head, face, neck and spinal cord. Traumatic brain herniation: cleft upper lip and palate; Malformations bridles upper and lower lips and tongue; Hoan atresia; Congenital cysts and fistulas neck (medial, lateral); microcephaly, hydrocephalus; Spynomozkovi hernia. 6 13 Congenital malformations of the musculoskeletal system: Congenital dislocation ctehna, congenital clubfoot, Congenital muscular torticollis ; Congenital malformations of the hand and foot, webbing, polydactyly, ektrodaktyliya. 6 14 Congenital and acquired spinal deformity in children: Juvenile kyphosis, Congenital scoliosis Idiopathic scoliosis Congenital malformations of the chest in children: Liykopodibna deformation; Kilevydna deformation; Isolated deformation ribs. 6 15 Congenital tumors in children: Benign tumors; Malignant neoplasm; 3. Tumors of the abdominal cavity; 4. Tumors pozaocherevynoho space. 6 Total 90 Themes independent work for students 6th degree courses "Pediatrics". Number from / Theme Amount of hours Type of control 1. endoscopic operations: In the stomach and the esophagus; On the airways and lungs; At the distal parts of the gastrointestinal tract; On the urogenital system. 5 Workbook 2. Parenteral feeding children. Rolls bowel syndrome. 5 Workbook 3. Enteral feeding at atsetonemichnomu syndrome in children. Features enteral feeding in early preoperative period. 5 Workbook 4. Differential diagnosis of hydronephrosis. 5 Workbook 5. Ekstrofiya bladder. 5 Workbook 6. The rare defects in children. 5 Workbook 7. Cysts neck. 5 of parenchymal cysts Workbook 8. First aid with respiratory failure. Emergency in cardiovascular disease. 5 Workbook 9. Prenatal surgery: In congenital diaphragmatic hernia; In meninhotselye; Exit procedure. 5 Workbook 7. TOTAL 45 Thematic plan of practical classes for students of 6th courses in specialties "General Medicine", "Medical-prophylaxis". № p / p Themes of practical employments number of academic hours 1 Malformations of the respiratory system. Organic, compression and functional airway stenosis; Vascular rings and loops; Agenesis, aplasia, hypoplasia of the lungs; Congenital pulmonary cysts; congenital emphysema; Pulmonary sequestration. diaphragmatic hernia. esophageal atresia. 6 2 malformations, accompanied by intestinal obstruction. pyloric stenosis; duodenal ileus; Abnormalities rotation and fixation of the intestine; atresia and stenosis of small intestine and colon; Hirschsprung's disease; anorectal malformations. Malformations of the anterior abdominal wall, liver and biliary tract. omphalocele, GS; Umbilical and inguinal hernia. 6 3 Malformations of the musculoskeletal system. Congenital hip sprain; congenital torticollis; Congenital kosolapist; congenital torticollis; Congenital limb pathology; Congenital spinal deformity. 6 Total 18 Themes independent work of students 6th courses in specialties "Medicine", "Medical-prophylaxis" Number from / Theme Hours Type of control 8. Defects of the liver and biliary tract. Biliary atresia. Etiology, pathophysiology. Clinical manifestations, the possibility of early diagnosis. The principles of operating treatment. Portoentnrostomiya (Kasai operation) and liver transplantation. Postoperative management of patients. Opportunities to improve treatment outcomes biliary atresia. Cysts of the liver and choledochus. Classification. Etiology, pathophysiology. Diagnosis. Surgical treatment. Complications forecast. 4 Workbook 9. Malformations of the urinary system. Anomalies of position and kidneys. Mehaureter, hydronephrosis. Violation terrain pelvis-ureter segment. Vesico-ureteric reflux. Cryptorchidism, testicular ectopia. Hypospadias; epispadias. Varicocele. Ekstrofiya bladder. 4 Workbook 10. Congenital and acquired spinal deformity in children. Youth kyphosis. Congenital scoliosis. Idiopathic scoliosis. Disease Shoyermana Mau. Calve disease. 4 Workbook 11. Congenital malformations of the chest in children. Liykopodibna deformity of the chest. Kilevydna deformation. Clinical signs, treatment principles. Polanda syndrome .. KurarinoSilverman syndrome. Congenital splitting the sternum. Isolated deformation ribs. 4 Workbook 12. Total 12 The types of educational activities of students according to the curriculum are: a) lectures b) practical classes, c) independent work of students (IWS), organizations which have a significant role consulted teachers. Thematic plans of lectures, practical classes, IWS provide realization in the educational process of all those who are part of the content modules. Topics of lectures reveal problematic issues relevant sections of discipline. Practical exercises include: • Supervision of patients; • study of patients with surgical pathology; • study of the functional state of vital organs and systems of patients; • practical use of surgical diagnosis and treatment; • solve situational problems and clinical tests; • mastering the elements of medical technology on patients, mock; • mastering the skills of operative technique during surgery and work in dressings; Methods of practical classes. Workshop to be conducted in a clinical dismantling of patients directly "at the bedside" in the dressing room, operating room, diagnostic rooms small groups of students (4 - 6 persons), preferably with the inclusion of interns, clinical residents, and postgraduate students. Discussion of survey results patient group (team) students in the training group performed under the supervision of the accuracy of the diagnosis, the amount designated examination, treatment strategy, and others. It is assumed diary keeping students in the "workbook" locked formulovanyh diagnoses, treatment plans and patient survey performed manipulations. Mastering of theme (current control) is controlled at workshops according to specific objectives. We recommend using the following methods for determining the level of training of students: 1. answers to test questions; 2. The computer tests; 3. Clinical solving situational problems; 4. Evaluation and interpretation of clinical laboratory and instrumental examinations; 5. The control of capture practical skills and elements of medical equipment in the patient Supervision. Distribution points that are students. Current control is performed during training shot and aims at checking mastering educational material. In evaluating the mastering of each topic for current educational activity the student score for the 4-point scale (traditional) scale taking into account the approved evaluation criteria. This takes into account all types of work, provided the curriculum. The student must obtain an assessment of each topic. Evaluation forms are standardized and include control of theoretical and practical training. The maximum number of points that a student can collect for current educational activity at the study subjects is 200 points. The minimum number of points that a student must collect for current educational activity for enrollment courses is 120 points. Calculating the number of points is based on student evaluations received by traditional scale while learning subjects during the semester, by calculating the arithmetic (SA), rounded to two decimal places. The resulting value is converted into points by multi-scale as follows: x = CA x 200/5 For convenience, a table converting 200-point scale. Table 1 4-scale 200-scale 4-scale 200- scale 4- scale 200- scale шкаа 4- scale 200- scale 5 200 4,45 178 3,92 157 3,37 135 4,97 199 4,42 177 3,89 156 3,35 134 4,95 198 4,4 176 3,87 155 3,32 132 4,92 197 4,37 175 3,84 154 3,3 131 4,9 196 4,35 174 3,82 153 3,27 130 4,87 195 4,32 173 3,79 152 3,25 129 4,85 194 4,3 172 3,77 151 3,22 128 4,82 193 4,27 171 3,74 150 3,2 127 4,8 192 4,25 170 3,72 149 3,17 126 4,77 191 4,22 169 3,7 148 3,15 125 4,75 190 4,19 168 3,67 147 3,12 124 4,72 189 4,17 167 3,65 146 3,1 123 4,7 188 4,4 166 3,62 145 3,07 122 4,67 187 4,12 165 3,57 143 3,02 121 4,65 186 4,09 164 3,55 142 3 120 4,62 185 4,07 163 3,52 141 <3 Недост. 4,6 184 4,04 162 3,5 140 4,57 183 4,02 161 3,47 139 4,52 181 3,99 160 3,45 138 4,5 180 3,97 159 3,42 137 4,47 179 3,94 158 3,4 136 The minimum number of points that a student must collect for current To form the final control disciplines which are diffusion. test: The maximum number of points that a student can collect for current educational activity per semester for admission to diffusion. set-off is 120 points. The minimum number of points that a student must collect for current training activities per semester for admission to diffusion. standings is 72 points. Calculating the number of points received is based on student ratings for the traditional scale while learning discipline by calculating the arithmetic mean (SA), rounded to two decimal after the decimal point. The resulting value is converted into points by multi scale as follows: X = CA × 120/5 For convenience, a table converting 200-point scale: Table 2 4-scale 200- scale 4- scale 200- scale шкаа 4- scale 200- scale 4- scale 200-scale шкаа 5 120 4.45 107 3.91 94 3.37 81 4.95 119 4.41 106 3.87 93 3.33 80 4.91 118 4.37 105 3.83 92 3.29 79 4.87 117 4.33 104 3.79 91 3.25 78 4.83 116 4.29 103 3.74 90 3.2 77 4.79 115 4.25 102 3.7 89 3.16 76 4.75 114 4.2 101 3.66 88 3.12 75 4.7 113 4.16 100 3.62 87 3.08 74 4.66 112 4.12 99 3.58 86 3.04 73 4.62 111 4.08 98 3.54 85 3 72 4.58 110 4.04 97 3.49 84 Менше 4.54 109 3.99 96 3.45 83 3 Недостатньо 4.5 108 3.95 95 3.41 82 ndependent work of students is evaluated during the current control of theme on the appropriate lesson. Mastering of themes which dart out only on independent work is controlled at the final control. Final control is carried out to assess learning outcomes at a particular educational qualification level and at the individual stages completed its national scale and scale ECTS. Final control includes control and certification semester student. Semester control is conducted in the form of semester differentiated credit (for the 5th year) and offset (for students 6 courses) with the subject "Pediatric Surgery" in the amount of educational material specified in the work program of the course and in the terms established working curriculum, individual curriculum student. Semester diffusion. credit (for the 5th year) - a form of final control of the student theoretical and practical material on the subject "Pediatric surgery" for a semester, carried out as a control measure. A student is considered to be admitted to semester diffusion. classification of pediatric surgery if he visited all the prescribed curriculum with courses for classroom training sessions or worked all missed Initial lecture classes, met all kinds of work envisaged working program of discipline and in its study during the semester scored score not less than the minimum (72 points). Semester diffusion. test conducted in writing on the last scheduled class. Methods of differentiated credit semester. 1. Writing and defense history, the disease (work with patients, control of practical skills, design history) - 0 - 15 points. 2. Rozvyazuvannya three situational tasks - 0 - 15 points (for every task from 0 to 5 points) 3. Rozvyazuvannya tests. 50 tests 1 point for each correctly solved, test (from 0 to 50 points). The maximum number of points that a student can get in the preparation diffusion. offset is 80. The minimum score in the preparation of diffusion. offset - at least 50. Determination of the number of points that a student scored on discipline. Evaluation of the course "Pediatric surgery" for students of the 5th year that ends diffusion. offset is defined as the sum of points for current educational activity (at least 72) and points by diffusion. test (at least 50) and in points computed according to Table 4. points Scale 5 170 – 200 5 140 – 169 4 139 – 120 3 Less then 120 2 Perelik pytanʹ, shcho vynosyatʹsya na potochnyy ta pidsumkovyy kontrolʹ. Hostri protsesy cherevnoyi porozhnyny 1. Suchasni pohlyady na etiolohiyu ta patohenez hostroho apendytsytu. 2. Osoblyvosti budovy cherevnoyi porozhnyny ta apendyksu, shcho vyznachayutʹ klinichnyy perebih apendytsytu u ditey. 3. Osoblyvosti hostroho apendytsytu u ditey rannʹoho viku (do 3-kh rokiv ). 4. Osoblyvosti obstezhennya ditey rannʹoho viku z pidozroyu na hostryy apendytsyt. 5. Dyferentsialʹna diahnostyka hostroho apendytsytu. 6. Diahnostyka ta likuvannya apendykulyarnoho infilʹtratu. 7. Atypovi formy hostroho apendytsytu. Osoblyvosti kliniky ta diahnostyky. 8. Pervynnyy pelʹvyoperytonit. Diahnostyka, likuvannya. 9. Perytonit. Klasyfikatsiya. Diahnostyka. 10. Dyferentsiyna diahnostyka hostroho apendytsytu ta pervynnoho perytonitu. 11. Symptom porivnyalʹnoyi dozovanoyi perkusiyi (Za A.R. Shurinkom ). Metodyka obstezhennya ta kryteriyi otsinky. 12. Dopomizhni metody obstezhennya ditey z pidozroyu na hostryy apendytsyt, yikh informatyvnistʹ ta diahnostychna tsinnistʹ. 13. Vidkryta ta laparoskopichna apendektomiya: perevahy i nedoliky. 14. Pokhodzhennya ta roztashuvannya dyvertykula Mekkelya. 15. Dyvertykulit Mekkelya. Klinichni proyavy, diahnostyka, likuvannya. 16. Osnovni prychyny, klinichni proyavy perytonitu u novonarodzhenykh. 17. Kryteriyi hotovnosti patsiyenta do operatsiyi pry perytoniti. 18. Pryntsypy peredoperatsiynoyi pidhotovky patsiyenta z perytonitom. Kryteriyi hotovnosti dytyny do operatsiyi. 19. Pryntsypy likuvannya apendykulyarnoho abstsesu. 20. Osoblyvosti kliniky i likuvannya perytonitu u novonarodzhenykh z ekstremalʹno nyzʹkoyu masoyu tila. Nabuta kyshkova neprokhidnistʹ. Invahinatsiya 1. Klasyfikatsiya kyshkovoyi neprokhidnosti u ditey. 2. Osnovni klinichni symptomy idiopatychnoyi invahinatsiyi u ditey. 3. Dayte kharakterystyku dodatkovym metodam diahnostyky invahinatsiyi u ditey. 4. Pokazannya do konservatyvnoho rozpravlennya invahinatu u ditey. 5. Protypokazannya do konservatyvnoho rozpravlennya invahinatu u ditey. 6. Sutʹ konservatyvnoho rozpravlennya invahinatu u ditey. 7. Renthenolohichni oznaky vysokoyi ta nyzʹkoyi kyshkovoyi neprokhidnosti. 8. Uskladnennya invahinatsiyi, yikh profilaktyka ta pryntsypy likuvannya. 9. Osnovni prychyny, klasyfikatsiya pislyaoperatsiynoyi zlukovoyi kyshkovoyi neprokhidnosti. 10. Osnovni patohenetychni chynnyky rannʹoyi pislyaoperatsiynoyi zlukovoyi kyshkovoyi neprokhidnosti. 11. Pryntsypy konservatyvnoho likuvannya rannʹoyi pislyaoperatsiynoyi zlukovoyi kyshkovoyi neprokhidnosti. 12. Osnovni prychyny spastychnoyi ta paralitychnoyi kyshkovoyi neprokhidnosti. 13. Pryntsypy peredoperatsiynoyi pidhotovky pry mekhanichniy kyshkoviy neprokhidnosti. Kryteriyi hotovnosti patsiyenta do operatsiyi. 14. Osoblyvosti peredoperatsiynoyi pidhotovky pry vysokiy i nyzʹkiy kyshkoviy neprokhidnosti. 15. Kharakterystyka osnovnykh medychnykh preparativ, yaki vykorystovuyutʹ dlya vidnovlennya obʺyemu tsyrkulyuyuchoyi krovi. 16. Bezoar yak prychyna vysokoyi kyshkovoyi neprokhidnosti. Klinichni proyavy, metody likuvannya. 17. Storonni tila shlunkovo-kyshkovoho traktu u ditey. Klinichni proyavy, diahnostyka, mozhlyvi uskladnennya. 18. Likuvalʹna taktyka pry storonnikh tilakh shlunkovo-kyshkovoho traktu u ditey. 19. Pislyaopikovi stenozy stravokhodu ta pilorychnoho viddilu shlunka yak prychyna porushennya prokhidnosti travnoho traktu u ditey. Osnovni prychyny, klinichni proyavy. 20. Pryntsypy likuvannya pislya opikovykh stenoziv stravokhodu ta pilorychnoho viddilu shlunka u ditey. Shlunkovo-kyshkovi krovotechi u ditey. 1. Kharakterni klinichni oznaky krovotech z verkhnikh viddilakh travnoho traktu (stravokhid, shlunok, 12-tpala kyshka). 2. Kharakterni klinichni oznaky krovotech z verkhnikh viddilakh serednikh viddiliv SHTK (tonkyy kyshechnyk). 3. Kharakterni klinichni oznaky krovotech z nyzhnikh viddilenʹ SHTK (pryama kyshka ). 4. Yaka prychyna krovotech iz varykozno rozshyrenykh ven stravokhodu? 5. Yaka prychyna krovotech pry dyvertykuli Mekkelya? 6. Yaka prychyna krovotech pry invahinatsiyi kyshechnyka ? 7. Yaka prychyna krovotech pry zavoroti kyshechnyka? 8. Shcho take portalʹna hipertenziya, formy portalʹnoyi hipertenziyi ? 9. Yaki naybilʹsh rozpovsyudzheni prychyny portalʹnoyi hipertenziyi? 10. Metody diahnostyky portalʹnoyi hipertenziyi. 11. Kharakterni oznaky portalʹnoyi hipertenziyi u ditey. 12. Osoblyvosti konstruktsiyi zondu Blekmora i dlya choho vin vykorystovuyetʹsya. Osoblyvosti yoho vstanovlennya u ditey. 13. Znachennya sandostatynu dlya zupynky krovotechi z SHKT u ditey. 14. Konservatyvni ta operatyvni metody vtruchannya zupynky krovotechi pry portalʹniy hipertenziyi u ditey . 15. Prychyny vynyknennya dopechinkovoyi formy syndromu portalʹnoyi hipertenziyi u ditey. 16. Metody portosystemnoho shuntuvannya. 17. Prychyny krovotech pry nekrotychno-vyrazkovomu enterokoliti u novonarodzhenykh. 18. Prychyny krovotech pry polipozi kyshechnyka u ditey, metody yikh diahnostyky. 19. Prychyny krovotech pry shlunkovo-stravokhidnomu reflyuksi (hryzhi stravokhidnoho otvoru diafrahmy, peptychni struktury, stravokhid Barreta). 20. Spravzhnya ta nespravzhnya krovotecha z sh.k.t. , prychyny u ditey. Torakalʹna travma. Destruktyvni zakhvoryuvannya lehenʹ i plevry 1. Torakalʹna travma. Varianty. Virohidni oznaky ushkodzhennya vnutrishnikh orhaniv. 2. Osoblyvosti torakalʹnoyi travmy v dytyachomu vitsi. 3. Patohenez rozladiv dykhannya ta krovoobihu pry torakalʹniy travmi. 4. Metody obstezhennya, yaki zastosovuyutʹsya pry travmi orhaniv hrudnoyi porozhnyny. 5. Ushkodzhennya trakheyi. Klinichni symptomy, likuvalʹna taktyka. Ekstraperykardialʹna tamponada sertsya. 6. Ushkodzhennya lehenʹ. Varianty, diahnostyka. Khirurhichna taktyka. 7. Pnevmotoraks. Klasyfikatsiya, etiolohiya, patohenez dykhalʹnykh rozladiv. 8. Pnevmotoraks. Klinika, fizykalʹna ta renthenolohichna diahnostyka, nevidkladna dopomoha. 9. Hemotoraks. Prychyny, likuvalʹna taktyka, pokazannya do operatyvnoho vtruchannya. 10. Travma sertsya. Varianty, patohenez nedostatnosti krovoobihu. 11. Travmatychni vady sertsya. Varianty, diahnostyka, pryntsypy likuvannya. 12. Tamponada sertsya. Varianty, klinichni symptomy, nevidkladna khirurhichna dopomoha. 13. Klinichni symptomy perforatsiyi stravokhodu. Prychyny perforatsiyi, yiyi uskladnennya. 14. Mediastynit. Etiolohiya, klinika, diahnostyka. 15. Metody diahnostyky pry ushkodzhennyakh stravokhodu. 16. Travmatychni ushkodzhennya diafrahmy. Chastota, patohenez dykhalʹnykh rozladiv, diahnostyka. 17. Klasyfikatsiya hostroyi destruktyvnoyi pnevmoniyi. 18. Leheneva forma hostroyi destruktyvnoyi pnevmoniyi. Varianty, diahnostyka, metody likuvannya. 19. Lehenevo plevralʹna forma hostroyi destruktyvnoyi pnevmoniyi. Varianty, diahnostyka, metody likuvannya. 20. Atelektaz ta kolaps leheni. Prychyny, diahnostyka, mozhlyvosti likuvannya. 21. Drenuvannya plevralʹnoyi porozhnyny. Pokazannya, sposoby aspiratsiyi plevralʹnoho vmistu. 22. Plevralʹna punktsiya. Metodyka vykonannya, neobkhidni instrumenty. Onkolohiya dytyachoho viku 1. Osoblyvosti onkolohiyi dytyachoho viku. Zahalʹni pryntsypy diahnostyky i likuvannya zloyakisnykh novoutvorenʹ u ditey. 2. Kryzhovo-kuprykova teratoma: vyznachennya, anatomo-morfolohichna klasyfikatsiya ta klinichni proyavy. 3. Diahnostyka kryzhovo-kuprykovoyi teratomy (mozhlyvosti prenatalʹnoyi diahnostyky, instrumentalʹni metody doslidzhennya, pukhlynni markery) ta likuvalʹna taktyka. 4. Dyferentsiyna diahnostyka kryzhovo-kuprykovoyi teratomy ta meninhotselye. 5. Hemanhioma: vyznachennya, klasyfikatsiya, klinichni proyavy. 6. Likuvalʹna taktyka pry hemanhiomakh u ditey. 7. Limfanhioma: vyznachennya, klasyfikatsiya, klinichni proyavy. 8. Metody diahnostyky ta pryntsypy likuvannya limfanhiom. 9. Dermoyidna kista: vyznachennya, typova lokalizatsiya, klinichni proyavy, pryntsypy likuvannya. 10. Nefroblastoma (pukhlyna Vilʹmsa): vyznachennya, klinichni proyavy, zvʺyazok z inshymy porushennyamy embriohenezu. 11. Yaki laboratorni ta instrumentalʹni metody zastosovuyutʹ dlya diahnostyky nefroblastomy? Pryntsypy likuvannya nefroblastomy. 12. Neyroblastoma: vyznachennya, typova anatomichna lokalizatsiya, klinichni proyavy. 13. Pryntsypy diahnostyky neyroblastomy (veryfikatsiya diahnozu, diahnostyka pervynnoho vohnyshcha, otsinka biolohichnoyi aktyvnosti pukhlyny, diahnostyka mozhlyvykh metastaziv). Pryntsypy likuvannya neyroblastomy. 14. Dyferentsiyna diahnostyka neyroblastomy zaocherevynnoho prostoru ta nefroblastomy (pukhlyny Vilʹmsa). 15. Yaki zloyakisni pukhlyny kistok naychastishe zustrichayutʹsya v dytyachomu vitsi? Znachennya travmy v etiolohiyi pukhlyn kistok. Klinichni proyavy pukhlyn kistok. 16. Laboratorni ta instrumentalʹni metody diahnostyky, pryntsypy likuvannya zloyakisnykh pukhlyn kistok. 17. Iz yakykh tkanyn poperednykiv rozvyvayutʹsya sarkomy mʺyakykh tkanyn? Yaki iz nykh naychastishe zustrichayutʹsya v dytyachomu vitsi? Pryntsypy diahnostyky i likuvannya. 18. Klinichni proyavy ta diahnostyka pukhlyn seredostinnya. 19. Typy ta klinichni proyavy dobroyakisnykh pihmentnykh novoutvorenʹ shkiry. 20. Faktory ryzyku rozvytku melanomy, yiyi ranni ta pizni klinichni oznaky. Akronim ABCD (assymetry, borders (bleed), change, diameter). Urolohiya dytyachoho viku 1. Dayte vyznachennya syndromu nabryakloyi kalytky. Nazvitʹ zapalʹni ta nezapalʹni zakhvoryuvannya, yaki proyavlyayutʹsya syndromom nabryakloyi kalytky. 2. Mekhanizm vynyknennya ta klinichni proyavy perekrutu yayechka u novonarodzhenykh i ditey rannʹoho viku (ekstaravahinalʹna forma perekrutu). 3. Mekhanizm vynyknennya ta klinichni proyavy perekrutu yayechka u ditey starshoho viku (intravahinalʹna forma perekrutu). 4. Diahnostyka ta pryntsypy likuvannya perekrutu yayeka u ditey. 5. Klinichni proyavy, dodatkovi metody obstezhennya ta pryntsypy likuvannya perekrutu hidatydy Morhanʹi u ditey. 6. Dyferentsiyna diahnostyka perekrutu yayechka ta perekrutu hidatydy Morhanʹi u ditey. 7. Osnovni vydy ta klinichni proyavy zakrytykh poshkodzhenʹ kalytky i yiyi orhaniv. 8. Likuvalʹna taktyka pry travmatychnykh poshkodzhennyakh kalytky ta yiyi orhaniv. 9. Osnovni etiolohichni chynnyky ta klinichni proyavy hostroho nespetsyfichnoho orkhoepididimitu. 10. Diahnostyka ta pryntsypy likuvannya hostroho nespetsyfichnoho orkhoepididimitu u ditey. 11. Uskladnennya khirurhichnykh zakhvoryuvanʹ orhaniv kalytky, yikh profilaktyka ta pryntsypy likuvannya. 12. Travma nyrky: klasyfikatsiya, klinichni proyavy. 13. Laboratorni ta instrumentalʹni metody obstezhennya, yaki ye naybilʹsh informatyvnymy pry travmi nyrok. 14. Travma sechovoho mikhura: mekhanizm, klasyfikatsiya. 15. Klinichni proyavy ta pryntsypy likuvannya ekstraperytonealʹnoho rozryvu sechovoho mikhura. 16. Klinichni proyavy ta pryntsypy likuvannya intraperytonealʹnoho rozryvu sechovoho mikhura. 17. Yaki osnovni mekhanizmy ta klinichni proyavy travmy uretry? 18. Yaki dodatkovi metody obstezhennya naybilʹsh informatyvni pry riznykh vydakh travmy uretry? 19. Osoblyvosti patohenezu, klinichnykh proyaviv ta diahnostyky sechokamʺyanoyi khvoroby u ditey. 20. Pryntsypy konservatyvnoho ta khirurhichnoho likuvannya sechokamʺyanoyi khvoroby u ditey. Politravma. Zakryta travma zhyvota. 1. Politravma u ditey: vyznachennya, epidemiolohiya i patohenez u dytyachomu vitsi. 2. Klasyfikatsiya travmatychnoho (hipovolemichnoho) shoku za stupenem vazhkosti. Diahnostychni kryteriyi I-III stupenyu travmatychnoho shoku. 3. Likuvalʹna taktyka pry travmatychnomu (hipovolemichnomu) shotsi I stupenyu. 4. Likuvalʹna taktyka pry travmatychnomu (hipovolemichnomu) shotsi II stupenyu. 5. Likuvalʹna taktyka pry travmatychnomu (hipovolemichnomu) shotsi III stupenyu. 6. Epidemiolohiya, mekhanizm zakrytoyi travmy zhyvota u ditey. Osnovni klinichni proyavy i tradytsiyni metody diahnostyky. 7. Dotsilʹnistʹ, diahnostychni ta likuvalʹni mozhlyvosti laparoskopiyi pry zakrytiy travmi zhyvota u ditey. Protypokazannya do provedennya laparoskopiyi pry zakrytiy travmi zhyvota u ditey. 8. Mekhanizm i klinichni proyavy travmy pidshlunkovoyi zalozy u ditey. 9. Laboratorna i instrumentalʹna diahnostyka travmy pidshlunkovoyi zalozy. Pryntsypy likuvannya travmatychnoho pankreatytu. 10. Etiolohiya, mekhanizm ta klinichni proyavy poshkodzhenʹ porozhnystykh orhaniv cherevnoyi porozhnyny. 11. Diahnostyka poshkodzhenʹ porozhnystykh orhaniv cherevnoyi porozhnyny. 12. Ushkodzhennya pechinky pry zakrytiy travmi zhyvota: klasyfikatsiya, klinichni proyavy. 13. Laboratorni ta instrumentalʹni metody doslidzhennya pry travmatychnomu urazhenni pechinky. 14. Likuvalʹna taktyka pry travmi pechinky. 15. Hemobiliya: vyznachennya, klinichni proyavy. 16. Laboratorni ta instrumentalʹni metody diahnostyky, pryntsypy likuvannya hemobiliyi. 17. Travma selezinky: klasyfikatsiya, klinichni proyavy. 18. Diahnostyka ta likuvalʹna taktyka pry travmi selezinky. 19. Dyferentsiyna diahnostyka ushkodzhenʹ parenkhimatoznykh ta porozhnystykh orhaniv pry zakrytiy travmi zhyvota. 20. Poshkodzhennya vnutrishnikh orhaniv cherevnoyi porozhnyny u novonarodzhenykh: prychyny, osnovni vydy poshkodzhenʹ, klinichni proyavy, diahnostyka, likuvalʹna taktyka. Hniyna khirurhichna infektsiya 1. Mizhnarodna klasyfikatsiya sepsysu (American College of Chest Phisicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine Cnsensus Conference, 1992). 2. Klinichni proyavy systemnoyi vidpovidi na zapalennya (SIRS). Osoblyvosti kryteriyiv systemnoyi vidpovidi na zapalennya (SIRS) u ditey zalezhno vid viku. 3. Klinichni kryteriyi septychnoho shoku. 4. Pryntsypy likuvannya sepsysu. Rolʹ EKMO (ekstrakorporalʹnoyi membrannoyi oksyhenatsiyi) u likuvanni sepsysu. 5. Anatomo-fiziolohichni osoblyvosti shkiry ta pidshkirnoyi klitkovyny u novonarodzhenykh, shcho vyznachayutʹ perebih hniyno-zapalʹnykh zakhvoryuvanʹ. 6. Nekrotychna flehmona novonarodzhenoho: etiolohichni chynnyky, patohenez, klinichni proyavy. 7. Diahnostyka ta pryntsypy likuvannya nekrotychnoyi flehmony novonarodzhenoho. 8. Hniynyy mastyt novonarodzhenykh: prychyny vynyknennya, klinichni proyavy, pryntsypy likuvannya. 9. Dyferentsiyna diahnostyka mastytu ta fiziolohichnoho nabukhannya molochnykh zaloz u novonarodzhenykh. 10. Omfalit: vyznachennya, prychyny vynyknennya, klasyfikatsiya, klinichni proyavy. 11. Diahnostyka ta likuvannya omfalitu zalezhno vid formy zakhvoryuvannya. 12. Prychyny vynyknennya, klinichni proyavy, pryntsypy likuvannya pararektalʹnoho abstsesu u ditey. 13. Osoblyvosti budovy ta krovopostachannya dovhykh kistok u ditey. 14. Klinichni proyavy hostroho hematohennoho osteomiyelitu (HHO) u ditey. 15. Laboratorni i instrumentalʹni metody diahnostyky hostroho hematohennoho osteomiyelitu u ditey. Kharakterni renthenolohichni oznaky HHO dovhykh kistok. 16. Dyferentsiyna diahnostyka HHO i tuberkulʹoznoho ostytu. 17. Pryntsypy likuvannya HHO u ditey. 18. Anatomichna lokalizatsiya, klinichni proyavy hostroho hematohennoho osteomiyelitu u novonarodzhenykh. 19. Renthenolohichni oznaky, pryntsypy likuvannya hostroho hematohennoho osteomiyelitu u novonarodzhenykh. 20. Klinichni ta renthenolohichni oznaky atypovykh form osteomiyelitu u ditey. Vady rozvytku u ditey 1. Etiopatohenez vrodzhenykh vad rozvytku. Ponyattya normy, anomaliyi ta vady. 2. Embiropatohenez vad rozvytku respiratornoyi systemy. Mozhlyvosti prenatalʹnoyi diahnostyky. 3. Klasyfikatsiya vrodzhenykh vad rozvytku dykhalʹnoyi systemy. 4. Klinichni symptomy ta syndromy pry vrodzhenykh vadakh dykhalʹnykh shlyakhiv ta lehenʹ. 5. Metody diahnostyky vrodzhenykh vad respiratornoyi systemy. Suchasni promenevi ta endoskopichni tekhnolohiyi. 6. Funktsionalʹni stenozy dykhalʹnykh shlyakhiv vnaslidok vrodzhenykh vad rozvytku. Larynhomalyatsiya ta trakheomalyatsiyi. Klinichna kartyna, diahnostyka, likuvannya. 7. Pidzvʼyazkovyy orhanichnyy stenoz: vrodzhenyy, postintubatsiynyy, hemanhioma . Klinika, diahnostyky, pryntsypy likuvannya. 8. Vrodzhenyy stenoz trakheyi (povni kilʹtsya). Varianty, klinika, diahnostyka, pryntsypy likuvannya. 9. Kompresiyni stenozy trakheyi. Anatomichni varianty sudynnoho kilʹtsya. 10. Povne sudynne kilʹtse: podviyna duha aorty ta pravobichna duha aorty. Klinika, diahnostyka, pryntsypy likuvannya. 11. Nepovne sudynne kilʹtse: aberantna prava pidklyuchychna arteriya, anomaliyi plechoholovnoho stovbura. Klinika, diahnostyka, pryntsypy likuvannya. 12. Petlya lehenevoyi arteriyi. Varianty, klinika, diahnostyka, pryntsypy likuvannya. 13. Kompresiyni stenozy trakheyi pry pukhlynakh ta kistakh seredostinnya. Varianty nozolohiy, klinichni proyavy, metody diahnostyky, pryntsypy likuvannya. 14. Vrodzhena izolʹovana trakheostravokhidna fistula. Klinika, diahnostyka, pryntsypy likuvannya. 15. Vrodzhena emfizema lehenʹ. Patohenez, klinika, diahnostyka, pryntsypy likuvannya. 16. Aplaziya, aheneziya leheni. Anatomichni ta patofiziolohichni osoblyvosti. 17. Aplaziya leheni. Patohenez, klinika, diahnostyka, dyferentsiyna diahnostyka, mozhlyvosti khirurhichnoho likuvannya. 18. Vrodzheni kisty lehenʹ. Klasyfikatsiya, diahnostyka, uskladnennya, khirurhichne likuvannya . 19. Leheneva sekvestratsiya. Varianty, osoblyvosti patohenezu, klinika, diahnostyka , likuvannya. 20. Bronkhoektazy. Klinika, diahnostyka, likuvannya. 21. Trakheostomiya. Pokazannya ta protypokazannya. Tekhnika vykonannya. 22. Klasyfikatsiya atreziyi stravokhodu. Mozhlyvosti prenatalʹnoyi diahnostyky atreziyi stravokhodu. 23. Klinichna kartyna atreziyi stravokhodu novonarodzhenoho. Prychyny rozvytku aspiratsiynoyi pnevmoniyi pry riznykh formakh atreziyi stravokhodu. 24. Klinichna kartyna atreziyi stravokhodu novonarodzhenoho. 25. Diahnostyka atreziyi stravokhodu (ohlyadova renthenohrafiya, zonduvannya stravokhodu, ezofahohrafiya). Prychyny rozvytku aspiratsiynoyi pnevmoniyi pry riznykh formakh atreziyi stravokhodu. 26. VACTERL asotsiatsiya pry atreziyi stravokhodu. Klinichni proyavy, pryntsypy diahnostyky i likuvannya. 27. Peredoperatsiyna pidhotovka u ditey z atreziyeyu stravokhodu. 28. Vybir khirurhichnoyi taktyky v zalezhnosti vid formy atreziyi stravokhodu. Hastrostomiya.yak metod pidhotovky do radykalʹnoyi operatsiyi pry atreziyi stravokhodu. Radykalʹna operatsiya pry atreziyi stravokhodu z nyzhneyu trakheo-stravokhidnoyu fistuloyu. 29. Uskladnennya operatyvnoho likuvannya atreziyi stravokhodu (nedostatnistʹ shviv anastomozu). Klinichni proyavy, pryntsypy diahnostyky i likuvannya. 30. Uskladnennya operatyvnoho likuvannya atreziyi stravokhodu (retsydyv trakheostravokhidnoyi fistuly). Klinichni proyavy, sposoby vizualizatsiyi, pryntsypy likuvannya. 31. Uskladnennya operatyvnoho likuvannya atreziyi stravokhodu (pislyaoperatsiynyy stenoz stravokhodu). Klinichni proyavy, metody diahnostyky, sposoby likuvannya. 32. Uskladnennya operatyvnoho likuvannya atreziyi stravokhodu (shlunkovostravokhidnyy reflyuks). Klinichni proyavy, diahnostyka, konservatyvne ta operatsiyne likuvannya. 33. Trakheomalyatsiya, asotsiyovana z atreziyeyu stravokhodu. Prychyny vynyknenya, klinichni proyavy, sposoby diahnostyky, metody likuvannya. 34. Vrodzhena izolʹovana trakheostravokhidna fistula- mistse v klasyfikatsiyi atreziyi stravokhodu, a yiyi pokhodzhennya, klinichna kartyna ta diahnostyka, pryntsypy likuvannya. 35. Larynhotrakheostravokhidna rozshchilyna. Diahnostyka ta pryntsypy likuvannya. 36. Vyznachennya ponyattya «vrodzhena diafrahmalʹna hryzha». Klasyfikatsiya. Mekhanizm formuvannya vady. 37. Leheneva hipoplaziya i leheneva hipertenziya pry vrodzheniy diafrahmalʹniy hryzhi. Prychyny formuvannya, morfolohichna kharakterystyka. 38. Sposoby prenatalʹnoyi diahnostyky vrodzhenoyi diafrahmalʹnoyi hryzhi. Yaki mozhlyvosti prenatalʹnoho prohnozuvannya vyzhyvannya novonarodzhenoho z VDH? 39. Yaki klinichni proyavy vrodzhenoyi diafrahmalʹnoyi hryzhi u novonarodzhenoho? Yaki metody diahnostyky vykorystovuyutʹ dlya pidtverdzhennya diahnozu? 40. Dopomoha novonarodzhenomu z vrodzhenoyu diafrahmalʹnoyu hryzheyu u polohoviy zali. Pryntsypy peredoperatsiynoyi stabilizatsiyi. 41. Pryntsypy khirurhichnoho likuvannya VDH. Operatsiyni dostupy. Sposoby zakryttya defektu diafrahmy. 42. Pislyaoperatsiyne vedennya novonarodzhenykh z VDH. 43. Yaki khirurhichni ta ne khirurhichni uskladnennya vynykayutʹ pislya korektsiyi vrodzhenoyi diafrahmalʹnoyi hryzhi? Mozhlyvosti yikh profilaktyky. 44. Osoblyvosti klinichnoho perebihu ta suchasni metody diahnostyky vrodzhenoho hipertrofichnoho pilorostenozu. 45. Peredoperatsiyna pidhotovka, khirurhichne likuvannya vrodzhenoho hipertrofichnoho pilorostenozu. Mozhlyvosti laparoskopiyi. 46. Duodenalʹna kyshkova neprokhidnistʹ: prychyny vynyknennya, prenatalʹna diahnostyka, diahnostychnyy alhorytm u novonarodzhenoho. 47. Etapy fiziolohichnoyi rotatsiyi kyshechnyka. 48. Klasyfikatsiya porushenʹ rotatsiyi i fiksatsiyi kyshechnyka. 49. Klinichni proyavy diahnostyka ta likuvannya porushennya rotatsiyi kyshechnyka, I period. 50. Syndrom (triada) Lyeda. Vyznachennya, klinichni proyavy, pryntsypy likuvannya. 51. Porushennya rotatsiyi kyshechnyka, III period. Vydy, klinichni proyavy, sposoby diahnostyky i pryntsypy likuvannya. 52. Uskladnennya rotatsiynykh anomaliy, yikh profilaktyka ta likuvannya. 53. Klasyfikatsiya atreziyi tonkoyi kyshky. Pre- i postnatalʹna diahnostyka. Pryntsypy likuvannya. 54. Khvoroba Hirshprunha. Vyznachennya, anatomichni formy. 55. Klinichni proyavy khvoroby Hirshprunha zalezhno vid formy perebihu. 56. Suchasni pryntsypy diahnostyky khvoroby Hirshprunha. 57. Pryntsypy khirurhichnoho likuvannya khvoroby Hirshprunha zalezhno vid anatomichnoyi formy, klinichnoho perebihu ta viku dytyny. 58. Intestinalʹnyy dys·hanhlioz, hipohanhlioz ta inshi porushennya motoryky kyshechnyka. Klinichni proyavy, mozhlyvosti diahnostyky ta dyferentsiynoyi diahnostyky z khvoroboyu Hirshprunha. 59. Mekonialʹna kyshkova neprokhidnistʹ. Etiolohiya, patohenez, klinichni proyavy. 60. Konservatyvne ta operatsiyne likuvannya mekonialʹnoyi kyshkovoyi neprokhidnosti. 61. Anorektalʹni vady rozvytku u khlopchykiv. Vydy, klinichni proyavy. 62. Anorektalʹni vady rozvytku u divchatok. Vydy, klinichni proyavy. 63. Kloakalʹna forma anorektalʹnoyi atreziyi. Klasyfikatsiya, suputni vady, klinichni proyavy, uskladnennya. 64. Suchasni pryntsypy likuvannya anorektalʹnykh vad rozvytku. 65. Uskladnennya pislya khirurhichnoyi korektsiyi anorektalʹnykh vad rozvytku, yikh profilaktyka. Sotsialʹna ta medychna reabilitatsiya. 66. Prenatalʹna diahnostyka vad rozvytku perednʹoyi cherevnoyi stinky: terminy vstanovlennya diahnozu, sposoby diahnostyky, biokhimichni markery. 67. Klinichni proyavy hastroshyzysu. 68. Likuvannya hastroshyzysu. 69. Vyznachennya, klasyfikatsiya, klinichni proyavy omfalotselye. Budova hryzhovykh obolonok. 70. Sposoby operatsiynoho likuvannya omfalotsele. 71. Suputni vady rozvytku, uskladnennya, prohnoz hastroshyzysu i omfalotselye. 72. Dyferentsiyna diahnostyka hastroshyzysu i omfalotselye. 73. Prychyny, osoblyvosti anatomichnoyi budovy pakhvynnykh hryzh u ditey. Pryntsypy khirurhichnoho likuvannya. 74. Uskladnennya pakhvynnoyi hryzhi u ditey, yikh profilaktyka, likuvannya. 75. Pupkova hryzha u ditey. Klinichni proyavy, mozhlyvi uskladnennya, pryntsypy likuvannya, terminy operatyvnoho vtruchannya. 76. Ridkisni formy vad rozvytku perednʹoyi cherevnoyi stinky. Aplaziya mʺyaziv («syndrom slyvovoho zhyvota») – klinichni proyavy, suputni vady, uskladnennya. 77. Khirurhichna anatomiya pechinky: vidnoshennya do ocherevyny, zvʺyazky pechinky, poverkhni, podil na sehmenty za Kuino, vorota pechinky. 78. Vyznachennya, klasyfikatsiya kist kholedokha. 79. Klinichni proyavy kisty kholedokha. 80. Sposoby diahnostyky kisty kholedokha. 81. Pryntsypy khirurhichnoho likuvannya kist kholedokha. Profilaktyka vyskhidnoho kholanhitu. 82. Biliarno atreziya: vyznachennya vady, imovirni prychyny vynyknennya, klasyfikatsiya. 83. Klinichni proyavy i sposoby diahnosty miliarnoyi atreziyi. 84. Sposoby likuvannya miliarnoyi atreziyi. Prohnoz zakhvoryuvannya. 85. Kisty pechinky: vydy, klinichni proyavy, sposoby diahnostyky, pokazannya do aktyvnoyi khirurhichnoyi taktyky. 86. Dyferentsiyna diahnostyka vrodzhenykh i parazytarnykh kist pechinky. 87. Yaki ye anomaliyi polozhennya, kilʹkosti i vzayemyn nyrok? Yikh klinichni proyavy, diahnostyka, prohnoz. 88. Kistozni anomaliyi nyrok: vydy, klinichni proyavy, uskladnennya, pryntsypy likuvannya. 89. Vrodzhenyy hidronefroz: prychyny vynyknennya, klinichni proyavy. 90. Sposoby diahnostyky hidronefrozu u ditey. Vyznachennya funktsiyi nyrok. 91. Pryntsypy khirurhichnoho likuvannya hidronefrozu u ditey. 92. Mikhurovo-sechovidnyy reflyuks u ditey: prychyny vynyknennya, klinichni proyavy, uskladnennya, pryntsypy likuvannya. 93. Ekstrofiya sechovoho mikhura: klinichni proyavy, uskladnennya, mozhlyvosti korektsiyi. 94. Epispadiya: vyznachennya, klinichni proyavy, pryntsypy likuvannya. 95. Hipospadiya: vyznachennya, vydy, klinichni proyavy, pryntsypy likuvannya. 96. Kryptorkhizm: vyznachennya, klasyfikatsiya, klinichni proyavy, pryntsypy likuvannya. 97. Fimoz: vyznachennya, prychyny vynyknennya, uskladnennya, pryntsypy likuvannya. Fiziolohichnyy fimoz. 98. Parafimoz. Vyznachennya, prychyny, klinichni proyavy, nevidkladna dopomoha. 99. Yunatsʹkiy kifoz: vyznachennya, klasyfikatsiya, klinichni proyavy. 100. Yunatsʹkiy kifoz: pryntsypy likuvannya, kryteriyi efektyvnosti. 101. Vrodzhenyy skolioz: vyznachnnya, klinichni proyavi, pryntsipi likuvannya. 102. Idiopatychnyy skolioz: vyznachennya, pryntsypy klasyfikatsiyi. 103. Idiopatychnyy skolioz: printsypy likuvannya v zalezhnosti vid stupenya deformatsiyi. 104. Khvoroba Kalʹve: vyznachennya, pryntsypy likuvannya. 105. Instrumentalʹni metody doslidzhennya khvorikh na skolioz. 106. Korsetoterapiya vad rozvytku khrebta u ditey. 107. Pryntsypy khirurhichnoho likuvannya skoliozu u ditey. 108. Dyferentsiyna diahnostika skoliotychnoyi postavy i skoliozu. 109. Do naybilʹsh poshyrenykh vad rozvytku oporno-rukhovoho aparatu u ditey vidnosyatʹ? 110. Shcho take mʺyazova kryvoshyya? 111. Shcho take vrodzhena klyshonohistʹ? 112. Yaki pizni symptomy vrodzhenoho vyvykhu stehna? 113. Yaki ranni symptomy vrodzhenoho vyvykhu stehna? 114. V yakyy termin pislya narodzhennya dytyny mozhna vstanovyty diahnoz vrodzhenoyi klyshonohosti? 115. Koly treba rozpochynaty konservatyvne likuvannya vrodzhenoyi klyshonohosti? 116. Yakyy v normi atsetabulyarnyy kut u novonarodzhenykh? 117. Suchasne likuvannya klyshonohosti? 118. Yaka operatsiya zastosovuyetʹsya pry likuvanni mʺyazovoyi kryvoshyyi? 119. Yakyy typ operatsiy dlya likuvannya liykopodibnoyi deformatsiyi hrudnoyi klitky zastosovuyetʹsya na suchasnomu etapi naychastishe? 120. Yakyy kharakternyy symptom liykopodibnoyi deformatsiyi hrudnoyi klitky u ditey Vy znayete? 121. Vada rozvytku yakoyi sudyny lezhytʹ v osnovi patohenezu syndroma Polanda? 122. Yakyy pokaznyk zastosovuyetʹsya dlya vyznachennya stupenyu deformatsiyi pry liykopodibniy deformatsiyi hrudnoyi klitky? 123. Vkazhitʹ symptomy, kharakterni dlya syndromu Marfana? 124. Optymalʹnyy vik dlya khirurhichnoho likuvannya LDHK? 125. Yakomu stupenyu deformatsiyi vidpovidaye indeks Hizhytsʹkoyi 0,48 u patsiyentiv z liykopodibnoyu deformatsiyeyu hrudnoyi klitky? 126. Yake spivvidnoshennya khlopchyky : divchata sered patsiyentiv z LDHK? 127. Yaka normalʹna ekskursiya hrudnoyi klitky? 128. Nazvitʹ uskladnennyam operatyvnoho likuvannya deformatsiy hrudnoyi klitky? The list of issues included the current and final control. Acute processes abdominal cavity 1. Current views on the etiology and pathogenesis of acute appendicitis. 2. avilable abdominal cavity and appendix, determining the clinical course of appendicitis in children. 3. Features of acute appendicitis in young children (under 3 years). 4. Features inspection infants with suspected acute appendicitis. 5. Differential diagnosis of acute appendicitis. 6. Diagnosis and treatment of appendiceal infiltrate. 7. Atypical forms of acute appendicitis. Clinical and diagnostics. 8. Primary pelvyoperytonit. Diagnosis, treatment. 9. Peritonitis. Classification. Diagnosis. 10. Differential diagnosis of acute appendicitis and peritonitis primary. 11. Symptom comparative dosage percussion (by AR Shurinkom). Methods of examination and evaluation criteria. 12. Supporting methods of examination of children with suspected acute appendicitis, their informative and diagnostic value. 13. The open and laparoscopic appendectomy: advantages and disadvantages. 14. The origin and location of Meckel diverticulum. 15. Diverticulitis Meckel. Clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment. 16. The main causes, clinical manifestations of peritonitis in infants. 17. Criteria for patient readiness for surgery when peritonitis. 18. Principles of preoperative preparation of a patient with peritonitis. Criteria child's readiness for surgery. 19. Principles of treatment of appendicular abscess. 20. Clinical and treatment of peritonitis in infants with extremely low birth weight. Acquired intestinal obstruction. Intussusception 1. Classification of intestinal obstruction in children. 2. The main clinical symptoms of idiopathic intussusception in children. 3. Describe additional methods of diagnosis of intussusception in children. 4. Indications Conservative smoothing intussusceptum children. 5. Contraindications to conservative smoothing intussusceptum children. 6. The essence of conservative smoothing intussusceptum children. 7. X-ray signs of high and low intestinal obstruction. 8. Complications intussusception, their prevention and treatment principles. 9. The main reasons for classification of postoperative adhesive intestinal obstruction. 10. The main pathogenetic factors of early postoperative adhesive intestinal obstruction. 11. The principles of conservative treatment of early postoperative adhesive intestinal obstruction. 12. The main causes of spastic and paralytic ileus. 13. Principles of preoperative preparation with mechanical intestinal obstruction. Criteria for patient readiness for surgery. 14. Features of preoperative preparation at high and low intestinal obstruction. 15. Description of basic medicines, which are used to restore blood volume. 16. bezoar as the cause of high intestinal obstruction. Clinical manifestations, treatment. 17. Foreign bodies of the gastrointestinal tract in children. Clinical manifestations, diagnosis, possible complications. 18. Therapeutic tactics in foreign bodies gastrointestinal tract in children. 19. The post burning stenosis and pyloric stomach as the cause of impaired patency of the gastrointestinal tract in children. The main causes, clinical manifestations. 20. Principles of treatment after burn stenosis and pyloric stomach in children. Gastrointestinal bleeding in children. 1. Typical clinical signs of bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract (esophagus, stomach, colon tpala 12). 2. Typical clinical signs of bleeding from upper secondary departments SHTK (small intestine). 3. Typical clinical signs of bleeding from the lower branches SHTK (rectum). 4. What is the cause of bleeding from esophageal varices? 5. What is the cause of bleeding in Meckel diverticulum? 6. What is the cause of bleeding in intussusception? 7. What is the cause of bleeding during bowel volvulus? 8. What is portal hypertension, portal hypertension shape? 9. What are the most common causes of portal hypertension? 10. Methods of diagnosis of portal hypertension. 11. Characteristic signs of portal hypertension in children. 12. Design Features probe Blackmore and what it is used. Features install it in children. 13. Value sandostatin to stop bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract in children. 14. Conservative and operational methods of intervention to stop bleeding in portal hypertension in children. 15. Causes dopechinkovoyi forms of portal hypertension syndrome in children. 16. Methods portosystemnoho bypass. 17. The causes bleeding in ulcer-necrotic enterocolitis in infants. 18. The causes of bleeding during bowel polyps in children, methods of diagnostics. 19. The causes of bleeding in the gastro-esophageal reflux (hiatal hernia, peptic structure, Barrett's esophagus). 20. A true and genuine bleeding sh.k.t. , Causes in children. Maxillofacial trauma. The destructive disease of the lungs and pleura 1. Thoracic trauma. Options. Probable signs of damage to internal organs. 2. Features thoracic trauma in childhood. 3. Pathogenesis of respiratory and circulatory disorders in the thoracic trauma. 4. Methods of examination used in the trauma of the chest cavity. 5. Damage to the trachea. Clinical symptoms, medical tactic. Ekstraperykardialna cardiac tamponade. 6. Damage to the lungs. Options diagnosis. Surgical tactic. 7. pneumothorax. Classification, etiology, pathogenesis of respiratory disorders. 8. pneumothorax. Clinic, physical and radiological diagnosis, first aid. 9. hemothorax. Causes, treatment tactics, indications for surgical intervention. 10. Injury heart. Variations, pathogenesis of heart failure. 11. Traumatic heart disease. Options, diagnosis, treatment. 12. cardiac tamponade. Options, clinical symptoms, emergency surgical care. 13. Clinical symptoms of esophageal perforation. Reasons perforation its complications. 14. mediastinitis. Etiology, clinic, diagnostics. 15. Methods of diagnosis of injuries in the esophagus. 16. Traumatic injuries diaphragm. The incidence, pathogenesis of respiratory disorders, diagnosis. 17. Classification of acute destructive pneumonia. 18. The pulmonary form of acute destructive pneumonia. Options, diagnosis, treatment. 19. Pulmonary pleural destructive forms of acute pneumonia. Options, diagnosis, treatment. 20. atelectasis and lung collapse. Causes, diagnosis and treatment options. 21. thoracostomy. Indications, methods pleural aspiration content. 22. pleural puncture. Methods of necessary tools. Childhood Oncology 1. Features of childhood cancer. General principles of diagnosis and treatment of malignant tumors in children. 2. sacrococcygeal teratoma: definition, anatomical and morphological classification and clinical manifestations. 3. Diagnosis sacrococcygeal teratomas (the possibility of prenatal diagnosis, instrumental methods, tumor markers) and therapeutic tactics. 4. Differential diagnosis of sacrococcygeal teratomas and meninhotselye. 5. Hemangioma: definition, classification, clinical manifestations. 6. Therapeutic management of hemangiomas in children. 7. chylangioma: definition, classification, clinical manifestations. 8. Methods of diagnosis and treatment guidelines limfanhiom. 9. dermoid cyst: definition, typical localization, clinical manifestations, treatment principles. 10. nephroblastoma (Wilms tumor): definition, clinical features, connection with other violations of embryogenesis. 11. What laboratory and instrumental methods used for the diagnosis of nephroblastoma? Principles of treatment nefroblastoma. 12. Neuroblastoma: definition of typical anatomic localization, clinical manifestations. 13. Principles of diagnosis of neuroblastoma (verification of diagnosis, diagnosis of primary focus, evaluation of biological activity of tumor metastases diagnosis possible). Principles of treatment of neuroblastoma. 14. Differential diagnosis of retroperitoneal neuroblastoma and nephroblastoma (Wilms tumor). 15. What malignant bone tumor often found in childhood? Value trauma in the etiology of bone tumors. Clinical manifestations of bone tumors. 16. Laboratory and instrumental methods of diagnosis, principles of treatment of malignant bone tumors. 17. Of the tissues predecessors developing soft tissue sarcoma? Which of them are most often found in childhood? Principles of diagnosis and treatment. 18. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of mediastinal tumors. 19. Type and clinical manifestations of benign pigmented skin tumors. 20. Risk factors for melanoma of early and late clinical signs. The acronym ABCD (assymetry, borders (bleed), change, diameter). Urology childhood 1. Define syndrome swollen scrotum. What are inflammatory and non-inflammatory disease, a syndrome manifested swollen scrotum. 2. The mechanism of occurrence and clinical manifestations of testicular torsion in infants and young children (ekstaravahinalna form torsion). 3. The mechanism of occurrence and clinical manifestations of testicular torsion in older children (intravaginal torsion form). 4. Diagnosis and treatment guidelines yayeka torsion in children. 5. Clinical manifestations, additional methods of examination and treatment guidelines hidatydy Morgagni torsion in children. 6. Differential diagnosis of testicular torsion and torsion hidatydy Morgagni children. 7. The main types of clinical manifestations and damage to private purse and its organs. 8. The therapeutic management of traumatic injuries of the scrotum and its organs. 9. The main etiological factors and clinical manifestations of acute nonspecific orchiepididymitis. 10. Diagnostics and principles of treatment of acute nonspecific orchiepididymitis children. 11. Complications of surgical diseases of the scrotum, their prevention and treatment principles. 12. Injury of the kidney: classification, clinical manifestations. 13. Laboratory and instrumental methods of examination that are most informative when kidney injury. 14. Injury to urinary bladder: a mechanism classification. 15. Clinical manifestations and treatment principles ekstraperytonealnoho bursting bladder. 16. Clinical manifestations and treatment principles intraperitoneal bladder rupture. 17. What are the basic mechanisms and clinical manifestations of urethral injury? 18. What additional survey of the most informative methods in different types of urethral injury? 19. Features of pathogenesis, clinical manifestations and diagnosis of urolithiasis in children. 20. Principles of conservative and surgical treatment of urolithiasis in children. Polytrauma. Closed abdominal trauma. 1. polytrauma in children: definition, epidemiology and pathogenesis of childhood. 2. Classification traumatic (hypovolemic) shock, the degree of severity. Diagnostic criteria and third-degree traumatic shock. 3. Therapeutic tactics in traumatic (hypovolemic) shock and feet. 4. Therapeutic tactics in traumatic (hypovolemic) shock second degree. 5. Therapeutic tactics in traumatic (hypovolemic) shock III degree. 6. Epidemiology, mechanism of closed abdominal trauma in children. The main clinical manifestations of traditional diagnostic methods. 7. Feasibility, diagnostic and therapeutic possibilities of laparoscopy in closed abdominal trauma in children. Contraindications to laparoscopy in closed abdominal trauma in children. 8. The mechanism and clinical manifestations of pancreatic injuries in children. 9. Laboratory and instrumental diagnostics of pancreatic injury. Principles of treatment of traumatic pancreatitis. 10. The etiology, mechanism and clinical manifestations of damage to hollow organs of the abdominal cavity. 11. Diagnosis of damaged hollow organs of the abdominal cavity. 12. Damage to the liver in a closed abdominal trauma: classification, clinical manifestations. 13. Laboratory and instrumental methods for traumatic lesions of the liver. 14. Therapeutic tactics in liver injury. 15. Hemobiliya: definition, clinical manifestations. 16. Laboratory and instrumental methods of diagnosis, treatment guidelines hemobiliyi. 17. spleen trauma: classification, clinical manifestations. 18. Diagnostic and therapeutic management of trauma spleen. 19. Differential diagnosis of parenchymal damage and hollow organs in the abdomen closed trauma. 20. Damage to the internal abdominal organs in infants: Causes, the main types of damage, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment tactics. Purulent surgical infection 1. International Classification of sepsis (American College of Chest Phisicians / Society of Critical Care Medicine Cnsensus Conference, 1992). 2. Clinical manifestations of systemic response to inflammation (SIRS). Features of the criteria for systemic inflammatory response (SIRS) in children depending on age. 3. Clinical criteria for septic shock. 4. Principles of treatment of sepsis. The role of ECMO (extracorporeal membrane oxygenation) in the treatment of sepsis. 5. The anatomic and physiological features of the skin and subcutaneous tissue in infants that determine the course of inflammatory diseases. 6. Necrotic phlegmon newborn: etiological factors, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations. 7. Diagnosis and treatment guidelines necrotic phlegmon newborn. 8. purulent mastitis newborns: causes, clinical manifestations, treatment principles. 9. Differential diagnosis of mastitis and breast engorgement physiological newborns. 10. omphalitis: definition, causes, classification, clinical manifestations. 11. Diagnosis and treatment omphalitis depending on the form of the disease. 12. Causes, clinical manifestation, treatment guidelines adrectal abscess in children. 13. Features of the structure and blood supply of long bones in children. 14. Clinical manifestations of acute hematogenous osteomyelitis (MGO) in children. 15. Laboratory and instrumental methods of diagnosis of acute hematogenous osteomyelitis in children. Typical radiological signs MGO long bones. 16. Differential diagnosis of tuberculous osteitis and MGO. 17. Principles of treatment of MGO in children. 18. anatomic localization, clinical manifestations of acute hematogenous osteomyelitis in newborns. 19. Radiographic signs, principles of treatment of acute hematogenous osteomyelitis in newborns. 20. Clinical and radiological signs of atypical forms of osteomyelitis in children. Malformations in Children 1. Etiopathogenesis birth defects. The notion of rules anomalies and defects. 2. Embiropatohenez malformations of respiratory system. Features prenatal diagnosis. 3. Classification of congenital malformations of the respiratory system. 4. Clinical symptoms and syndromes of congenital respiratory tract and lungs. 5. Methods of diagnosis of congenital respiratory system. Modern ray and endoscopic technologies. 6. Functional airway stenosis due to birth defects. Larynhomalyatsiya and tracheomalacia. The clinical picture, diagnosis, treatment. 7. organic Pidzv'yazkovyy stenosis, congenital, postintubatsiynyy, hemangioma. The clinic, diagnosis, treatment principles. 8. Congenital tracheal stenosis (full ring). Options, clinic, diagnosis, treatment. 9. Compression tracheal stenosis. Anatomical variations of vascular ring. 10. Complete vascular ring, double sided aortic arch and aortic arch. The clinic, diagnosis, treatment. 11. Incomplete vascular ring: aberrant right subclavian artery anomalies plechoholovnoho barrel. The clinic, diagnosis, treatment. 12. Loop pulmonary artery. Options, clinic, diagnosis, treatment. 13. Compression tracheal stenosis in tumors and cysts of the mediastinum. Options nosology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic methods, treatment principles. 14. traheostravohidna congenital isolated fistula. The clinic, diagnosis, treatment. 15. Congenital emphysema. Pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment. 16. aplasia, agenesis of the lung. The anatomical and pathophysiological characteristics. 17. aplasia lungs. Pathogenesis, clinical picture, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, the possibility of surgical treatment. 18. Congenital pulmonary cysts. Classification, diagnosis, complications, surgical treatment. 19. Pulmonary sequestration. Options peculiarities of pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment. 20. Bronchiectasis. The clinic, diagnosis, treatment. 21. tracheostomy. Indications and contraindications. Technique. 22. Classification of esophageal atresia. Features prenatal diagnosis of esophageal atresia. 23. Clinical esophageal atresia newborn. Causes of aspiration pneumonia in various forms of esophageal atresia. 24. Clinical esophageal atresia newborn. 25. Diagnosis of esophageal atresia (plain radiography, probing the esophagus, esophagogram). Causes of aspiration pneumonia in various forms of esophageal atresia. 26. VACTERL association with esophageal atresia. Clinical manifestations, principles of diagnosis and treatment. 27. Preoperative preparation in children with esophageal atresia. 28. The choice of surgical tactics depending on the form of esophageal atresia. Hastrostomiya.yak method of preparation for radical surgery for esophageal atresia. Radical surgery at esophageal atresia with lower trachea-esophageal fistula. 29. Complications of surgical treatment of esophageal atresia (insufficiency of anastomosis stitches). Clinical manifestations, principles of diagnosis and treatment. 30. Complications of surgical treatment of esophageal atresia (relapse trachea-esophageal fistula). 7 list of educational and methodical literature. 1. Хірургія дитячого віку: підручник / В.І. Сушко, Д.Ю. Кривченя, О.А. Данилов, В.А. Дігтяр та ін.; за ред. В.І. Сушка, Д.Ю. Кривчені. – 2-е вид., перероб. і доп. – К.: Медицина, 2009. – 800 с. 2. Сушко В.І. Хірургія дитячого віку. – К.: Здоров’я, 2002. – 704 с. 3. Дольницький О.В., Кривченя Д.Ю., Поліщук М.Є. Дитяча травматологія. – К.: Книга плюс, 2006. – 472 с. 4. Вади розвитку у дітей (самостійна аудиторна та поза аудиторна робота студентів) /В.А.Дігтяр, В.І.Сушко, Л.М.Харитонюк, О.М.Барсук та ін.. / Дніпропетровськ, 2011 – 334 с. 5. Ашкрафт К.У., Холдер Т.М. Детская хирургия, в 3-х томах / Пер. с англ. СПб.: Хартфорд, 1996. 6. Д.Ю.Кривченя, С.В.Лисак, О.М.Плотников. Хірургічні захворювання у дітей – Вінниця, «Нова книга», 2008 – 256 с. 7. Исаков Ю.Ф. Хирургические болезни детского возраста. – М.:Медицина, 2004. – в 2х томах. 8. Детская хирургия : национальное руководство / под. ред. Ю.Ф.Исакова, А.Ф.Дронова. – М. : ГЭОТАР-Медиа, 2009. – 1168 с. 9. Оперативная хирургия с топографической анатомией детского возраста: Учебник для студ. мед. ин-тов / Исаков Ю.Ф., Лопухин Ю.М., Степанов Э.А., Михельсон В.А., Тихонов Ю.А. и др.; Под ред. Ю.Ф. Исакова, Ю.М. Лопухина. - 2-е изд., перераб. и доп. - М.: Медицина, 1989. - 592 с. Додаткова література. 1. Природжені вади розвитку. Основи діагностики та лікування: монографія / О.В.Дольницький, В.О.Галаган, О.В.Ромадіна – К., 2009 – 1040 с. 2. Исаков Ю.Ф. Хирургические болезни детского возраста. – М.:Медицина, 2004. – в 2х томах. 3. Детская хирургия : национальное руководство / под. ред. Ю.Ф.Исакова, А.Ф.Дронова. – М. : ГЭОТАР-Медиа, 2009. – 1168 с. 4. Оперативная хирургия с топографической анатомией детского возраста: Учебник для студ. мед. ин-тов / Исаков Ю.Ф., Лопухин Ю.М., Степанов Э.А., Михельсон В.А., Тихонов Ю.А. и др.; Под ред. Ю.Ф. Исакова, Ю.М. Лопухина. - 2-е изд., перераб. и доп. - М.: Медицина, 1989. - 592 с. 5. Баиров Г.А. Неотложная хирургия детей – Л.: Медицина, 1983 – 218 с. 6. Немилова Т.К., Караваева С.А. с соавт. «Пороки развития пищеварительного тракта у новорожденных» - СПб, 2002. 7. Соловьев А.Е. Неотложная хирургия детского возраста. – Запорожье, 2000.- 421с 8. Хірургічні хвороби./ под.ред. Грубника В.В. – Одеса, 2003г. – 447с. 9. Шунько Е.Е., Ханес Г.С., Лакша О.Т.Перинатальный сепсис. Учебно-метод. Пособие. Киев. Рутения, 2002. 10. Атлас детской оперативной хирургии / под ред. П.Пури, М.Гольварта; пер. с англ. ; под общ. Ред. Проф. Т.К.Немиловой. – М. : МЕДпресс-информ, 2009. – 648 с. : тил. 11. А.Г.Пугачев. Детская урология : руководство для врачей. – М. : ГЭОТАР-Медиа, 2009. – 832 с. : ил. 12. Історія хірургії дитячого віку України : навч. Посібник/ [О.К.Толстанов, Ю.В.Вороненко, В.Ф.Рибальченко та ін..] ; за ред.. О.К.Толстанова, Ю.В.Вороненка, В.Ф.Рибальченка, А.Ф.Левицького, А.А.Переяслова, П.С.Русака. – Тернопіль : ТДМУ, 2012. – 432 с. 13. М.Дж. Мак-Дональд, Дж. Рамасезу. Перевод с англ. Пожарский В.В. Атлас манипуляций в неонатологии. – 2011 – 496 с. 14. Харнесс Дж. К. Ультразвуковая диагностика в хирургии: основные сведения и клиническое применение – 2012, 597с. 15. Кузнечихин Е.П. Хирургическая патология верхней конечности у детей. Руководство для врачей – 2012, 840с. 16. Дронов А.Ф., Смирнова А.Н. Гнойно-воспалительные заболевания мягких тканей и костей у детей – 2008, 260 с. 17. Тихомирова В.Д. Детская оперативная хирургия: Практическое руководство, М: МИА, 2011, 872 с. 18. Кривченя Д.Ю., Дубровин А.Г., Андреещев С.А. Диагностика и лечение стеноза пищевода у детей – К.: Лига-Информ, 2008. – 182 с.