Chapter One Study Guide Questions: Earth Layers, Continental Drift
advertisement

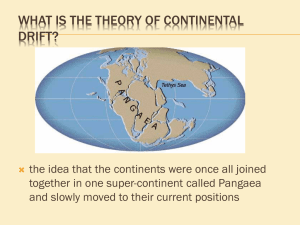
Chapter One Study Guide Questions: Earth Layers, Continental Drift, Plate Tectonics Plus…Fossils, Geologic Time Periods and Extinctions 1. How is the inner and outer core similar? How is the inner core and outer core different? 2. Why is the outer core important to life on Earth? What would happen if Earth did not have this layer? 3. How did oobleck behave under high pressure compared to low pressure? How did oobleck behave under conditions of high temperature compared to low temperature? What is the name of the property of oobleck that is like the property of magma in the mantle? 4. What happens, on average, every 250,000 years, to Earth’s magnetic field? 5. Define convection as a way that heat can be transferred? 6. A) What causes convection currents in the mantle? B) Which “groovy” product was demonstrated in class to show convection currents in action? 7. Explain four (4) things that Alfred Wegener noticed to back up his theory of Continental Drift. 8. List four (4) things you know about the life of Alfred Wegener. 9. What are the names of the three (3) reptiles and one plant that Alfred Wegener mapped on distant continents? (matching habitat zones) 10. What are the names of the three Supercontinents we learned about in class? (two from the past, and one in the future) 11. Why is it strange to find COAL deposits in Pennsylvania? 12. List the SEVEN (7) major and minor plates . (Be able to identify them on a blank map of the Earth’s plates) 13. What are the three (3) ways that tectonic plates can be in contact with one another? (three plate boundary types) Draw arrows to show the direction of plate motion for each of the three types of boundaries. 14. What ideas did Marie Tharp and Harry Hess contribute to the theory of Plate Tectonics? 15. What are the two (2) main causes of crustal plate movement? 16. What is the average rate of plate movement? (Compare to fingernail growth) 17. What is the difference between continental plates and oceanic plates? What rock type is typical of each. 18. Earth’s magnetism experiences “reversals” periodically. How does Sea Floor Spreading indicate that reversals have occurred? 19. What two (2) features are associated with subduction zones? 20. What is a Hot Spot? (Note: Yellowstone, and Hawaii) 21. Explain what happened to form the Himalayan Mountain Range. 22. Where would you expect to find the oldest rocks on the sea floor? 23. A) How long ago did Pangaea begin separating? B) What is the name of the Pangaean Superocean (and its minor sea)? 24. Pangaea first separated about 200 million years ago into a northern and southern region. What were the names of these two (2) regions? 25. Which two (2) inventions used in the 1960s helped to prove why the continents drift, by providing a map of the ocean floor? 26. Which country in the Northern Atlantic Ocean has the MidOceanic Ridge running through it? 27. The red needle on a compass always points to what? 28. Which type of pole, geographic or magnetic, wanders in response to action in the outer core of our planet? 29. Which fossils are found in Montana, which help to show that plate movement has occurred.? 30. What are the names of the four (4) geologic time eras, and what type of life was predominant during that time? 31. Besides the current “Mass Extinction,” how many previous “Mass Extinctions” have there been during the history of the Earth? What is a “Mass Extinction?” 32. When fossil fuels (coal or petroleum/oil and gas) are burned, we release carbon dioxide into the air. This contributes to what problem? 33. How many humans live on earth today? Chapter One Study Guide Answers: Earth Layers, Continental Drift, Plate Tectonics Plus…Fossils, Geologic Time Periods and Extinctions 1. Inner Core/Outer Core = both made of metallic, magnetic Iron and Nickel Inner Core = SOLID, Outer Core = LIQUID 2. Outer core generates Earth’s protective Magnetic Field, which blocks harmful radiation. Without it, too much UV would reach the surface, and we would not survive. 3. Oobleck under high pressure = solid, under low pressure = liquid Oobleck under high temp = liquid, under low temp = solid (Plasticity) 4. Earth’s magnetic field experiences a reversal every 250,000 years or so. 5. Convection = circulation of hot matter rising above a heat source, then cool matter becoming more dense and sinking (happens in the mantle) 6. A) Convection: caused by heat transfer from the core. B) Lava Lamp 7. Alfred Wegener noticed the A) puzzle fit of continents B) matching fossils on distant coastlines C) matching rock types on distant coastlines D) matching glacial deposits on distant coastlines 8. Alfred Lothar Wegener was born in Germany in 1880, died in 1930 in Greenland, was first to develop idea of drifting continents, wrote a book about it in 1910, died not knowing the world would believe his theory. 9. Lystrosaurus (shovel mouth reptile) Cynognathus (dog jaw reptile) and Mesosaurus (middle reptile) and Glossopteris (plant: tree) 10. Rodinia (past), Pangaea (past), and Pangaea Ultima (future) 11. Coal is formed in TROPICAL regions (from decayed tropical vegetation) 12. MAJOR: North American, South American, African, Eurasian, Antarctic, Indo-Australian, Pacific MINOR: Juan De Fuca, Nazca, Cocos, Caribbean, Arabian, Scotia, Philippine 13. Convergent: (plate collision) * Divergent: (plate separation) * Transform: (plates sliding past each other in opposite directions) -------- -------14. Marie Tharp was the first to discover the Mid-Ocean Ridge system. Harry Hess surveyed the ocean floor using Sonar and discovered that the sea floor is spreading. (He also noticed that the age of ocean crust varies the farther you move away from the ridge.) 15. Crustal Plates move due to convection currents in the mantle which drive the process of Sea Floor Spreading, which in turn cause continents to move. 16. Plates move 2.5 cm per year on average (same rate as fingernail growth) 17. Continental plates are thicker and less dense than oceanic plates. Continental rock = granite, Oceanic rock = Basalt 18. Identical magnetic pole reversal stripes develop on each side of the Mid-Oceanic Ridges as the sea floor spreads apart. 19. Deep Sea Trenches and Volcanoes are associated with subduction zones. 20. Hot Spot = stationary break in center of a plate (magma rises through it) 21. India collided with Asia 20 million years ago, forming the Himalayas 22. The oldest rocks are those farthest away from the MidOcean Ridge, and the youngest rocks are closest to the Mid-Ocean Ridge. 23. A) Pangaea started separating about 225 million years ago. B) Pangaean Superocean = Panthallassic Ocean (and Tethys Sea). 24. Pangaea first separated into northern Laurasia and southern Gondwanaland 25. Sonar and Deep Sea Submarines 26. Iceland 27. Red needle points to the dominant magnetic pole, which is currently NORTH. 28. The magnetic poles wander over time, as the core changes 29. Tropical Fish and Shark fossils are found in Montana. 30. Started 4.6 billion years ago (7/8ths of all time on Earth): * Precambrian Eon (Age of No Life to Primitive Life in the Oceans) Started 540 million years ago: * Paleozoic Era (Age of Fish) Started 250 million years ago: * Mesozoic Era (Age of Dinosaurs) > Triassic, Jurassic, Cretaceous Periods Started 65 million years ago to present: * Cenozoic Era (Age of Mammals and Birds) 31. There have been five (5) previous “Mass Extinctions” on Earth. A “Mass Extinction” is when over 50% of all species of life on the planet go extinct. (Extinction means that a form of life is gone forever.) 32. The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming. 33. Approximately SEVEN (7+) BILLION humans live on Earth today, and that number is increasing exponentially…causing the 6th Mass Extinction?