Preliminary Project Proposal for HP-III Submitted to DEA, Ministry of
advertisement
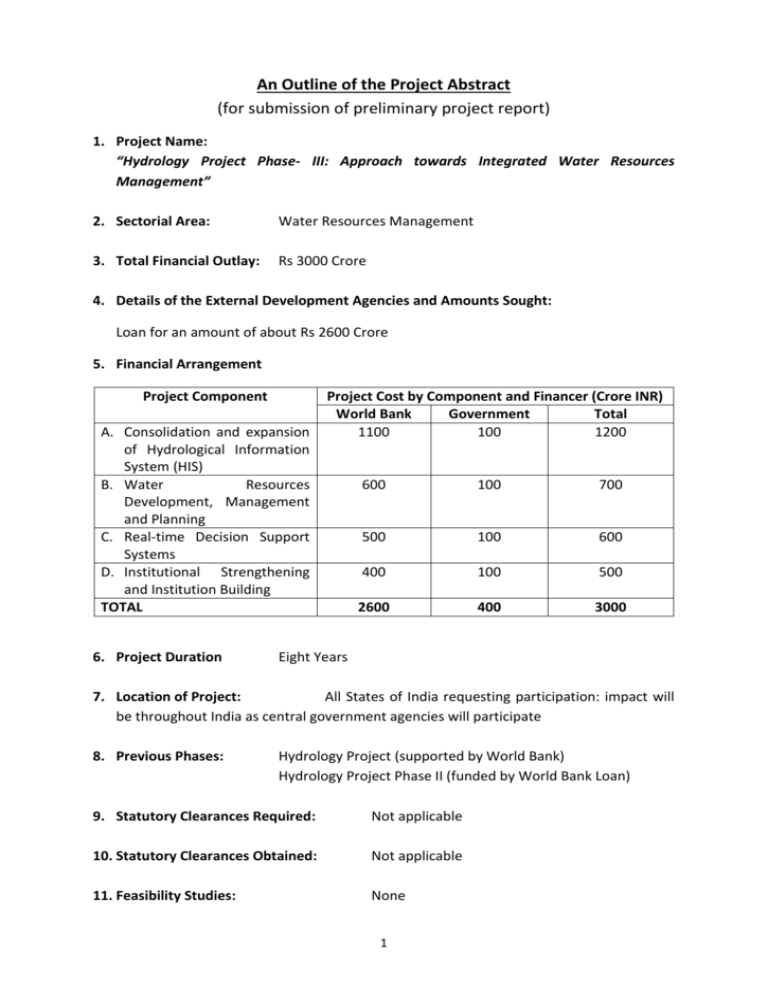
An Outline of the Project Abstract (for submission of preliminary project report) 1. Project Name: “Hydrology Project Phase- III: Approach towards Integrated Water Resources Management” 2. Sectorial Area: Water Resources Management 3. Total Financial Outlay: Rs 3000 Crore 4. Details of the External Development Agencies and Amounts Sought: Loan for an amount of about Rs 2600 Crore 5. Financial Arrangement Project Component A. Consolidation and expansion of Hydrological Information System (HIS) B. Water Resources Development, Management and Planning C. Real-time Decision Support Systems D. Institutional Strengthening and Institution Building TOTAL 6. Project Duration Project Cost by Component and Financer (Crore INR) World Bank Government Total 1100 100 1200 600 100 700 500 100 600 400 100 500 2600 400 3000 Eight Years 7. Location of Project: All States of India requesting participation: impact will be throughout India as central government agencies will participate 8. Previous Phases: Hydrology Project (supported by World Bank) Hydrology Project Phase II (funded by World Bank Loan) 9. Statutory Clearances Required: Not applicable 10. Statutory Clearances Obtained: Not applicable 11. Feasibility Studies: None 1 12. Implementation Agencies: Ministry of Water Resources (Lead implementing agency), Water Resources Departments of Participating States, Other Central and State Government Bodies 13. Basic Design of the Project 13.1 Rationale Hydrology Project Phase-I and Phase-II have been a World Bank funded Projects and focused on establishment of Hydrological Information System (HIS) and increased geographical coverage and analytical usage of facilities created under the first phase of the Project respectively. Phase I of the project ran from 1995 to 2003, while Phase II has run from 2006 and is scheduled for completion in 2014.Hydrology Projects have covered 13 States and eight (8)Central Organisations across in India. The focus has been on establishing improved data collection networks and improved data handling processes to improvement management of key information. Under HP-II, Central and State organisations procured State of the Art equipment, tools and technology. Following key items/ applications have been developed for the first time in the country: i) Real-time Hydro-meterological Data Acquisition Systems were procured and installed in several parts of the country, which provide data through means like satellites, telephony or V-SAT. ii) Real-Time Decision Support System (RT-DSS) has been developed for flood control and reservoirs operations in Bhakra Beas Management Board and in Maharashtra. iii) Decision Support Systems- Planning (DSS-P) for surface & ground water planning, irrigation management, drought monitoring management and conjunctive use of surface water & ground water etc. have also been developed iv) Real-time Water Quality equipment has also been successfully installed at 10 different locations on river Ganga and measures upto 10 parameters. v) The Pilot Phase of the Aquifer Mapping Programme of MoWR has seen the application of Heliborne survey for aquifer mapping for the first time in the country. This technique is just a few years old and India joins the league of few nations like USA, Netherlands, Denmark, Canada, Australia etc. While much of India has been covered in Phases I and II of the project, there are large northern States that have not yet been involved. These include the States in the Ganga and Brahmaputra Basins (including much of Madhya Pradesh).Several States/Central organisations have now proposed that the applications developed under the HP-II needed to be upscaled for the entire country, including those States which have not been covered under Hydrology Projects. Many of these States, viz. North-eastern States, West Bengal, 2 Haryana, U.P., Jharkhand etc. have conveyed their keenness to participate in the Phase III of the Project. The States/Central organisations were of the view that the HIS and their consequent applications like DSS etc. developed under HP-II need to be replicated throughout the country, so as to bring the entire nation at par. Any new phase of Hydrology Project should be closely aligned with National Water Policy, Five Year Plans etc. The National Water Policy (2012) has identified basic principles for water resources management in India. These include management within national perspectives, equity and social justice to inform use and allocation of water, sustainability of water use, managed as a community resource, efficient water use, recognition of environmental needs and recognising interlinking of water quality and water quantity. All these point to a need to develop Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM) within a river basin unit. Hydrology Project Phase III would also take into account these principles with the project Development Objectives (PDO).There are a number of areas where a further project might have a role to support: – – – – Development of HIS in non-Hydrology Project States Continued support for development of HIS in Hydrology Project States Introduction of new techniques and technologies to participating Agencies Continued support for central agencies. Continued support for the existing Hydrology Project Agencies is needed, as sustainability without external support has not yet been firmly established in many of the States. Some of the developments within HP-II (such as the Hydrological Design Aids; the Decision Support System for Planning; the surface water and groundwater database systems) are areas where continued support would prove to be very important to guarantee and consolidate improvements made under HP-II. For sustainability, it seems appropriate to concentrate on development of the capacity and focus of central agencies to provide technical support to the State Agencies – through training programmes, advice on matters relating to observations (networks, equipment, Standard Operating Procedures etc.) and data management, and also to advise regarding appropriate solutions to water resources management issues. Further, cross learning from participating States would not only benefit the new States, but would also help the Old States to consolidate their gains. 13.2 Proposed Project Activities India is under water stress since the early 2000’s, and its main challenge is to produce more food with less water; other important issues concern Water Quality, reservoir sedimentation, climate and land use change impacts on water resources availability, etc. Thus many States and Central organisations have submitted their requests to take up several activities under the next phase of Hydrology Project. Most of the activities are directly or indirectly focussed on the development of Integrated Water Resources 3 Management (IWRM). Some of the activities that can be taken up under the next phase of the Project are given as below: A. Consolidation and expansion of HIS B. Extend HIS to all non-HP States of India including the procurement and installation of equipment, software and data sets, development of HIS infrastructure including State and Regional Data Centres. Upgrading and expansion of existing HIS networks, advanced monitoring equipment, additional groundwater observation wells. Upgrading of existing HIS monitoring stations with Real-time Data Acquisition (RTDAS) systems; develop mobile-based applications for addressing flood forecasting and flood risks. Installation of additional RT-WQMS stations in important surface water bodies for the assessment of water quality in polluted river stretches; Rehabilitation and upgrading of WQ laboratories established under HP-I (15 to 20 years old). Introduce web-based data processing (including mobile applications) throughout India through e-SWIS, e-GEMS and e-WQIS and enhance the capabilities and functionalities of these software as per requirement. Include the monitoring of water use and water demand data in HIS, as well as agricultural and irrigation related data Ground-water exploration to delineate aquifers Improvement/Strengthening of India-WRIS portal to provideweb services to other portals Water Resources Development, Management and Planning Objective: Move from data to information to application; integration of tools developed in HP-I and HP-II in design, planning and operational practices throughout the country and scaling-up the utilization of HIS data for IWRM and planning. Scale-up the application of DSS-Planning to other river basins and promote greater use of these systems for water resources planning and management issues, including surface water and groundwater development and planning, irrigation system management, drought monitoring and management, conjunctive use of surface water and groundwater, optimization of reservoir operations, etc. Pilot studies for catchment-wide water resources assessment including actual water use, return flows, impact of climate change, environmental flow needs, appropriate allocation of water resources in the catchment, development of alternatives for improved water management in the catchment, thereby supporting IWRM. Introduce Web-Based Hydrological Design Aids (HDA) to all State SW agencies in order to improve current design practices of water resources infrastructure; expansion of tools in the HDA toolbox, e.g. with hydrological models. Carry out reservoir sedimentation studies, reservoir bathymetric surveys and river sediment load monitoring. 4 C. Impact of climate change on water resources. Address multiple issues through Purpose Driven Studies Support to CGWB and to State Groundwater Departments to shift from “Groundwater Development” to “Groundwater Management” including: Aquifer Mapping, Participatory Groundwater Management, Technological upgrading, etc. Introduction and application of different groundwater modelling software. Pilot studies to develop methodologies for water quality assessment, including coordinated and collaborative laboratory improvement programs and improved scientific interpretation and reporting of water quality data. Pilot studies for increasing Water Use Efficiency. Pilot Studies to develop Aquifer Management Plans Studies to determine Environment Flow. Development of Aquifer Information & Management Systems by the State Governments Census of Major & Medium Water Resources Projects and establishment of an assest management service. Preparation reference Evapo-transpiration Atlas for country. Development of Aquatic life assessment in major rivers of India Development of android based application for hydrological observation site management and data updation. Improvement in Glacial Lake Monitoring and forecasting of unusual weather effects. Development of standard packages for minor distribution networks and structures to speed up execution. Real-time Decision Support Systems Implement RTDSS systems for i) flood forecasting and flood management, ii) WR system operation and iii) drought management for major water resources systems, irrigation canal system operations, reservoir operations, etc. Utilization of real-time data monitoring and data processing (RTDAS/RTDSS) for improved reservoir management, canal operation, optimization of hydropower generation, flood forecasting, and flood and drought management, with particular attention to inter-state rivers. Rationalization of the operation and management of medium and major irrigation systems through RTDAS/RTDSS systems for improved water use efficiency, automation of tube well operations, etc. Introduction and exploration of Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems for optimal irrigation system management Introduction of flood plain mapping, flood inundation modeling, flood risk zoning and flood vulnerability mapping Introduction of dam break analysis, flood modeling and flood forecasting Explore the feasibility of using Meteosat/INSAT satellite based estimation of precipitation (based on Cold Cloud Temperatures) and actual evapo-transpiration, in conjunction with real-time field measurements of rainfall and other hydro5 meteorological parameters, as input to flood forecasting and drought monitoring & management systems. D. Institutional Strengthening and Institution Building Establishment of a permanent HIS Coordination Secretariat (HIS-CS) in MoWR (CWC/CGWB) to coordinate HIS activities across HP-States beyond Hydrology Project. Development of the capacity and focus of Central Agencies to provide technical support to State Agencies – through training programmes, advice on matters relating to observations, data management etc. Development of Central and State Water Resources Information Centres (merging of SW and GW branches of HIS, including Data Centres) Support to the establishment of River Basin Organizations (RBO) for selected major river basins Provision of field equipment, GPS, GIS data sets, toposheets, Data Centres (buildings and hardware/ software), vehicles and office infrastructure. Establishment of Hydrological Observation Training institute, including current meter calibration facilities (proposed by CWC) and Centre of Expertise in hydrometric monitoring equipment to advise all monitoring agencies on appropriate choice of equipment, its specification, and appropriate management and maintenance Training programs at various HIS levels, domestic study tours and international study tours, cross learning from participating States, introduction of HDA, e-SWIS, e-GEMS, e-WQIS, etc. Promote data sharing and dissemination, joint data validation and data utilization for design, planning and management purposes; Enhance relevance of the HDUG and promote improved dialogue between the data managers and the data users; support to data user awareness programs Support to agencies in developing websites enabling easy data access and dissemination Sustainability HIS requires to cover all of India in the HIS, improve inter-agency coordination mechanisms, central data storage, standardization of equipment, AMCs, and O&M training Interventions on data sharing and dissemination, joint data validation and data utilization for design, planning and management purposes, including both operational and long-range WRD planning; Integrate HIS with India-WRIS, and create National and State Water Informatics Centres. Link IMD, CPCB and the Ministry of Agriculture to the India-WRIS platform to enable complete availability of data on the country’s water resources. Collaboration with research institutes and private agencies for conducting research and developed activities for designing of low cost indigenous sensors and other hydro-meteorological equipment within India 6 Incremental staff cost (recurrent cost) for strengthening data collection and data management services Technical Assistance and Management Consultancy to support project implementation and management, fiduciary assistance, and technical support; a MIS would need to be developed to monitor physical and financial progress of Project implementation, as well as the monitoring of results and outcomes of the Project. 14. Target Population: Improved water resources management and improved management of floods that will follow from the project will benefit the entire population of India. 15. Detailed Action Plan: Hydrology Project Phase-III Year Action Plan Yr1 HIS Establishment in New States; consolidation of HP-II in Old States and Central organisations Yr2 HIS Establishment in New States; consolidation of HP-II in Old States and Central organisations HIS Establishment in New States; consolidation of HP-II and development of applications in Old States and central organisations HIS Establishment in New States; consolidation of HP-II and development of applications in Old States and central organisations Consolidation of HIS and Development of Applications in New States; consolidation of HP-II and extension of development of applications in Old States and central organisations Consolidation of HIS and Development of Applications in New States; consolidation of HP-II and extension of development of applications in Old States and central organisations. Yr3 Yr4 Yr5 Yr 6 Yr 7 Yr 8 Consolidation of HIS and Development of Applications in New States; consolidation of HP-II and extension of development of applications in Old States and central organisations Consolidation of HIS and Development of Applications in New States; consolidation of HP-II and extension of development of applications in Old States and central organisations 7 16. Quantitative and qualitative target indicators: TBD (To be decided) 17. Environmental Sustainability of Project: The direct environmental impact of the project (the impact of work done under the project in terms of construction and physical development) will be minimal as little construction will be involved – some additional buildings around the country (to accommodate staff and equipment). The potential positive impact of the project on environment is, however, likely to be very significant: improved knowledge of water behaviour obtained through improved monitoring and analysis of data will lead to improved management of natural resources, hence improved ability to monitor the impact of all development on rivers and groundwater, and development appropriate measures to mitigate such impacts effectively. Training programmes to be included in the project will be focused on establishing technical sustainability of the project. 18. Land Acquisition / Re-settlement Not Applicable 19. Linkage with Similar Projects: (i) Information regarding projects in similar areas undertaken previously: Hydrology Project Phase-I and Phase-II have been World Bank funded Projects and focused on establishment of Hydrological Information System (HIS) and increased geographical coverage and analytical usage of facilities created under the first phase of the Project respectively. Phase I of the project was from 1995 to 2003, while Phase II began in 2006 and has completed on 31st May, 2014.Hydrology Projects have covered 13 States and eight (8) Central Organisations across in India. The focus has been on establishing improved data collection networks, improved data handling processes for improvement management of key information, development of Decision Support Systems in 13 river sub-basins, etc. (ii) Does the Project form part of the sectoral strategy umbrella project? No. 20. Finance Plus Elements: While great steps have been taken under the Hydrology Project towards establishment of HIS and development of DSS, there is still a significant way to go to make sure there are sufficient good quality data and decision support systems for the management of India’s water resources. The value of bringing in experience and knowledge from rest of the world, providing reliable datafor optimising water resources management within the country is so great that the importance of furtheringsuch work is hard to overemphasise. Extensive work has also begun in the field of integrated water resources management across the world. To avoid re-inventing the wheel, it is time to learn from their experience and bring the latest technology to India. The experience and achievements of 8 Hydrology Project, coupled with international best practices, are essentially required for an integrated approach towards water resources management. ***** 9