Unit 5B Study Guide
advertisement
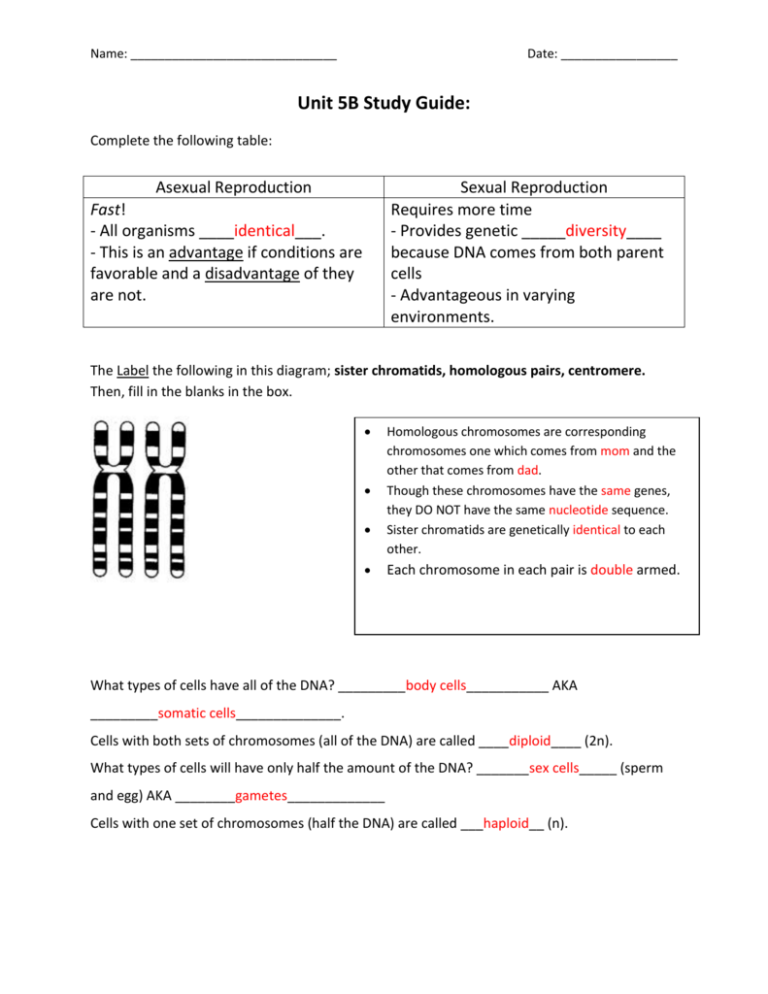
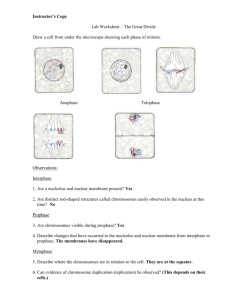
Name: ______________________________ Date: _________________ Unit 5B Study Guide: Complete the following table: Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Requires more time - Provides genetic _____diversity____ because DNA comes from both parent cells - Advantageous in varying environments. Fast! - All organisms ____identical___. - This is an advantage if conditions are favorable and a disadvantage of they are not. The Label the following in this diagram; sister chromatids, homologous pairs, centromere. Then, fill in the blanks in the box. Homologous chromosomes are corresponding chromosomes one which comes from mom and the other that comes from dad. Though these chromosomes have the same genes, they DO NOT have the same nucleotide sequence. Sister chromatids are genetically identical to each other. Each chromosome in each pair is double armed. What types of cells have all of the DNA? _________body cells___________ AKA _________somatic cells______________. Cells with both sets of chromosomes (all of the DNA) are called ____diploid____ (2n). What types of cells will have only half the amount of the DNA? _______sex cells_____ (sperm and egg) AKA ________gametes_____________ Cells with one set of chromosomes (half the DNA) are called ___haploid__ (n). [Type text] Complete the following table: Organism Number of chromosomes in each body cell (2n) Number of chromosomes in a each sex cell (n) Corn plant 20 10 Housefly 12 6 Fruit fly 8 4 Complete the graphic organizer: Mitosis Fertilization 23 (n) egg 23 (n) + 46 (2n) 46 (2n) 46 (2n) sperm = 46 (2n) Mitosis zygote 46 (2n) 46 (2n) Mitosis 46 (2n) List the three sources of genetic variation that result from meiosis and sexual reproduction: 1. ___Crossing over_________ 2. ___Independent assortment____ 3. ___Random combination of sperm and egg___ [Type text] Use the graphic organizer of meiosis to review the key points during the production of gametes. Be sure to label and define in your own words: tetrads, crossing over, independent assortment, and nondisjunction. Meiosis I Stage Interphase I Description -Growth -DNA replication -Preparing for cell division Prophase I -Crossing over occurs when pieces of nearest chromatid (between homologues) trade places. -Chromatin condenses to chromosomes -Spindle form -Nuclear envelop disappears -Homologous chromosomes pair up (tetrads) Metaphase I -Independent assortment occurs when homologous pairs line up randomly across the middle of the cell -Homologous pairs (tetrads) line up in the middle -Spindle fibers attach at the centromere Anaphase I Nondisjunction can occur here -Spindle fibers pull homologous pairs apart Telophase I -Nuclear envelop returns -Spindle fibers break down -Sometimes chromosomes relax to chromatin -Cleavage furrow or cell plate begins to form Cytokinesis I -Cytoplasm splits -End up with 2 cells that have a haploid number of double armed chromosomes Picture [Type text] Meiosis II Stage (Interphase II) Description -Not a true interphase -Most cells skip this step -NO additional DNA replication Prophase II -If necessary, chromatin condenses to chromosomes -spindle forms -Nuclear envelope goes away Metaphase II -Double armed chromosomes line up in the middle -Spindle attaches at the centromere Anaphase II Nondisjunction can occur here -Sister chromatids split apart and move to opposite sides of the cell Telophase II -Nuclear envelope comes back -Spindle breaks down -Chromosomes relax into chromatin -Cleavage furrow or cell plate begins to form Cytokinesis II -Cytoplasm splits -End up with 4 cells with a haploid number of single armed chromosomes Picture [Type text] Describe what is happening in this picture: _Homologous chromosomes are exchanging parts of their chromosomes with each other (crossing over)._________ In which phase of meiosis does this occur? _______During Prophase I____ Define gametogenesis: __Gametogensis is the production of gametes or sex cells using the process of meiosis. ______________________________________________________________________________ Use the diagrams below to describe how gametogenesis is different in males and females. Process:___Oogenesis__ Result: _Production of 1 egg cell ______________________ Process:_Spermatogenesis Result: _Production of 4 sperm cells_________________ [Type text] Most chromosomal disorders (like Down syndrome) result from the improper separation of chromosomes during meiosis. This is called __Non-disjunction____. What is trisomy? _An extra chromosome in a gamete (sex cell) which leads to an offspring with 3 copies of a chromosome._______________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ Analyze the following karyotype: a. Is this from a human cell? ___Yes______ b. How do you know? _23 homologous pairs__________ c. What chromosomal disorder does this patient have? ___Edwards’ syndrome/trisomy 18 d. Is this a male or female? ____Female_____________ Match the phase of meiosis to the statement that describes it: __BC___ Nucleus reforms around 23 single armed chromosomes as cleave furrow forms __C___ Spindle fibers attach to homologous chromosomes line up along “equator” or middle of cell __AC___ Nucleus breaks down, centrioles migrate, and chromatin condenses into 23 double armed chromosomes WORD BANK a. Interphase I b. Prophase I c. Metaphase I d. Anaphase I __B___ Nucleus breaks down, centrioles migrate, tetrads form, crossing over occurs, chromatin condenses into 46 double armed chromosomes e. Telophase I __D___ Spindle fibers shorten and pull apart homologous chromosomes ab. Interphase II __BC___ 4 gametes are formed from 2 haploid cells ac. Prophase II __AD___ Spindle fibers attach to centromeres of 23 double armed chromosomes ad. Metaphase II __E___ 2 haploid cells with double armed chromosomes are formed in this process ae. Anaphase II __AE___ Spindle fibers shorten and pull apart sister chromatids bc. Telophase II