Plate Tectonic Study Guide 2015-Answer Guide
advertisement

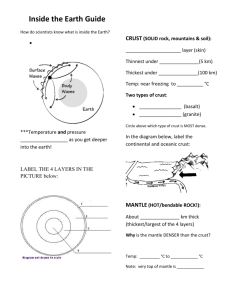
Name:____________________________________________________Date:_____________Pd Study Guide: Layers of the Earth, Continental Drift, and Plate Tectonics (S6E5a., S6E5e., S6E5f., and S6E5g.) 1.List and describe (composition) the layers of the Earth starting from the outermost layer. Draw a diagram (Crust, Lithosphere, Asthenosphere, Mesosphere, Outer Core, and Inner Core) 2. What is the inner core’s material? 3. What happens to the temperature, density, and pressure when you descend from the crust to the inner core? 4. List the layers from the least dense to most dense. 5. What is the Continental Drift Theory and who proposed the theory? 1.crust (oceanic (more dense/thinner) and continental (thicker)), 2.mantle (most of Earth’s Mass) (lithosphere, asthenosphere, mesosphere), 3.outer core 4. inner core 1. Crust 2. Lithosphere (Tectonic Plates)- Crust and rigid upper mantle- Rock 3. Asthenosphere (Convection Currents-caused by heat from the core- Rock 4. Mesosphere (Lower Mantle- Rock 5.Outer Core (Liquid Metal- iron and nickel- Metal 6. Inner Core (Solid Metal-iron and nickel- Metal Solid Iron and nickel/hottest, the most dense layer, under to most pressure They all increase Crust, mantle, outer core and inner core Crust, Lithosphere, asthenosphere, mesosphere, outer core, and inner core Theory that was proposed by Alfred Wegener that stated that the continents were in one large landmass called Pangaea and drifted apart overtime 6. Describe 5 key pieces of evidence that Wegener discovered to support his theory of Continental Drift. Why was Wegener theory rejected by other scientist? 7. What was the name of the supercontinent proposed by Wegener? What does the name mean? 8. Describe the process of sea-floor spreading. Where does the sea floor spread? --mesosaurus fossil found on different continents- continents were once closer together (too small to swim in the ocean) --tropical plant fossils found in artic regions --coastlines of the continents fit together like puzzle pieces --mountain ranges on different continents lineup --coal found in artic regions --glacial grooves found in rocks match up (warm climates ) 9. What is the midocean ridge? What type of plate boundary movement exists at the mid-ocean ridge? What type of crust forms at the mid-ocean ridge? Longest chain of underwater volcanic mountains in the world found in the earth’s oceans -Mid-Ocean Ridge forms at divergent plate boundary movement -new oceanic crust forms at the Mid-Ocean Ridge (New sea floor or ocean basin) 10. Describe the process of subduction. What is a deep ocean trench (diagram)? when two plates(oceanic-oceanic or continental-oceanic) collide (converge) together the most dense (oceanic plate) plate is subducted (sinks) back into the Asthenosphere melts and becomes magma **The theory was rejected because Wegener could NOT explain how the continents moved* Pangaea- “all Lands” or “all Earth” Sea-floor spreading happens at the Mid-Ocean Ridge Process where new oceanic curst forms, when magma is Heated in the asthenosphere, it becomes less dense and rises out through the mid-ocean ridge creating new oceanic crust. Magma rises when it is heated( it becomes less dense) Under water canyon (trench) can form at subduction zones 11. Why does Oceanic Crust subduct beneath Continental Crust? The oceanic crust is more dense 12. What is the plate tectonic theory? What are tectonic plates? The theory that states Earth’s lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that float or move on top of the asthenosphere- (convection currents in the asthenosphere cause this to occur) tectonic plate-pieces of the lithosphere 13. What is the driving force that moves the tectonic/lithospheric plates? Where does this occur? Convection currents in the Earth’s Asthenosphere is the driving force that moves the tectonic plates Convention-heat rises from the core and creates a Difference in density in the material in the asthenosphere which causes the material to circulate 14. Describe Convection Currents. A circulation pattern in which material is heated and rises in one area, then cools and sinks in another area, flowing in a continuous loop -occurs in the asthenosphere -diving force of the movement of the tectonic plates (lithosphere) 15. Describe how the plates moves at each of the following boundaries: convergent, divergent, and transform Convergent Boundary- Plates push together/collide (move toward each other) Divergent Boundary- Plates pull apart (move away from each other) Transform Boundary- Plates slide by each other 16. Describe what occurs at continental-oceanic convergent boundary? --the more dense oceanic crust will sink (subduct) beneath the continental crust Landforms: volcanic mountains, deep ocean trenches Geological events: volcanic eruptions, earthquakes (Subduction Zones) 17. What are volcanic mountains, how do they form, and where do they form? --rock that is melted in subduction zones form magma, which rises to the Earth’s surface and erupts to form volcanic mountains. Volcanic mountains can also form under sea. These mountains form at an oceanic-continental convergent boundary. 18. Describe what occurs at a continentalcontinental convergent boundary? --both plates will collide, buckle and thicken Landforms: folded mountains Geological events: earthquakes 19. What are folded mountains, how do they form, and where do they form? --formed when rock layers (continental crust) are squeezed together (compression) and pushed upward and form mountains. --they form at a continental-continental convergent boundary 20. What landforms could be created at convergent boundary? Continental -Continental convergent- folded mountains Continental- Oceanic Convergent- volcanoes (volcanic Mountains) and trenches (Subduction Zones) Oceanic-Oceanic Convergent- Ocean trenches, Volcanic Islands (Subduction Zones) 21. Describe what occurs at an oceanic-oceanic convergent boundary? --the more dense oceanic crust will sink (subduct) beneath the other plate-deep Ocean trenches can form. What happens to the oceanic crust that gets subducted? It gets melted in the Asthenosphere- What force pulls the plate down into the asthenosphere? Gravity 22. What is a fault? Along what type of plate boundary do most faults form? What types of geological events occur along faults? A fault is a break in the Earth’s Crust (San Andreas) Most faults occurs along transform boundaries Earthquakes occur along fault lines 23. Where does most Along the boundaries of tectonic plates tectonic activity (earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, mountains, volcanic eruptions) occur? 24 . What is the Ring of Fire? Volcanism is mostly focused at plate margins 25. What are Hot Spots? Hot mantle plumes breaching the surface in the middle of a tectonic plate