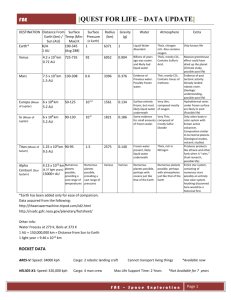
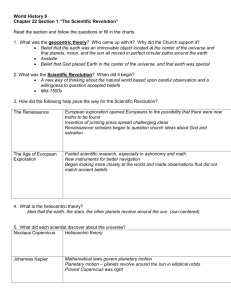
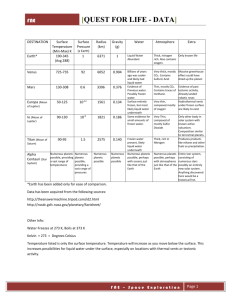
iLEAP STUDY GUIDE Name - Metairie Academy for Advanced Studies
advertisement

iLEAP STUDY GUIDE Name: _____________________________________________________ Answer: Answers will vary. Never eat or drink during science activities. Wear goggles when there is a possibility of eye injury. Always walk with pointed objects like scissors down. Tell the teacher if there is an accident. Follow all of the teacher’s instructions. Answer: Question: Quantitative comes from the word quantity and means What is the difference between number descriptions like measurements. Qualitative qualitative and quantitative comes from the word quality and are descriptions that are descriptions? not measurements using your 5 senses to describe. Answer: Question: Mass is measured in grams by a triple beam balance. List three physical properties of Volume is measured by liters and can be measured by a matter and the way they are graduated cylinder or by displacement of water. Density is measured. mass per unit volume. Other properties are color, conductivity, and malleability to name a few. Question: Answer: Which is more dense water or Water is the densest. Oil floats on the water so is less oil? Explain your answer. dense than the water. Answer: Question: Solids have a definite volume and shape regardless of their How do the physical properties of container. Liquids take the shape of their container, but solids and liquids differ? have a definite volume. Question: Describe three safety measures you observe during a science activity. Question: How are the physical properties of mass and volume observed in solids and liquids? Question: Distinguish between physical and chemical changes. Explain your reasoning and use a match stick as an example. Answer: To find the mass of a solid you can put it on a triple beam balance. To find the mass of a liquid you can put it in a container, put the container on a triple beam balance, and then subtract the mass of the container. To find the volume of a solid you can put it in a container of liquid and find out how much liquid is displaced or measure and multiply LXWXH. Answer: Chemical changes occur when the properties of the substance are changed by rearranging the atoms. When a match is burned carbon dioxide and water vapor are released from the wooden match stick forever changing it. New substances are formed. Physical changes occur when the appearance of a substance is changed but the chemical characteristics remain the same like when a match stick is broken into pieces. No new substances are formed. Question: List 3 things that can be observed when a chemical change is occurring (evidence that a chemical reaction is occurring.) Question: Describe the pattern for atomic numbers of elements on the periodic table as you move down a column and across a row. Question: Name 3 elements that have similar properties. Give their symbols and the number of protons of each. You may refer to a periodic table. Question: What are the 3 subatomic particles, where are they located, and what is the charge of each? Question: If a car is traveling 60 miles per hour, how far has it traveled in 2 hours? Question: What forces are working on someone jumping out of a plane in a parachute? Question: When does potential energy change to kinetic energy when bouncing a basket ball? Question: List three renewable, three nonrenewable, and three inexhaustible natural resources and/or sources of energy. Answer: a change in color temperature change formation of a precipitate formation of a gas Answer: Atomic numbers increase down columns (families/groups) and also increases from left to right across a row. Answer: Answers may vary but the three elements should be in the same column for example: fluorine, F, 9; chlorine, Cl, 17; bromine, Br, 35. Another example: lithium, Li, 3; sodium, Na, 11; potassium, K, 19. Answer: 1)proton, in nucleus, positive charge 2)neutron, in nucleus, no charge (neutral) 3) electron, outside of nucleus, negative charge Answer: If the car can travel 60 miles in 1 hour, it can travel 120 miles in 2 hours. 60 miles/hr X 2 hrs = 120 miles Answer: Gravity is pulling the parachute down and air is resisting the downward pull. Answer: When the ball is in your hand before you release it the ball has potential energy. The moment the ball is in motion it has kinetic energy. At the very top of the bounce when the ball is momentarily stopped it has potential energy again. Answer: Renewable= lumber, crops, water, renewable energy (wind, hydro, biomass, geothermal) Non-renewable= ores (metals), minerals, energy-fossil fuels(coal, oil, gas) Inexhaustible= air, energy- wind and solar Question: Name some materials that conduct heat and electricity. Question: Describe the difference between a parallel and a series circuit. Question: Where in a battery powered circuit which includes a light bulb is one form of energy converted to another form of energy. Question: Give 3 examples of the different forms of energy that electricity can transform into. Question: What is the source of heat and light on the sun? Question: Explain why the objects in the sky appear to move from east to west. Question: What organelles are found in an animal cell? Question: Compare plant and animal cells. Question: Explain 3 ways diseases are spread in a population. Answer: Paper clip, copper wire, metals, salt water. Answer: Parallel circuits branch and series circuits do not. Making a break in a parallel circuit with several lights attached may not result in turning off all off the all of the lights (depending on where the circuit is broken). If a break is made anywhere on a series circuit it will put out all of the lights on the circuit. Answer: The battery converts chemical energy to electrical energy. The light bulb converts electrical energy to light and heat energy. Answer: heat, light, mechanical Answer: Nuclear fusion which converts hydrogen to helium Answer: Stars and planets appear to move from east to west on a nightly basis in response to the rotation of Earth. Answer: Nucleus, Nucleolus (within nucleus), Cytoplasm, Mitochondria, Vacuoles, Lysosomes, Cell membrane, Ribosomes, Endoplasmic Reticulum Answer: Plant cells have a cell membrane but in contrast to animal cells they also have a rigid cell wall. Plant cells also contain chloroplasts and animal cells do not. Plant cells usually contain larger vacuoles than plant cells. Answer: physical contact, contaminated food, body fluids, objects, airborne inhalation, or through vector organisms (insects and their relatives, parasites, etc) Question: Name the levels of organization of living things starting with the most basic unit- the cell. Question: What is a dichotomous key and what is it used for? MEMORIZE THIS!!!!!! Know how to answer problems looking at a dichotomous key. Question: Name the developmental stages of a frog in correct order starting with the egg. Question: Compare the raw materials and products of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Question: Explain the difference between living and non-living components in an ecosystem and give examples. Question: What is meant by biotic and abiotic? Question: Select one biome and name 2 animals and 2 plants with their adaptations to that biome. Answer: Cell, tissue , organ, organ system, organism (population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere) Answer: Dichotomous key, a device that can be used to identify an unknown organism, consists of a series of 2 part statements that describe characteristics of organisms. Answer: Egg, tadpole, adult frog. Answer: Photosynthesis: Raw materials= CO2 (carbon dioxide) + H20 (water); Products= O2 (oxygen gas) + C6H1206 (glucose) Respiration: Raw materials =O2 (oxygen gas) + C6H1206 (glucose); Products = CO2 (carbon dioxide) + H2O (water) Answer: Living components include the plants, animals and all other organisms in an ecosystem. Non-living components are things that make up the physical environment (rainfall, temperature, sunlight, mineral, etc) Answer: Biotic=living components in an ecosystem Abiotic = non-living components in an ecosystem Answer: Example: Desert Plants- cactus, Joshua tree, creosote bush, sagebrush Animals: Kangaroo rat, camels, snakes or lizards that burrow during day and hunt at night. Answer: Populations need food, habitat and mates. Question: Identify resources that are needed to sustain a population of birds. Question: What is the role of Answer: decomposers in a food chain? Decomposers break down dead organic matter. Question: Explain the difference between a food chain and a food web. Question: Name 3 different ecosystems found in Louisiana. Question: Explain what happens if one of the producers in a food web disappears. Question: Give an example of a food chain which includes a decomposer. Question: Describe 3 consequences of human activities on local ecosystems. Question: Explain how the stream table model is like and not like a real earth process. Question: Compare constructive and destructive Earth forces. Question: Explain 2 ways that tectonic plates change the face of the earth. Answer: Food chains follow a single path as animals eat each other. Food webs show how plants & animals are interconnected by different paths. Answer: Wetlands (swamps, fresh, intermediate and salt marsh); temperate forests (upland and bottomland); estuarine (Lake Pontchartrain estuary) Answer: Any consumer in the food web that directly feeds only on that producer would die out. The entire food web can be affected. If they eat other things, they might survive. Answer: Example: Grassgrasshopperrobin (dies) bacteria or fungi (decomposers) Answer: Examples: Cars emit exhaust that gets washed into local waterways and pollutes, levees are built that prevent flood waters from depositing silt so that land subsides (sinks) over time, and over fishing of certain species like red fish causes the species to become endangered. Answer: Like a real stream, a stream table has sand/soil on an inclined surface and as the water flows through the sand/soil it causes erosion and deposition of the sand/soil. The limitations of the stream table are the changes that occur over time in a river system like subsidence and seasonal changes such as flooding and drought. Answer: Destructive Earth forces like hurricanes and erosion do not build land. Constructive Earth forces like deposition and volcanoes do build land. Answer: Plate tectonics can cause faults which move rock layers, river beds, etc. The faults and subduction zones can uplift layers producing mountains or drop layers causing valleys. Question: Give an example of an igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rock. Question: Name three rocks or minerals found in Louisiana. Question: List 3 organic and 3 inorganic components of soil. Question: Explain how a river can be a constructive force and a destructive force. Question: Explain how the uneven heating of the earth’s surface causes wind. Question: Describe the molecular motion that occurs when ice turns into liquid water then into steam. Question: Describe the carbon/oxygen cycle. Focus on how these cycles are inter-related. Answer: Igneous ex= granite, basalt Sedimentary ex=sandstone, shale, conglomerate, limestone Metamorphic ex= gneiss, slate, marble Answer: Rocks= limestone, chert, agate, sandstone, coal Minerals= sulfur, salt Answer: Organic= decayed plant, animals and their waste, leaves Inorganic= rock fragments, air, water Answer: Rivers can constructively build deltas, sandbars and levees. Destructively, rivers can cause floods, scour its bed to change its path or cause major erosion. Answer: Wind is simply air in motion. During the day, the air above the land heats up more quickly than the air over water. The warm air over the land expands and rises, and the heavier, cooler air rushes in to take its place, creating wind. At night, the winds are reversed because the air cools more rapidly over land than over water. Answer: The water molecules in ice vibrate in a lattice formation. As vibration increases the water molecule formation becomes more random. In a liquid the molecules slide past one another. In steam the molecules bump into each other and spread apart. Answer: In the carbon cycle plants capture carbon dioxide gas from the atmosphere and make glucose sugar. The glucose is then used by plants for food or ingested by animals for food. In the process of making glucose, plants release oxygen into the atmosphere. Both plants and animals take in this oxygen in order to break down the glucose in cellular respiration to release the energy in the molecule. During cellular respiration carbon dioxide is released. When the plants and animals die microorganisms breakdown the plants and animals releasing carbon back to the environment. Question: What factors can affect the carbon/oxygen cycle? Question: Why does conservation have an impact on the carbon cycle? Question: How does excess nitrogen affect waterways? Question: Explain how the water cycle is powered. Question: What does the symbol for a stationary front look like on a weather map? Question: Name the characteristics of each climate zone- tropical, temperate, arctic. Question: Name an animal and a plant found in each climate zonetropical, temperate, arctic, desert. Question: Explain how the moon is visible on some nights and invisible on other nights. Answer: There are many ways to disrupt the cycle such as: 1) When there is a scarcity of plants to make glucose the process can be disrupted. 2) When there is a scarcity of animals that can eat plants to recover the glucose for energy the process is disrupted. 3) When there is a lack of decomposition the cycle can be disrupted. Answer: When people conserve resources like oil and natural gas by not burning fuel, the carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere is reduced. This is only one impact; there are many more. Answer: Excess nitrogen compounds in bodies of water will cause excessive growth of algae (algal blooms). It acts as a fertilizer. Answer: Energy from the sun drives the water cycle. Answer: Answer: Tropical- Hot, humid with lots of rainfall and no detectable changes in seasons. Temperate- Seasonal weather changes, moderate climate and rainfall. Arctic- Freezing temperatures most of the year and very little precipitation. Answer: Tropical- examples: anaconda snake, orchid Temperate- examples: brown bear, oak tree Arctic- examples: polar bear, tundra plants Desert- examples: rattle snake, cactus Answer: The moon goes through "phases" and rises and sets at a different time every day. Sometimes the moon is opposite the sun and is visible in the nighttime sky. Other times the moon is on the same side of the earth as the sun and is in our daytime sky. You will not be able to see it if it has not yet risen or if it has already set. Some believe that the moon is always in the night sky. That is not the case. Question: Explain why shadows appear to move in a clockwise manner throughout the day. Question: Describe the solar system including the planets and the order in which they occur from the sun. Answer: The sun’s shadow always falls on the opposite side of an object than the sun. North of the equator, the Sun rises in an easterly direction, this makes a shadow point to the west. Then it arches across the southern sky, making a shadow get shorter and rotate to the north. It then sets in a westerly direction, making a shadow point to the east. Answer: The solar system includes the sun, planets, their moons, asteroid, meteoroids, and comets. The planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Pluto is no longer considered a planet. Answer: The four smaller inner planets, Mercury, Venus, Question: Earth and Mars, called the terrestrial planets, are primarily Compare the major composed of rock and metal. The four outer planets, characteristics of the inner and Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune, are called the gas outer planets. giants. They are composed mainly of gases or of ices, such as water, ammonia and methane. Answer: Question: If the sun were closer, Earth’s temperature would increase. Explain what would happen if the The water cycle would be affected as evaporation would earth were closer to the sun. increase and ice in glaciers and caps would melt. Answer: Telescope- A telescope like Hubble is able to bring pictures Question: back Earth that people are not able to see otherwise. List 3 advances in technology that Space shuttle- Transports people into space. enable the exploration of space. Robots- A robot on an unmanned flight into space can Explain why each is important. endure hardships that people cannot to do experiments make observations. Answer: Since Polaris does not move and because it is located over the North Pole, it can be used to find Question: directions. Moving in a direction toward Polaris is heading Explain the significance of the in a northerly direction, moving in a direction opposite North Star. Polaris is heading in a southerly direction. The other directions can be determined from sighting Polaris Answer: A moon is a natural satellite that orbits a planet. An asteroid is typically defined as a large body of rock or Question: iron floating through space, a meteoroid is smaller, Compare the moon to asteroids, meteors are flaming meteoroids as they are entering meteoroids, meteors, meteorites. Earth’s atmosphere, and a meteorite is what survives impact with the ground. Question: What new technology has made forecasting weather more accurate? Question: Explain how fossils are formed. Answer: Doppler radar is one of many new technologies that has made weather forecasting more accurate. Answer: Fossils are formed when organisms, parts of organisms, or evidence of organisms (trails, burrows, etc) are preserved by various methods (petrifaction, mummification, mineralization, freezing, etc) Answer: A force applied to the object. Question: What is required to change the direction or motion of an object? Question: Answer: How much of the earth is covered About 70% of the earth is covered by water and about 2by water. How much of the 3% is fresh water. water is drinkable?