Lines, Angles, Shapes Curriculum: Grades G/F to A*
advertisement

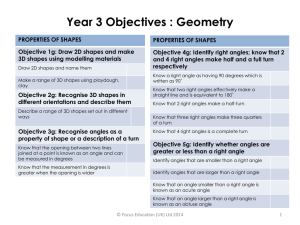
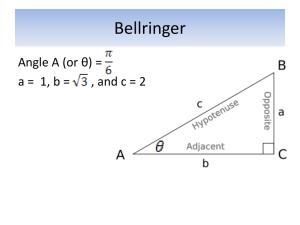
Unit 2: Lines, Angles and Shapes Level 1 & Level 2 Recognise and name familiar 2D and 3D shapes. Describe their properties using everyday language and begin to link to mathematical language. Level 3 (≈ Grade G/F) Classify lines, triangles, quadrilaterals and polygons using mathematical language. Level 4 (Grade E) Recognise line properties such as parallel and perpendicular in simple shapes and use the correct notation and labelling conventions for lines and shapes. Sort collections of 2D and 3D shapes by their properties using terms such as faces, edges, sides and corners. Classify 3D shapes in various ways using mathematical properties. Make 2D and 3D mathematical models by linking given edges or faces, eg. Pentominoes, tetrominoids. Understand angle as a measurement of turn including clockwise and anticlockwise. Recognise right-angles in shapes. Level 5 (≈ Grade D) Identify parallel and perpendicular lines in a variety of shapes, classify simple shapes by their angle and symmetry properties and further develop use of geometrical language. ( Use the language associated with angles. Know the angle sums of triangles, points and straight lines. Use ruler and protractor to measure and draw lines to the nearest mm and angles to the nearest degree. Measure and draw angles to the nearest degree. Estimate to the nearest 5o. Use ruler and protractor to construct triangles given SAS and ASA, and to construct simple nets. Unit 2: Lines, Angles and Shapes Level 5 (≈ Grade D) Identify parallel and perpendicular lines in a variety of shapes, classify simple shapes by their angle and symmetry properties and further develop use of geometrical language. Level 6 (≈ Grade C) Classify quadrilaterals using mathematical properties. Level 7 (≈ Grade B) Know the parts of the circle and their properties (NOT area and calculation of circumference) Level 8 and E.P. (≈ Grade A/A*) Use and apply Pythagoras’ theorem to problems in 2-dimensions. Apply Pythagoras’ theorem to problems in 3dimensions. Recognise and use common 2D representations of 3D objects. Understand basic congruence of shapes. Use the language associated with angles. Identify opposite, alternate and corresponding angles in systems of intersecting and parallel lines. Solve problems using these properties. Use sine, cosine and tangent in right angled triangles to solve problems in 2- or 3-D. Know the angle sums of triangles, points and straight lines. Understand a proof that the sum of the angles in a triangle is 180o and a quadrilateral is 360o. Use these properties to solve problems. Use the sine and cosine rule to solve problems in 2- or 3-dimensions. Solve problems using angle and symmetry properties of polygons and explain these properties. Explain how to find, calculate and use properties of the interior and exterior angles of regular and irregular polygons. Measure and draw angles to the nearest degree. Estimate to the nearest 5o. Use bearings to specify direction and solve problems. Determine the locus of an object moving according to a rule. Use ruler and protractor to construct triangles given SAS and ASA, and to construct simple nets. Use straight edge and compasses to do standard constructions including, perpendicular bisector of a line segment, constructing a perpendicular to a given line from a given point and recognising this as the shortest distance to the line and bisecting a given angle. Construct triangles using SSS, SAS, ASA and RHS information and apply these conditions to establish congruence of triangles. Apply angle facts, triangle congruence, similarity and properties of quadrilaterals to derive results about angles and sides, including Pythagoras’ Theorem, and use known results to obtain simple proofs.


![Property`s Of 2D and 3D Shapes.! :] - Odessa R-VII](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005712562_2-5f3fcc92381e7510fd57ce4e0ef497c8-300x300.png)