File
advertisement

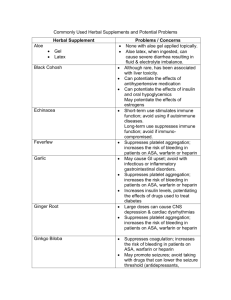
Iron (Ferrous fumarate: 33% elemental iron, ferrous sulfate: 30% elemental iron, ferrous gluconate: 12%) Why is pt receiving this? PO: prevention/treatment of iron-deficiency anemia Dosage Aproximate equivalent doses: fumarate (197 mg), sulfate (324), gluconate (560) PO: deficiency: 120-240 mg/day (2-3 mg/kg/day) in 2-4 divided doses; Prophylaxis: 60-100 mg/day SE nausea, constipation, dark stools, diarrhea, epigastric pain, GI bleeding; staining of teeth; IRON OVERLOAD CAN PRESENT AS ANEMIA Med administration concern: Oral iron supplements decreases absorption of tetracylcines, bisphosphonates, fluoroquinolones, levothyroxine; may decrease effects of levodopa and methyldopa. Concurrent administration w/ PPI’s and H2 antagonists decreases absorption of iron. Oral preparation (liquid form) may stain teeth (use w/ straw). Take w/ OJ to promote absorption, DO NOT take w/ coffee or tea. Administer 1 hr before or 2 hr after meals. Pt teaching points How to take/when to take. S/sx of iron overload, pt may develop hemochromocytoma. Importance of regular follow ups. Stools may become dark black or green. deferoxamine (Desferal) Antidotes, heavy metal antagonists Why is pt receiving this? Acute toxic iron ingestion, secondary iron overload syndromes. Chelates unbound iron, forming water soluble complex (ferrioxmaine) in plasma that is easily excreted by kidneys Dosage Acute iron ingestion: 1 g, then 500 mg q 4 hr for 2 doses, additional doses of 500 mg q 4 hr for 2 doses ; Chronic Iron overload: IM, IV. 500 mg- 1 g daily IM; additional doses of 2 g should be given IV for each unit of blood transfused, NOT to exceed 1 g/day in absence of transfusions (6 g if transfusions received)Reconstitute 500 mg vial w/ 2mL water and 2 g vial w/ 8 mL of sterile water for injection of [213 mg/mL] IV: [95 mg/mL], diluent: D5W, NS, 1/2NS, LR; Max infusion rate is 15mg/kg/hr SE blurred vision, cataracts, otoxicity, hypotension, tachycardia, abd pain, diarrhea, RED URINE, erythema, flushing, urticarial, induration/pain at injection site; leg cramps, ALLERGIC REACTIONS, shock Med administration concern: Assess toxicity, monitor either early acute (abd pain/bloody diarrhea/emesis), late acute (decreased LOC, metabolic acidosis), monitor vital signs, monitor for otoxicity (AUDIOVISUAL EXAMS SHOULD BE PERFORMED EVERY 3 MO IN PTS w/ Chronic iron overload) monitor I and O, IM route is preferred Pt teaching points Reinforce need to keep iron preparations out of reach of children, reassure red coloration of urine is normal, advise not to take Vitamin C prepreations b/c TOXICITY CAN INCREASE , pts requiring chronic therapy should keep follow up appts epoetin alpha (Epogen) Antianemiics, hormones, erythropoiesis stimulating agents (ESA) Why is pt receiving this? Anemia assoc. w/ kidney Disney, anemia secondary to AZT in HIV HAART therapy, anemia from chemotherapy in patients with NONMYEOID malignancies; unlabeled use in anemia of prematurity in neonates; Stimulates erythropoiesis Dosage Anemia of chronic kidney disease: Subcut, IV: 50-100 units/kg 2 times weekly (use lowest dose possible to decrease need for transfusions); if hemoglobin increases, will need to decrease dose Anemia from chemotherapy: discontinue when chemotherapy course is completed; SubQ 150 units/kg 3 times weekly or 40,000 units weekly. SE SEIZURES, HA, HF, MI, Storke, Thromboembolitic events, HYPERTENSION, transient rashes, restored fertility, resumption of menses, increased mortality and increased tumor growth Med Admin Concerns IF BP increases by 12 mmHg or MORE, increased risk of MI, stroke; increased viscosity=increased risk of clots. Monitor BP before and druing therapy (notify HCP for severe hypertension), monitor hematocrit and hemoglobin regularly, monitor dialysis shunts Pt education points pt must read medication guide and sign acknowledgement before each course of therapy/refill; explain rational; discuss ways of preventing self-injury in pts at risk for seizues; may result in shortened overall survival and/or decreased time to tumor progression. Notify for signs of blood clots. Stress compliance w/ dietary restrictions, medications, and dialysis. aspirin salicylate ; generation 1 cox inhibitor; NSAID Why is pt receiving this? Inflamatory disorders incl. rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis. Mild to moderate pain. Fever. Prophylaxis of transient ischemic attacks and MI. Inhibits Cox-1 and Cox-2 which prevents production of prostaglandins. Decreases platelet aggregation Dosage PAIN/FEVER: PO, rect 325-1000 mg q 4-6 hrs; XR 650 mg q 8 hrs INFLAMATION: PO 2.4 g/day initially, increased to maintanence dose of 3.6-5.4 g/day PREVENTION OF TIA: PO 50-325 mg once daily; PREVENTION OF MI: PO (typically 81 mg), 80-325 mg/day SE tinnitus, GI BLEEDING, dyspepsia, epigastric distress,abd pain, anorexia, hepatotixicy, SJS, TENS , anemia, hemolysis, increased bleeding time ; ALLERGIC RXNS ; RYE’S SYNDROME Med administration concerns May increase risk of bleeding w/ warfarin, heparin, thrombolytic agents, and valporic acid; Ibuprofen may negate cardioprotective antiplatelet effects of ASA, may decrease beneficial effects of probenecid. Corticosteroids may decrease levels. Urinary acidification mya increase reabosprtion and increases erum levels. (opposite true w/ alkalinization). May blunt reponse to diuretics or other antihypertensives. Increased risk of GI irritation w/ other NSAIDS. Pts who have asthma, allargies @ greater risk of developing hypersensitivity, assess for rash, pain, fever. Administer after meals or w/ antacids to minimize gastric irritation. Pt education points Take w/ full glass of water, report tinnitus/bleeding of gums/ black tarry stools, or fever lasting >3 days. AVOID concurrent use of alcohol to prevent gastric irritation. Heparin Parenteral anticoagulant HIGH ALERT Why is pt receiving this? Prophylaxis AND treatment of various thromboembolitic disorders, incl venous thromboembolism, pulmonary embolism, Afib w/ embolization, acute and chronic consumptive coagluopathies,, peripheral arterial thromboembolism. USED IN LOW DOSES to maintain patency of IV catheters (heparin flush) Potentiates inhibitory effect of antithrombin on factor Xa and thrombin by binding. Dosage Given IV or Sub Q (for thromboembolism) Varies based on facility protocol. Low does prevents conversion of prothrombin to thrombin: HIGH RISK PTS UNDERGOING PROCEDURE W/ RISK OF BLOOD LOSS High does neutralize thrombin, preventing fibrinogen-> fibrin, FOR DIC, EMBOLISM, or THROMBUS MGMT (IS NOT A CLOT BUSTER) SE BLEEDING, HEPARIN INDUCED THROMBOCYTOPENIA (HIT) Med admin concern: MEASURED via PTT (partial thromboplastin time; measures intrinsic coag) or AntiXa and adjusted accordingly. DO NOT ASPIRATE w/ SUB Q. DO NOT ADMINISTER SUB Q 2 CM FROM DRAIN, SURGICAL SITE, or UMBILICUS. Potentiates risk of bleeding w/ other meds (i.e. ASA) Pt education points Bleeding precautions: electric razors, monitor joint pain, Avoid vitamin K (source for clotting cascade factors), longer than normal hemostasis for injections, venipunctures (don’t walk away) enoxaparin (Lovenox) Parenteral anticoagulant; low molecular weight heparin HIGH ALERT Why is pt receiving this? Prophylaxis of venous thromboembolism, DVT, and/or PE in post surgical/medical patients; Treamtent of DVT w/ or w/out PE (w/ warfarin); prevention of ischemic complications from unstable angina and non STEMI. Treatment of acute STEMI . Inhibit factor Xa, does not bind to thrombin. Dosage Given SubQ, 30-40 mg q 12 hr starting 12-24 hr postop for 7-10 days; (for hip replacement pts can give 40 mg one daily starting 12 hr before surgery). Varies based on surgery. SE dizziness, HA, insomnia, edema, increased liver enzymes, n/v, urinary retention, alopecia, ecchymoses, rash, BLEEDING Med admin concern: NO need to check PTT q 4 because less protein binding occurring, meaning cascade is controlled predictably. THIS AND REG HEPARIN NEVER GIVEN IM . Potentiates effects that affect platelet function incl warfarin, asparin, NSAIDS. Pt education points Teach how to self inject. Assess for bleeding frequently. Don’t take NSAIDS. Report s/sx of abnormal bleeding. Protamine sulfate Antiheparin; antidote Why is pt receiving this? Acute mgmt. of sever heparin overdosage. A strong base that forms complex w/ acidic heparin Dosage IV: 1 mg/ 100 units of heparin. If given >30 min after heparin, give .5 mg/100 units of heparin ( not to exceed 100 mg/2hr). Further doses determined by Coag tests (PTT). Unlabeled use in LMW heparin overdoses. IV: dilutent, can be undiluted, or diluted in D5W or NS; conc [10 mg/mL], administer slowly IVP over 1-3 min SE dyspnea, bradycardia, hypertension/hypotension, n/v, flushing, bleeding, HYPERSENSITIVITY including anaphylaxis, angiodemea, and PE Med admin concern: Assess for bleeding and hemorrhage throughout therapy. Hemmorhage may recur 8-9 hours (rebound effects). Assess for allergy to fish. Observe pt for s/sx of hypersensitivity. Keep epi close by. Assess for hypovolemia before therapy (can result in cardiovascular complex). May need to administer w/ FFP. Pt education points Explain rationale behind medication. Advise pt to avoid activities resulting in bleeding until risk of hemmorage has passed (shaving/brushing teeth, receiving injections or ambulating) warfarin (Coumadin) Oral anticoagulant HIGH ALERT Why is pt receiving this? Prophylaxis and treatment of venous thrombosis, PE, Afib w/ embolization. Mgmt of MI (Decreases risk of death subsequent MI and future thromboembolitic event). Interferes with hepatic synthesis of vitamin K dependent clotting factors (II, VII, IX, and X). Dosage Doses individualized, generally 2-10 mg daily. PO, IV SE cramps, nausea, dermal necrosis, BLEEDING, fever. Med admin concern: Measured by PT, and INR (reflective of extrinsic pathway). Decreased Vit K will intensify effects, excess vitamin K will deplete effects. Androgens, disulfiram, fluroquinolones, thrombolytics, sulfonamides, quinidine, NSAIDs, and ASA may increase response to warfarin. Chronic use of acetaminophen may increase risk. Chronic ETOH ingestion may decrease effects. Barbituates, estrogens, and rifampin may decrease anticoagulant response to warfarin. LONG ½ life (36 hr) Pt education points Continued monitoring (q 2-4 weeks) of both PT and INR normal. Do NOT stop abruptly. If abnormal bleeding is noticed, could be controlled by omitting dose. Heparin Coumadin Heparin and Coumadin Not interchangeable Once Heparin started, Coumadin will probably follow Heparin will be d/c when INR brought to normal range (2-3) Dietary sources of Vitamin K Asparagus, leafy green vegetables, brussel sprouts, broccoli streptokinase (Streptase) Thrombolytic agent HIGH ALERT Why is pt receiving this? Acute MI, massive PE, DVT, arterial thrombi, or occluded ateriovenuous cannulae. Combines w/ plasminogen to form activator complex, which converts plasminogen to plasmin. Plasmin degrades fibrin in clots. Dosage Can only be given parenterally. MI: 1.5 mil units given as continuous infusion over 60 min. DVT< PE, AE< or Arterial thrombosees: 250,000 unit loading dose over 30 min, followed by 100,00 unit/hr for 24 hr for PE or arterial, 72 for DVT Intracoronary: Dilute 250,000 IU vial to total of 125 mL w/ NS or D5W. Administer 20,000 units via bouls over 15 sec-2 min. Intermitent infusion: 5 mL of NS or D5W, DO NOT SHAKE, dilute further w/ NS for toal volume of 45-500 mL. SE ALLERGIC RXNS, Intracranial hemmorage, epistaxis, gingival bleeding, hypotension, reperfusion, GI Bleeding, retroperitoneal bleeding, GU tract bleeding Med administration concerns Increased risk of bleeding w/ concurrent use w/ NSAIDS, ASA, warfarin, heparin, LMW Heparin, direct thrombin inhibitors (although typically used together in sequence). CHANGE IN LOC=IMMEDIATELY STOPPING THERAPY; DO VEINUPUNCTURES BEFORE THERAPY Pt educaton points Explain purpose of therapy, ned for bedrest and minimal handling during therapy to avoid injury. Bleeding precautions. clopidogrel (Plavix) Antiplatelet agents; platelet aggregation inhibitors Why is pt receiving this? Reduction of atherosclerotic events (i.e. MI, stroke) in pts at rsik incl. recent MI,a cute coronary syndrome, stroke, or peripheral vasc disease. Inhibits platelet aggregation by irreversibly inhibiting binding of ATP to platelet receptors. Dosage Recent MI, stroke, or periph. PO 75 mg once daily; Acute coronary syndrome, PO 300 mg initially, then 75 mg once daily; aspirin should be given concurrently SE Bleeding, chest pain ,edema, hypertension, abd pain, diarrhea, drug rash, neutropenia, thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura, hypercholesterolemia, fever, hypersensitivity. Med administration concerns May only be effective in smokers? (some pts genetically unable to respond to therapy). Addative risk of bleeding w/ aspirin, NSAIDs, heparin, warfarin Pt educaton points Instruct to take exactly as prescribed. Do not double doses. Notify if fever/chills/sore throat, rash, or unusal bleeding occurs. Female pts should notify if pregnancy is planned/suspected or if breastfeeding.