Regents Earth Science Name
advertisement

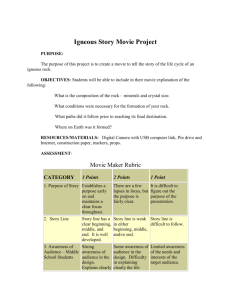
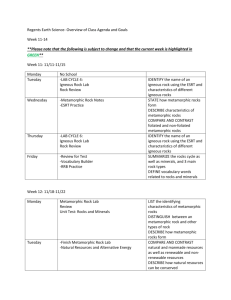
Regents Earth Science Igneous Rocks Time 78 min Name ___________________ Date Started ________________ Due date _________ Period ___ Igneous Rock Lab Equipment: Igneous rock collection #1-12, hand lens, ESRT, text book Objective: to practice classifying, identifying and describing various environments of formation. Environment of formation: example: basalt is formed when molten material rich in Plagioclase feldspar and Pyroxene solidify quickly, probably at the surface in a lava flow. Procedure: Observe each of the rocks with a hand lens. Note texture, presence of key minerals or other characteristics in which to give a clue to the environment of formation. Show your notes below: 1. _______________________________________________________________________ 2._______________________________________________________________________ 3. _______________________________________________________________________ 4. _______________________________________________________________________ 5. _______________________________________________________________________ 6. _______________________________________________________________________ 7. _______________________________________________________________________ 8. _______________________________________________________________________ 9. _______________________________________________________________________ 10. _______________________________________________________________________ 11. _______________________________________________________________________ 12. _______________________________________________________________________ Open your E.S.R.T. to page 6 and notice the Scheme for Igneous Rock Identification data table. Review the environment of formation for the rocks (ex. Peridotite is a coarse textured, intrusive igneous rock that was formed deep within the Earth ). Align the igneous rocks in your kit to the data table to see the relationships between the rock characteristics and the environment of formation. Questions: Please answer all questions in complete sentences. Use the index of the text to find out about particular rocks, as well as the ESRT. Use on-line resources. Example: Google the term “pegmatite”, see what kind of pictures and information are revealed. 1. How is Obsidian similar to Granite? (ESRT p. 6) __________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ ES Igneous Rock Lab 11.2013 Over 2. Why is a Pegmatite non vesicular? Include the environment of formation (ESRT p.6) __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 3. What is the grain size (mm) of Andesite? (ESRT p. 6) ____________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 4. How is the composition of Rhyolite similar to Gabbro? (ESRT p. 6) _________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________