What advantage was obtained by implementing the List interfece
advertisement
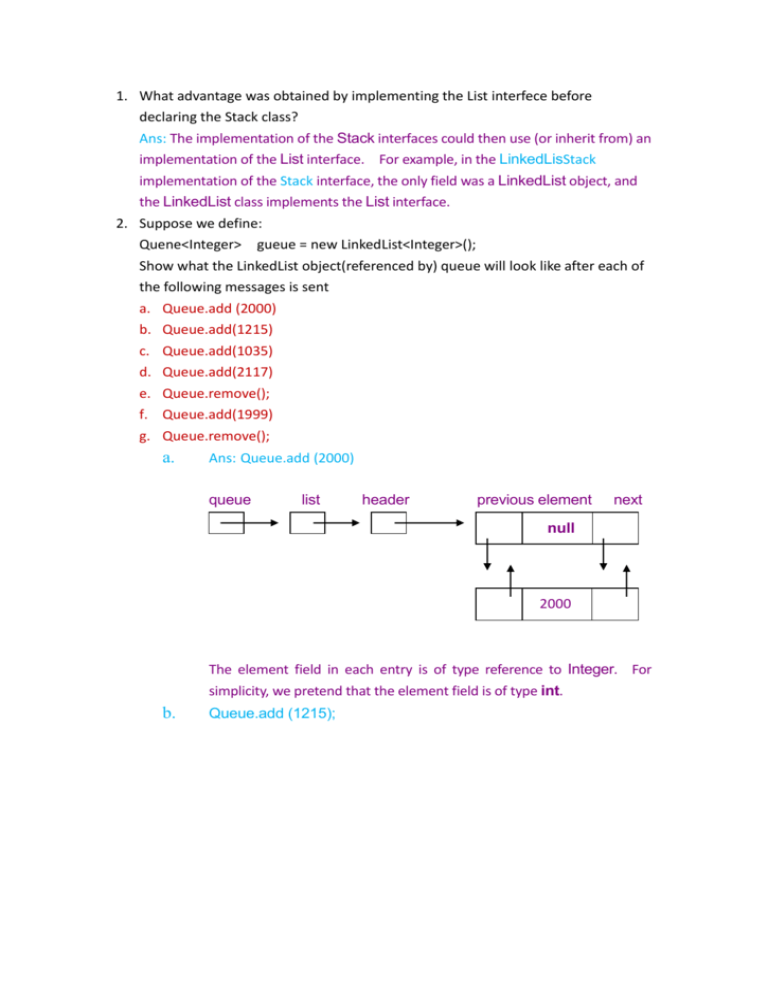
1. What advantage was obtained by implementing the List interfece before
declaring the Stack class?
Ans: The implementation of the Stack interfaces could then use (or inherit from) an
implementation of the List interface. For example, in the LinkedLisStack
implementation of the Stack interface, the only field was a LinkedList object, and
the LinkedList class implements the List interface.
2. Suppose we define:
Quene<Integer> gueue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
Show what the LinkedList object(referenced by) queue will look like after each of
the following messages is sent
a. Queue.add (2000)
b. Queue.add(1215)
c. Queue.add(1035)
d. Queue.add(2117)
e. Queue.remove();
f. Queue.add(1999)
g. Queue.remove();
a.
Ans: Queue.add (2000)
queue
list
header
previous element
next
null
2000
The element field in each entry is of type reference to Integer. For
simplicity, we pretend that the element field is of type int.
b.
Queue.add (1215);
queue
list
header
previous element
next
null
2000
1215
c.
Queue.add (1035);
queue
list
header
previous element
next
null
2000
1215
1035
d.
Queue.add (2117);
queue
list
header
previous element
null
2000
1215
1035
next
2117
e.
Queue.remove();
queue
list
header
previous element
next
null
1215
1035
f.
2117
Queue.add (1999);
queue
list
header
previous element
null
1215
1035
2117
1999
g.
queue.remove();
next
queue
list
header
previous element
next
null
1035
2117
1999
3. Re-do Ecercise
2. parts a through g, for a stack instead of a queue. Start with
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack.push(2000)
Ans:
b. stack.push (1215);
stack
list
header
previous element
next
null
2000
1215
c. stack.push (1035);
stack
list
header
previous element
null
2000
next
1215
1035
d. stack.push (2117);
stack
list
header
previous element
next
null
2000
1215
1035
2117
e. stack.pop();
stack
list
header
previous element
null
2000
next
1215
1035
f. stack.push (1999);
stack
list
header
previous element
next
null
2000
1215
1035
1999
g.
stack.pop();
stack
list
header
previous element
null
next
2000
1215
1035
4. Suppose that elements “a”, “b”, “c”, “d”, “e” are pushed, in that order, onto an
initially empty stack, which is then popped four times, and as each element is
popped, it is enqueued into an initially empty queue. If one element is then
dequeued from the queue, what is the next element to be dequeued?
Ans: The next element to be dequeued is “d”.
5. Translate the following expressions into postfix notation:
a. x + y * z
b. (x + y) * z
c. x – y – z * (a + b)
d. (a + b) * c – (d + e * f/((g/h + i – j)* k))/r
Test your answers by running the Infix to Postfix.
Ans: a.
xyz*+
b.
xy+z*
c.
xy–zab+*–
d.
ab+c*def*gh/i+j-k*/+r/Translate each of the expressions in Exercise 5 into prefix notation.
Ans:
a.
+x*yz
b.
*+xyz
c.
--xy*z+ab
d.
-*+abc/+d/*ef*-+/ghijkr
6. Declare and test the PureStack class with a LinkedList field.
Hint:Each of the definitions is a one-liner
6 的類題:
Define the LinkedListPureStack class implementation of the PureStack interface.
Test your implementation with a driver.
Hint: Each of the definitions is a one-liner.
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedListPureStack<E> implements PureStack<E>
{
protected LinkedList<E> list;
/**
* Initializes this LinkedListPureStack object to have no
* elements.
*/
public LinkedListPureStack()
{
list = new LinkedList<E>();
} // default constructor
/**
* Initializes this LinkedListPureStack object to contain a
* shallow copy of otherStack.
*
* @param otherStack - a LinkedListPureStack from which
*
the calling object will be initialized.
*/
public LinkedListPureStack (
LinkedListPureStack<E> otherStack)
{
list = new LinkedList<E> (otherStack.list);
} // default constructor
/**
* Returns the number of elements in this
* LinkedListPureStack object.
*
* @return an int containing the number of elements in the
*
LinkedListPureStack.
*/
public int size()
{
return list.size();
} // method size
*
/**
* Returns true if this LinkedListPureStack object has no
* elements. Otherwise, returns false.
*
* @return a boolean indicating if the LinkedListPureStack is
empty or not.
*
*/
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return list.isEmpty();
} // method isEmpty
/**
* Inserts element at the top of this LinkedListPureStack
* object.
*
* @param element a reference of type E to be pushed on
*
the LinkedListPureStack.
*/
public void push (E element)
{
list.addFirst (element);
} // method push
/**
* Removes (and returns)the element that was at the top of
* this non-empty LinkedListPureStack object just before this
* method was called.
*
* @return the element that was removed from the top of this
*
LinkedListPureStack.
* @throws NoSuchElementException – if this
LinkedListPureStack
*
object is empty.
*
*/
public E pop()
{
return list.removeFirst();
} // method pop
/**
* The element at the top of this non-empty
* LinkedListPureStack object has been returned.
*
* @return the element that is the top element of the
*
LinkedListPureStack.
* @throws NoSuchElementException – if this
LinkedListPureStack
*
object is empty.
*
*/
public E peek()
{
return list.getFirst( );
} // method peek
} // LinkedListPureStack class
// in a separate file:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedListPureStackDriver
{
protected Scanner fileScanner;
protected PrintWriter fileWriter;
public PrintWriter openFiles()
{
final String IN_FILE_PROMPT =
"\n\nPlease enter the path for the input file: ";
final String OUT_FILE_PROMPT =
"\n\nPlease enter the path for the output file: ";
Scanner keyboardScanner = new Scanner (System.in);
String inFilePath,
outFilePath;
boolean pathsOK = false;
while (!pathsOK)
{
try
{
System.out.print (IN_FILE_PROMPT);
inFilePath =
keyboardScanner.nextLine();
fileScanner = new Scanner (new File
(inFilePath));
System.out.print
(OUT_FILE_PROMPT);
outFilePath =
keyboardScanner.nextLine();
fileWriter = new PrintWriter
(new FileWriter (outFilePath));
pathsOK = true;
} // try
catch (IOException e)
{
System.out.println (e);
} // catch I/O exception
} // while
return fileWriter;
} // method openFiles
protected void printStack (LinkedListPureStack<String> stack)
{
final String LINKED_LIST_PURE_STACK_MESSAGE =
"\n\nHere is the LinkedListPureStack: ";
LinkedListPureStack<String> tempStack =
new LinkedListPureStack<String> (stack);
fileWriter.println
(LINKED_LIST_PURE_STACK_MESSAGE);
while (!tempStack.isEmpty())
fileWriter.println (tempStack.pop());
} // method printStack
public void testLinkedListPureStackMethods()
{
final String LINE_MESSAGE = "\nThe line is\n";
final String CONSTRUCTOR =
"LinkedListPureStack";
final String DEFAULT_CONSTRUCTOR_MESSAGE
= "The default constructor has been called.";
final String COPY_CONSTRUCTOR_MESSAGE =
"The copy constructor has been called.";
final String SIZE = "size";
final String SIZE_MESSAGE = "The size is ";
final String IS_EMPTY = "isEmpty";
final String IS_EMPTY_MESSAGE =
"That the LinkedListPureStack is empty is ";
final String PEEK = "peek";
final String PEEK_MESSAGE = "The top element is ";
final String PUSH = "push";
final String PUSH_MESSAGE =
"The element pushed is ";
final String POP = "pop";
final String POP_MESSAGE =
"The element popped is ";
final String BAD_METHOD =
"The line entered does not represent a
legal method.";
Scanner lineScanner;
String line,
method,
argument;
LinkedListPureStack<String> stack = null,
otherStack;
while (fileScanner.hasNext())
{
try
{
line = fileScanner.nextLine();
fileWriter.println (LINE_MESSAGE + line);
lineScanner = new Scanner (line);
method = lineScanner.nextLine();
if (method.equals (CONSTRUCTOR))
{
if (lineScanner.hasNext())
{
// ignore other token; create dummy stack
fileWriter.println
(COPY_CONSTRUCTOR_ME
SSAGE);
otherStack = new
LinkedListPureStack<String>()
;
otherStack.push ("yes");
otherStack.push ("no");
otherStack.push ("maybe");
stack = new LinkedListPureStack
<String>(otherStack);
} // if more tokens
else
{
fileWriter.println
(DEFAULT_CONSTRUCTOR
_MESSAGE);
stack = new LinkedListPureStack<String>();
} // default constructor
} // constructor
else if (method.equals (SIZE))
{
fileWriter.println (SIZE_MESSAGE +
stack.size());
} // size method
else if (method.equals (IS_EMPTY))
{
fileWriter.println
(IS_EMPTY_MESSAGE +
stack.isEmpty());
} // isEmpty method
else if (method.equals (PUSH))
{
argument = tokens.nextToken();
fileWriter.println (PUSH_MESSAGE +
argument);
tack.push (argument);
} // push method
else if (method.equals (POP))
{
fileWriter.println (POP_MESSAGE +
stack.pop());
// pop method
else if (method.equals (PEEK))
fileWriter.println (PEEK_MESSAGE +
stack.peek());
} // peek method
else
fileWriter.println
(BAD_METHOD);
printStack (stack);
} // try
catch (Exception e)
{
fileWriter.println (e + "\n\n");
} // catch Exception
} // while
} // method testLinkedListPureStackMethods
} // class LinkedListPureStackDriver
// in a separate file:
import java.io.*;
public class LinkedListPureStackDriverMain
{
public static void main (String[ ] args)
{
PrintWriter writer = null;
try
{
LinkedListPureStackDriver driver =
new LinkedListPureStackDriver();
writer = driver.openFiles();
driver.testLinkedListPureStackMethods();
} // try
finally
{
writer.close();
} // finally
} // method main
} // class LinkedListPureStackDriverMain
7. Declare and test the PureStack class with a ArrayList field
Hint:For the sake of efficiency, the top of the stack should be at index size() – 1.
7 的類題:
Define an implementation of the PureStack class based on an ArrayList. Hint:
In the ArrayListPureStack class, the top of the stack is at index size() – 1.
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayListPureStack<E> implements PureStack<E>
{
protected ArrayList<E> list;
/**
* Initializes this ArrayListPureStack object to have no elements.
*/
public ArrayListPureStack()
{
list = new ArrayList<E>();
} // default constructor
/**
* Initializes this ArrayListPureStack object to contain a shallow
* copy of otherStack.
*
* @param otherStack - a ArrayListPureStack from which the
*
calling object will be initialized.
*/
public ArrayListPureStack(ArrayListPureStack<E> otherStack)
{
list = new ArrayList<E> (otherStack.list);
} // default constructor
/**
* Returns the number of elements in this ArrayListPureStack
* object.
*
* @return an int containing the number of elements in the
*
ArrayListPureStack.
*
*/
public int size()
{
return list.size();
} // method size
/**
* Returns true if this ArrayListPureStack object has no
elements.
* Otherwise, returns false.
*
* @return a boolean indicating if the ArrayListPureStack is
empty
*
or not.
*
*/
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return list.isEmpty();
} // method isEmpty
/**
* Inserts element at the top of this ArrayListPureStack object.
* The averageTime(n) is constant and worstTime(n)is O(n).
*
* @param element a reference of type E to be pushed on the
*
ArrayListPureStack.
*/
public void push (E element)
{
list.add (element);
} // method push
/**
* Removes (and returns) the element that was at the top of this
* non-empty ArrayListPureStack object just before this method
was
* called.
*
* @return the element that was removed from the top of this
*
ArrayListPureStack.
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException – if this
ArrayListPureStack
*
*
*/
object is empty.
public E pop()
{
return list.remove (list.size() - 1);
} // method pop
/**
* The element at the top of this non-empty ArrayListPureStack
* object has been returned.
*
* @return the element that is the top element of the
*
ArrayListPureStack.
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException – if this
ArrayListPureStack
*
object is empty.
*
*/
public E peek()
{
return list.get (list.size() - 1);
} // method peek
} // ArrayListPureStack class