Chapter 10
advertisement

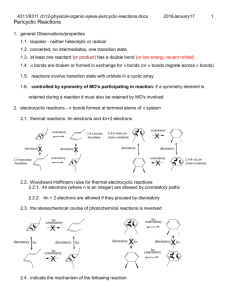
CS10a pericyclic reactions.docx 4April2012 page 1 I. Pericyclic Reactions: General Observations/Characteristics A. isopolar - neither heterolytic or radical B. concerted, no intermediates, one transition state C. at least one reactant (or product) has a double bond D. bonds are broken or formed in exchange for double bonds E. reactions involve orbitals in a cyclic array F. controlled by symmetry of MO's participating in reaction: if a symmetry element is retained during a reaction it must also be retained by MO's involved II. electrocyclic reactions - bonds formed at terminal atoms of system A. thermal reactions: 4n electrons and 4n+2 electrons conrotatory X disrotatory 2,4-trans,trans -hexadiene 2,4-cis,trans, -hexadiene X disrotatory 2,4,6-trans,cis,trans-octatriene conrotatory X disrotatory disrotatory conrotatory conrotatory 2,4,4-cis,cis,trans-octatriene X B. the stereochemical course of photochemical reactions is reversed h conrotatory h conrotatory X disrotatory h disrotatory h disrotatory Xh h conrotatory X h disrotatory h conrotatory X III. Frontier Orbital method (acid-base theory) A. HOMO of one system overlaps with LUMO of another B. allowed reaction if no new nodes are created in transition state CS10a pericyclic reactions.docx 4April2012 page 2 C. use HOMO for single system LUMO = 3 LUMO = 2 HOMO = 2 HOMO = HOMO = 3 HOMO = D. photolysis reverses stereochemistry since HOMO is next higher orbital IV. Aromatic Transition State or Möbius-Hückel Method A. construct basis set, connect forming odd or even nodes, calculate MO energies B. Hückel transition state has even number of nodes C. Möbius transition state has odd number of nodes Hückel disrotatory Möbius conrotatory D. Möbius transition state allowed for 4n electrons E. Hückel transition state allowed for 4n+2 electrons V. Correlation Diagram Method A. choose symmetry elements that are preserved during rearrangement and distinguish the two pathways CS10a pericyclic reactions.docx 4April2012 page 3 B. label MO's antisymmetric or symmetric according to symmetry elements C. connect orbitals of like symmetry, indicates where electrons end up in product D. reaction is not symmetry allowed if reaction creates exicted state (and vice versa) plane A S A S C2 axis A A S S 4 3 2 1 S A A S S A A S