Unit 12 Review Game: World War II
advertisement

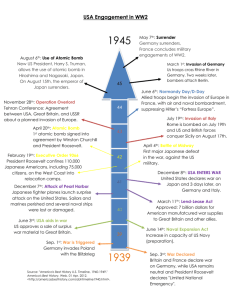
Unit 12 Review Game: World War II 1. Name 2 reasons Germany was angry about the conditions of the Treaty of Versailles after World War I 2. Name 3 characteristics of “totalitarianism” 3. Name 3 totalitarian dictators and the countries they controlled 4. Name 1 territory that each of the following countries attacked before World War II began: (a) Japan, (b) Italy, and (c) Germany 5. Britain and France as the leaders of the League of Nations used the policy of __________ in which they gave in to German, Italian, and Japanese demands in order to avoid war. 6. Place the following events in the correct chronological order: (a) Nazi-Soviet Nonaggression Pact, (b) German invasion of Poland, (c) German annexation of Austria, (d) outbreak of World War II 7. What 3 countries made up the “Axis Coalition” (the Tripartite Pact)? 8. Name 3 of the many countries that formed the Allied Powers in WWII 9. What military tactic did Germany use to take control of Europe and France by 1942? 10. What did the Neutrality Acts of 1935-1937 outlaw? 11. In 1939, the USA altered the Neutrality Acts to allow arms sales to Britain, but we did not pro vide loans nor did the USA offer to ship weapons to Britain on American ships. What was this program called? 12. In 1941, France had fallen, Britain was under siege, and the USSR was attacked by the Nazis. In responses, the USA altered the Neutrality Acts by giving full support to the Allies through arms sales and transportation of these weapons on American ships. What was this program called that made the USA the “arsenal of democracy? 13. What was 1 of the 2 things that Britain and the USA agreed to when they drafted the Atlantic Charter in 1941? 14. Place the following events in the correct chronological order: (a) Lend-Lease Act, (b) Neutrality Acts, (c) Cash-and-Carry program, (d) Pearl Harbor attack 15. Why did the Japanese bomb Pearl Harbor on Dec 7, 1941? 16. What was the purpose of the U.S. gov’t agency the War Production Board? 17. Name 3 ways the USA committed to total war during World War II 18. Name 1 similarity and 1 difference African Americans experienced during World War I and World War II 19. Name 1 similarity and 1 difference women experienced during World War I and WWII? 20. Why did FDR issue Executive Order 9066 that forced Japanese Americans into internment camps? 21. Who was A Philip Randolph and what significant change did he help bring about on the U.S. home front during World War II? 22. Which of the following European battles helped the USA get Lend-Lease supplies into Europe: (a) Stalingrad, (b) Battle of the Atlantic, (c) Battle of the Bulge, (d) D-Day 23. Which of the following European battles proved to be the “turning point” that allowed the Soviet Union to push towards Germany and eventually seize Berlin? (a) Stalingrad, (b) Battle of the Atlantic, (c) Battle of the Bulge, (d) D-Day 24. Which of the following European battles was planned by Dwight Eisenhower and allowed the Allies to launch and invasion of Nazi-occupied France and push towards German from the West? (a) Stalingrad, (b) Battle of the Atlantic, (c) Battle of the Bulge, (d) D-Day 25. What reason did FDR give as to why he did not order Nazi concentration camps (with Jewish victims of the Final Solution) liberated or attacked when we knew they existed? 26. Which of the following battles against Japan proved to be the “turning point” in the war in the Pacific? (a) Iwo Jima, (b) Midway, (c) Okinawa, (d) Guadalcanal 27. What strategy did the military develop that allowed the United States to quickly take control of the Pacific Ocean in its fight towards Japan? 28. What desperate strategy did the Japanese use to attack U.S. naval ships during the fighting in the Pacific? 29. Pick any 2 of the following people and explain what role they played in developing the atomic bomb: (a) Albert Einstein, (b) Franklin Roosevelt, (c) Robert Oppenheimer 30. Explain the significance of each: (a) Manhattan project; (b) Los Alamos, New Mexico; (c) Potsdam Declaration 31. Two part question: (a) Which U.S. president gave the order to drop the atomic bomb? (b) Which 2 cities were atomic bombed? 32. Name 2 things that FDR, Churchill, and Stalin agreed to at the Yalta Conference in February 1945 33. What was the significance of the Potsdam Conference in July 1945? 34. Put the following Pacific theater events in the correct order: (a) Doolittle raid on Tokyo; (b) Japanese surrender; (c) Island hopping strategy developed; (d) Battle of Midway 35. Name 2 impacts of WWII on the United States Unit 12 Review Game: World War II The Answers 1. Germany had to accept war guilt, pay $33 billion in reparations to the Allies, lost all overseas colonies, high inflation of their currency, economic depression 2. Dictators with complete power, single party rule, demands loyalty of the people, use police power to control the people, increased militarism, territorial expansion, promoted extreme nationalism 3. Hitler in Germany, Mussolini in Italy, Stalin in the Soviet Union, Hideki Tojo in Japan, Francisco Franco in Spain 4. (a) Manchuria, China, East Indies (b) Ethiopia, Libya, Albania; (c) Austria, Sudetenland (part of Czechoslovakia), all of Czechoslovakia, Poland 5. Appeasement 6. C, A, B, D 7. Germany, Italy, Japan 8. USA, Britain, France, USSR, China, Australia, Canada 9. Blitzkrieg (“lightning war”) 10. Weapons sales or loans to any country at war 11. Cash-and-Carry program 12. Lend-Lease program 13. Developed a battle plan for war; Agreed to form a United Nations; agreed to Allied goals for the war 14. B, C, A, D 15. The USA cut off oil and iron from Japan (embargo) and the Japanese retaliated with an attack; The USA tried to stop the Japanese from expanding further into the Pacific; The USA tried to stop Japan from taking the Philippine Islands 16. To oversee military production during WW2 17. Draft, rationing, victory/war bonds, propaganda, limitations on individual rights (Japanese internment & censorship), government control of wartime industrial production, price controls 18. Similarities: Great Migration; drafted into the army but into segregated units; worked in industrial jobs; faced racial discrimination in new cities; received unequal pay (at least at the beginning the war) Differences: In WWII, African Americans moved North & WEST; A Philip Randolph helped force FDR to form the Fair Employment Practices Commission which gave black workers equal pay during the war; Black soldiers were allowed to fight in WWII (Tuskegee Airmen) 19. Similarities: Women worked factory job s; Women served in the military in clerical jobs; Helped ration goods & plant victory gardens; Received unequal pay Differences: During WWII, 6 million women entered the work force who had never worked before (during WWI, factory jobs were done almost exclusively by women who were already working in lower-paying jobs); Were pilots in the Army & Navy; Special noncombat units were created in the military just for women (WACs and WAVES); Women used daycare centers for their children 20. Americans believed that Japanese Americans would serve as spies or launch an invasion of the USA 21. He was an African American civil rights leader who was upset by unequal pay scales for black workers; After threatening to march on Washington D.C. during the war, FDR created the Fair Employment Practices Commission to give black factory workers equal pay to whites. 22. B (Battle of the Atlantic) 23. A (Stalingrad) 24. D (D-Day) 25. FDR believed that the best way to help those imprisoned in concentration camps was to win the war as early as possible; Liberating the camps would divert badly needed supplies from the troops fighting the Germans. 26. B (Midway) 27. Island hopping strategy 28. Kamikaze attacks (“divine wind”) 29. (a) Wrote FDR a letter suggesting that atomic energy could be used to build a nuclear bomb; (b) Created the Manhattan Project to develop the bomb; (c) Was in charge of the Manhattan Project and building the bomb 30. (a) Code name for the secret project to develop an atomic bomb; (b) Where the atomic bomb was secretly tested (Operation Trinity); (c) The warning President Truman gave to the Japanese before dropping the atomic bomb (Surrender or face prompt and utter destruction) 31. (a) Truman (b) Hiroshima and Nagasaki 32. Demanded the unconditional surrender of the Axis Powers, created the United Nations, allow freedom in Europe (self-determination), planned the oversight and division of Germany 33. Truman first learned that the atomic bomb was ready; Truman issued the Potsdam Declaration and ordered the dropping of the atomic bomb on Hiroshima; the USA and USSR divided Germany 34. A, D, C, B 35. The USA joined the United Nations; the Cold War began; the age of nuclear weapons began; the Great Depression came to an end; America entered an era of prosperity in the 1950s; Women lost their high paying industrial jobs; Israel was created; Nazi and Japanese officers were tried and executed for war crimes Unit 12 Review: World War II 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 1st Place _____________________________________________ 2nd Place _____________________________________________ 3rd Place _____________________________________________ 4th Place _____________________________________________ Unit 12 Review: World War II 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 1st Place _____________________________________________ 2nd Place _____________________________________________ 3rd Place _____________________________________________ 4th Place _____________________________________________