Meiosis Lab - Cloudfront.net
Name:
Date:
Class Period:
Meiosis Lab
What is Meiosis?
Meiosis produces daughter cells that have one half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
2N N
Meiosis enables organisms to reproduce sexually . Gametes (sperm and eggs) are haploid.
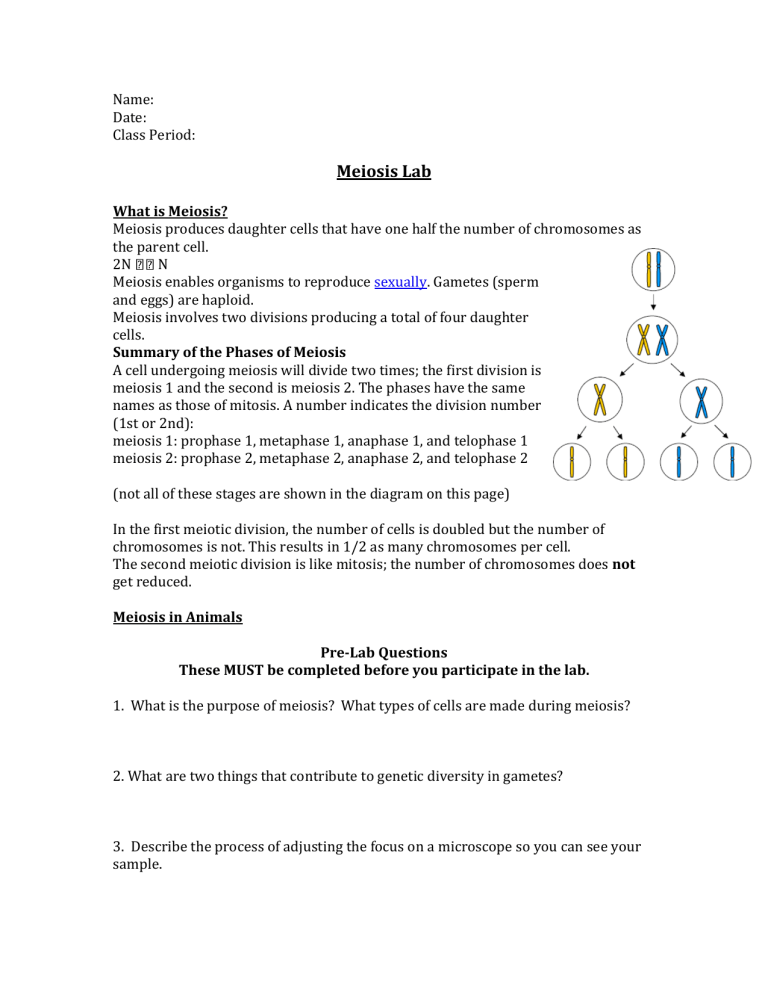
Meiosis involves two divisions producing a total of four daughter cells.
Summary of the Phases of Meiosis
A cell undergoing meiosis will divide two times; the first division is meiosis 1 and the second is meiosis 2. The phases have the same names as those of mitosis. A number indicates the division number
(1st or 2nd): meiosis 1: prophase 1, metaphase 1, anaphase 1, and telophase 1 meiosis 2: prophase 2, metaphase 2, anaphase 2, and telophase 2
(not all of these stages are shown in the diagram on this page)
In the first meiotic division, the number of cells is doubled but the number of chromosomes is not. This results in 1/2 as many chromosomes per cell.
The second meiotic division is like mitosis; the number of chromosomes does not get reduced.
Meiosis in Animals
Pre-Lab Questions
These MUST be completed before you participate in the lab.
1. What is the purpose of meiosis? What types of cells are made during meiosis?
2. What are two things that contribute to genetic diversity in gametes?
3. Describe the process of adjusting the focus on a microscope so you can see your sample.
Laboratory Procedure
1. Obtain a prepared slide of a cross-section of rat testes.
2. Place the slide under the microscope and adjust the focus until you can see the cells clearly.
3. Draw what you see at 100x. Use as much detail as you can, and label as many parts as you can.
4. Now increase the magnification to 500x and draw what you see. Label all the parts you can identify.
5. Write a brief conclusion in paragraph form. Please type it and attach it to this packet. Make sure to answer the following questions using complete sentences:
Were you able to see cells in different stages of meiosis? Why or why not?
Were you able to see chromosomes? Why or why not?
Why did we use rat testes to observe meiosis?
What went well in this lab? What did not go well?
If you were to do this lab again, what would you do differently?








