Supplementary Data for Occurrence and human exposure of
advertisement

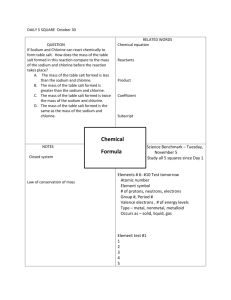
Supplementary Data for Occurrence and human exposure of parabens and their chlorinated derivatives in swimming pools Wenhui Li a, Yali Shi b, Lihong Gao a, Jiemin Liu a,*, Yaqi Cai b,* a School of Chemistry and Biological Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China; b State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100085, China *Corresponding author Tel: +86 10 62849182; fax: +86 10 62849182;E-mail: caiyaqi@rcees.ac.cn Tel.: +86 010 62333751; E-mail: liujm@ustb.edu.cn 1 Parameters are calculated according Exposure Factors Handbook (US EPA, 2011) The permeability coefficient of parabens (Kp, cm h-1) was calculated using the equation: log K p = −2.80 + 0.66 log K ow − 0.0056 MW (1) where Kp is the dermal permeability coefficient of parabens in water (cm h-1) ; Kow is the Octanol/water partition coefficient of the parabens (dimensionless) ; MW is the molecular weight (g mol-1) The dimensionless ratio of the permeability coefficient of a compound through the stratum corneum relative to its permeability coefficient across the viable epidermis (B, dimensionless) was calculated using the equation: B = Kp √𝑀𝑊 2.6 (as an approximation) (2) The effective diffusion coefficient (DSC, cm2 h-1) of the chemical in the stratum corneum was calculated using the equation: log( Dsc ⁄lsc ) = −2.80 − 0.0056 MW (3) where lsc is the Apparent thickness of stratum corneum (cm), and lsc = 0.001 cm. The lag time (τ, h) was calculated using the equation: τ = l2sc ∖ (6Dsc )=0.105×10(0.0056 MW) 2 (4) Captions: Table S1 Physicochemical characteristics of the target compounds Table S2 Details of pool design and operating parameter values Table S3 Experimental conditions of electrospray tandem mass spectrometry Table S4 Correlation coefficients (r), linear range, recoveries (%) and method detection limits (MDLs, S/N=3) of target compounds Table S5 Spearman's coefficients of the concentrations of target compounds and with operating parameters of 39 pools. Fig.S1. Box-and-whisker plots of concentrations of parabens and chlorinated derivatives in indoor and outdoor swimming pools Fig.S2. Box-and-whisker plots of concentrations of parabens and chlorinated derivatives on the weekend and weekdays. 3 Table S1 Physicochemical characteristics of the target parabens Analytes Structure SW (g mo1-1) (mg L-1) p-Hydroxybenzoic acid (PHBA) 138.12 14,500 2.7; 8.4 1.39[1] 1.13×10-11 [2] Methyl paraben (MeP) 152.15 5981 8.17[3] 1.66[3] 3.61×10-9 Ethyl paraben (EtP) 166.17 960[4] 8.22 2.19 4.79×10-9 Propyl paraben (PrP) 180.20 390[4] 8.35 2.71 6.37×10-9 Butyl paraben (BuP) 194.23 207[5] 8.37 3.24[4] 8.45×10-9 Pentyl Paraben (PeP) 208.25 n.a. n.a. 3.48 n.a. Heptyl paraben (HeP) 236.31 n.a. n.a. 4.41 1.98×10-8 Benzyl paraben (BzP) 228.24 160[5] 8.18[6] 3.56 [3] 2.92×10-10 Octyl paraben (OcP) 250.34 n.a. n.a. 4.88 n.a. Methyl 3-chloro-4-hydroxyb enzoate (3-Cl-MeP) 186.59 2.64[7] n.a. 2.27 n.a. 4 pKa logKow Hc MW (atm m3 mol-1) Methyl 3,5-dichloro-4-hydro xybenzoate (3,5-2Cl-MeP) Ethyl 3-chloro-4-hydroxyb enzoate (3-Cl-EtP) 221.04 3.29[7] n.a. 2.88 n.a. 200.62 2.31[8] n.a. n.a. n.a. Ethyl 3,5-dichloro-4-hydro xybenzoate (3,5-2Cl-EtP) 235.06 2.34[8] n.a. 3.32 n.a. The table includes information on the hydrophobicity (log Kow); aqueous solubility (Sw) at neutral pH; acid-base reactivity (pKa); Henry’s Law constant (Hc) at 25 °C. n.a.: not available 5 Table S2 Details of pool design and operating parameter values NO. Type Functional areas Disinfection type Size (m3) Date Opening Hours (h) Price (RMB) Visitors TOC (mg L-1) S01 Indoor Community Chlorine 500 Weekday 11 40 25 15.4 S02 Indoor Community Chlorine 600 Weekend 10 35 25 10.2 S03 Indoor School Chlorine 1200 Weekday 13 30 80 3.13 S04 Indoor School Chlorine 1700 Weekend 11 30 112 5.88 S05 Indoor School Chlorine 1200 Weekday 13.5 30 45 12.5 S06 Indoor School Chlorine 1200 Weekend 10 20 37 4.37 S07 Indoor School Ozone/ Chlorine 2000 Weekday 9.5 20 62 1.55 S08 Indoor Municipal Chlorine 1600 Weekend 10 50 192 9.50 S09 Indoor School Chlorine 400 Weekday 11 30 13 1.63 S10 Indoor School Chlorine 1600 Weekend 10 30 30 7.92 S11 Indoor Municipal Ozone/ Chlorine 600 Weekend 11 35 213 7.16 S12 Indoor Community Chlorine 480 Weekend 12 50 73 8.92 S13 Indoor Community Chlorine 400 Weekday 11 38 35 10.4 S14 Indoor Community Chlorine 300 Weekend 12 30 57 13.8 S15 Indoor Community Chlorine 400 Weekday 14 40 12 5.67 S16 Indoor Municipal Chlorine 600 Weekend 12 30 43 8.79 S17 Outdoor Municipal Chlorine 12000 Weekend 7 30 472 3.48 S18 Outdoor Municipal Chlorine 18000 Weekday 10 30 150 4.48 S19 Outdoor Municipal Chlorine 2400 Weekday 7.5 30 134 2.66 S20 Indoor Health club Chlorine 450 Weekend 13 35 28 11.9 S21 Indoor School Chlorine 400 Weekend 16 20 55 7.72 S22 Indoor School Chlorine 2000 Weekend 12 25 156 4.12 6 S23 Indoor School Chlorine 2250 Weekend 11.5 30 104 3.27 S24 Indoor Community Chlorine 1200 Weekend 14 40 17 6.88 S25 Indoor School Chlorine 2000 Weekday 12.5 50 76 7.94 S26 Indoor School Chlorine 2000 Weekday 12 50 46 7.66 S27 Indoor School Chlorine 2000 Weekend 12 50 74 6.69 S28 Indoor Municipal Chlorine 1600 Weekend 11 50 205 4.67 S29 Indoor Hotel Chlorine 3200 Weekday 12 100 1000 12.5 S30 Indoor Hotel Chlorine 240 Weekday 12 100 102 2.15 S31 Indoor Hotel Chlorine 160 Weekend 13 100 23 8.06 S32 Indoor Hotel Chlorine 500 Weekend 13 90 44 10.1 S33 Indoor Community Chlorine 600 Weekend 13 60 13 8.80 S34 Indoor Health club Chlorine 400 Weekday 12 40 12 9.83 S35 Indoor Health club Chlorine 1200 Weekend 12.5 50 121 10.6 S36 Indoor Community Chlorine 500 Weekend 12 40 23 10.0 S37 Indoor Municipal Chlorine 2000 Weekend 12 50 243 13.7 S38 Outdoor Municipal Chlorine 1600 Weekend 8 20 1131 12.9 S39 Indoor Health club Chlorine 600 Weekend 12 50 13 21.7 7 Table S3 Experimental conditions of electrospray tandem mass spectrometry Analytes Parent Daughter Declustering Entrance Collision Collision Collision cell ion ion Potential/ Potential/ cellent Energy/ exit potential/ (m/z) (m/z) MeP 151.0 EtP 165.0 PrP 179.0 BuP 193.0 PeP 207.1 HeP 235.1 BzP 227.0 OcP 249.1 PHBA 137.0 3-Cl-MeP 185.0 3,5-2Cl-MeP 218.9 3-Cl-EtP 199.0 3,5-2Cl-EtP 232.9 PHBA-d4 141.0 MeP-d4 EtP-d5 155.0 170.0 V V potential/V eV V a 91.9 136.0 93.0 a 137.0 93.0 136.0 a 91.9 a 136.0 91.9 a 93.0 92.0 a 135.9 91.9 136.0 a 93.0 a 136.0 93.0 a 65.1 126.0 a 142.0 160.0 a 176.0 127.0 170.9 a 161.1 a 205.0 -27 -27 -25 -25 -30 -30 -30 -30 -35 -35 -40 -40 -25 -25 -45 -45 -23 -23 -30 -30 -40 -35 -32 -32 -36 -36 -5 -5 -5 -5 -5 -5 -5 -5 -10 -10 -5 -5 -5 -5 -5 -5 -5 -5 -5 -5 -5 -5 -5 -5 -5 -5 -7 -6 -14 -7 -8 -6 -8 -8 -9 -9 -12 -8 -8 -8 -10 -10 -8 -8 -7 -7 -8 -8 -8 -7 -8 -8 -26 -27 -30 -17 -28 -20 -35 -21 -34 -30 -38 -25 -34 -18 -35 -27 -20 -43 -26 -24 -28 -28 -26 -20 -30 -22 -10 -14 -10 -13 -10 -14 -10 -13 -10 -10 -10 -14 -10 -14 -13 -10 -10 -8 -13 -14 -15 -15 -13 -15 -16 -18 97.1 a -23 -5 -8 -18 -10 69.1 -23 -7 -15 -40 -10 96.1 a -25 -10 -10 -28 -10 112.1 -25 -10 -10 -28 -10 91.9 -26 -5 -8 -30 -10 -26 -5 -8 -30 -10 94.0 PrP-d7 BuP-d9 BzP-d7 a 186.1 202.1 233.9 a 91.9 -30 -5 -8 -33 -10 94.0 a -30 -5 -8 -33 -10 91.9 a -30 -5 -8 -34 -10 136.0 -30 -5 -8 -35 -10 91.9 -40 -9 -10 -40 -11 136.0 a -40 -9 -26 -22 -13 quantitative ion 8 Table S4 Correlation coefficients (r2), linear range, recoveries (%) and method detection limits (MDLs, S/N=3) of target compounds Analytes Surrogates r2 Linear range (μg L-1) Recovery (%) MDLs (ng L-1) MeP MeP-d4 0.9997 0.1-500 97.5±7.4 0.07 EtP EtP-d5 0.9987 0.1-500 92.7±5.1 0.03 PrP PrP-d7 0.9993 0.1-500 94.3±5.7 0.08 BuP BuP-d9 0.9998 0.05-200 94.4±6.9 0.03 Pep BuP-d9 0.9984 0.05-500 97.6±3.8 0.03 Bzp BzP-d7 0.9923 0.05-200 104±1.9 0.02 Hep BuP-d9 0.9992 0.05-500 92.4±3.3 0.02 Ocp BuP-d9 0.9995 0.1-200 94.2±5.9 0.06 PHBA PHBA-d4 0.9907 1.0-500 85.9±11 0.40 3-Cl-MeP MeP-d4 0.9998 0.1-500 101±4.3 0.07 3,5-2Cl-MeP MeP-d4 0.9995 0.1-500 98.3±2.7 0.05 3-Cl-EtP EtP-d5 0.9996 0.1-500 95.0±5.3 0.10 3,5-2Cl-EtP EtP-d5 0.9996 0.1-500 101±5.6 0.16 9 Table S5 Pearson's coefficients of the concentrations of target compounds and with parameters of 39 pools Parameters ∑PBs Pearson ∑Cl-PBs Sig. (2-tailed) Pearson Correlation ∑PBs+∑Cl-PBs PHBA Sig. (2-tailed) Correlation Pearson Sig. (2-tailed) Correlation Pearson Sig. (2-tailed) Correlation Price (RMB) 0.336* 0.036 0.037 0.825 -0.229 0.160 0.326* 0.042 Vistors -0.083 0.617 -0.301 0.062 0.067 0.683 -0.093 0.573 Size (m3) -0.116 0.480 -0.350* 0.029 -0.091 0.583 -0.128 0.436 Opening Hours (h) 0.210 0.200 0.327* 0.042 0.077 0.642 0.220 0.178 TOC (mg L-1) 0.217 0.185 0.471** 0.002 0.118 0.475 0.237 0.147 **. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed); *. Correlation is significant at the 0.05 level (2-tailed) 10 Fig.S1. Box-and-whisker plots of concentrations of parabens and chlorinated derivatives in indoor and outdoor swimming pools. 11 Fig.S2. Box-and-whisker plots of concentrations of parabens and chlorinated derivatives on the weekend and weekdays. 12 Reference [1] Wang L, Kannan K. Alkyl protocatechuates as novel urinary biomarkers of exposure to p-hydroxybenzoic acid esters (parabens). Environ. Int., 2013, 59 27-32 [2] Wang L, Liao C Y, Liu F, et al. Occurrence and Human Exposure of p-Hydroxybenzoic Acid Esters (Parabens), Bisphenol A Diglycidyl Ether (BADGE), and Their Hydrolysis Products in Indoor Dust from the United States and Three East Asian Countries. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2012, 46 (21): 11584-11593 [3] Bledzka D, Gromadzinska J, Wasowicz W. Parabens. From environmental studies to human health. Environ. Int., 2014, 67 27-42 [4] Ramaswamy B R, Shanmugam G, Velu G, et al. GC-MS analysis and ecotoxicological risk assessment of triclosan, carbamazepine and parabens in Indian rivers. J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 186 (2-3): 1586-1593 [5] Haman C, Dauchy X, Rosin C, et al. Occurrence, fate and behavior of parabens in aquatic environments: A review. Water Res., 2015, 68 1-11 [6] Blanco E, del Carmen Casais M, del Carmen Mejuto M, et al. Simultaneous determination of p-hydroxybenzoic acid and parabens by capillary electrophoresis with improved sensitivity in nonaqueous media. Electrophoresis., 2008, 29 (15): 3229-3238 [7] Terasaki M, Abe R, Makino M, et al. Chronic toxicity of parabens and their chlorinated by-products in Ceriodaphnia dubia. Environ. Toxicol., 2013, DOI: 10.1002/tox.21944 [8] Terasaki M, Makino M, Tatarazako N. Acute toxicity of parabens and their chlorinated by-products with Daphnia magna and Vibrio fischeri bioassays. J. Appl. Toxicol., 2009, 29 (3): 242-247 13




![[1] - Boswellsgmt](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006603407_1-fadfbce8d94050a9fb3c38a07d86e8ee-300x300.png)