Waves Practice Test
advertisement
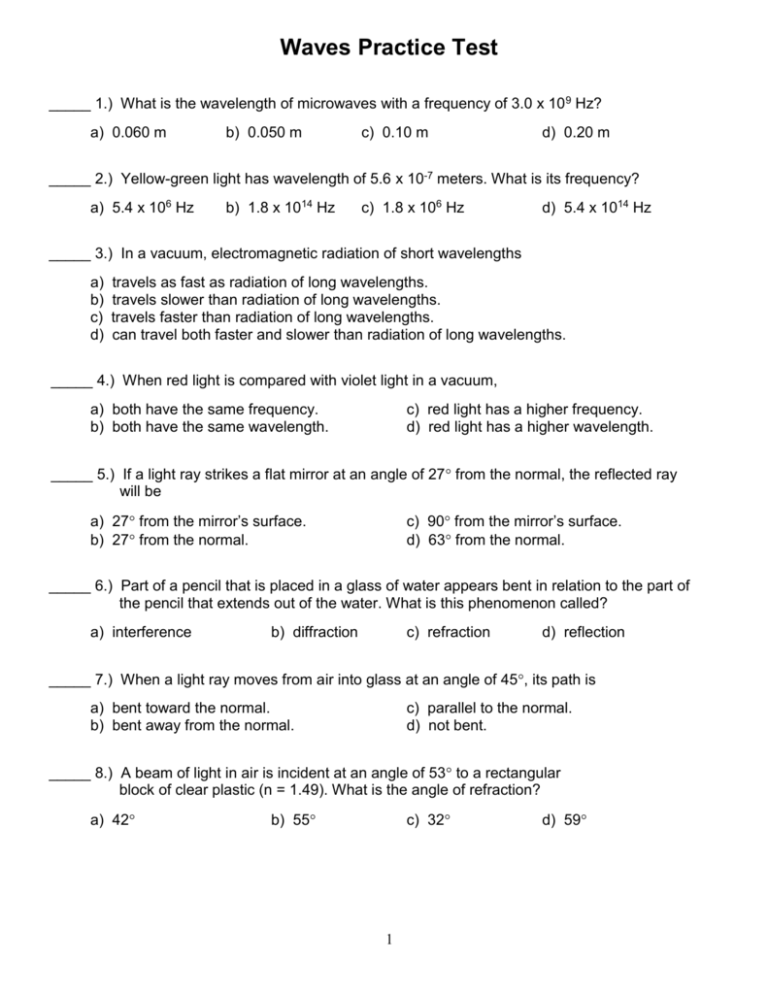
Waves Practice Test _____ 1.) What is the wavelength of microwaves with a frequency of 3.0 x 10 9 Hz? a) 0.060 m b) 0.050 m c) 0.10 m d) 0.20 m _____ 2.) Yellow-green light has wavelength of 5.6 x 10-7 meters. What is its frequency? a) 5.4 x 106 Hz b) 1.8 x 1014 Hz c) 1.8 x 106 Hz d) 5.4 x 1014 Hz _____ 3.) In a vacuum, electromagnetic radiation of short wavelengths a) b) c) d) travels as fast as radiation of long wavelengths. travels slower than radiation of long wavelengths. travels faster than radiation of long wavelengths. can travel both faster and slower than radiation of long wavelengths. _____ 4.) When red light is compared with violet light in a vacuum, a) both have the same frequency. b) both have the same wavelength. c) red light has a higher frequency. d) red light has a higher wavelength. _____ 5.) If a light ray strikes a flat mirror at an angle of 27 from the normal, the reflected ray will be a) 27 from the mirror’s surface. b) 27 from the normal. c) 90 from the mirror’s surface. d) 63 from the normal. _____ 6.) Part of a pencil that is placed in a glass of water appears bent in relation to the part of the pencil that extends out of the water. What is this phenomenon called? a) interference b) diffraction c) refraction d) reflection _____ 7.) When a light ray moves from air into glass at an angle of 45, its path is a) bent toward the normal. b) bent away from the normal. c) parallel to the normal. d) not bent. _____ 8.) A beam of light in air is incident at an angle of 53 to a rectangular block of clear plastic (n = 1.49). What is the angle of refraction? a) 42 b) 55 c) 32 1 d) 59 _____ 9.) Which of the following describes what will happen to a light ray incident on a glassto-air boundary at greater than the critical angle? a) total internal reflection b) total transmission c) partial reflection, partial transmission d) partial reflection, total transmission _____ 10.) Which of the following is NOT an electromagnetic wave? a) radio wave b) sound waves c) visible light d) gamma rays _____ 11.) If the frequency of a green light wave increased, this green light could turn into a) red light b) yellow light c) blue light d) orange light _____ 12.) Which of the following electromagnetic waves has the highest energy? a) radio wave b) microwaves c) visible light d) gamma rays c) glycerol d) lucite _____ 13.) Light travels slowest in which substance? a) air b) water _____ 14.) When a singer hits a high pitched note, a glass on the opposite side of the opera hall shatters. Which statement best explains this? a) b) c) d) The note was polarized after hitting the walls. The amplitude of the note increased as it traveled across the hall. The frequency of the note matched the natural frequency of the glass. The singer and the glass were exactly one wavelength apart. _____ 15.) A light wave can be distinguished from a sound wave by its ability to be a) polarized b) reflected c) amplified d) transmitted _____ 16.) Increasing the amplitude of a sound wave produces a sound with a) lower speed b) shorter wavelength c) higher pitch d) greater loudness _____ 17.) A police car traveling at a speed of 30 m/sec sounds its siren, which has a frequency of 1 × 103 hertz. As the police car approaches a stationary pedestrian, the pedestrian detects a siren frequency of a) 30 Hz b) 1 × 103 Hz c) 9.19 × 102 Hz d) 1.10 × 103 Hz _____ 18.) A wave having a frequency of 5 Hz and a speed of 10 m/sec has a wavelength of a) 0.50 m b) 5.0 m c) 2.0 m 2 d) 50. m _____ 19.) Two pulses traveling in the same uniform medium approach each other, as shown in the diagram at right. Which diagram best represents the superposition of the two pulses? _____ 20.) Which diagram best represents the shape and direction of a series of wave fronts after they have passed through a small opening in a barrier? a) b) c) Part I Answer Key: 1.) c 2.) d 3.) a 4.) d 5.) b 6.) c 7.) a 8.) c 9.) a 10.) b 11.) 12.) 13.) 14.) 15.) 16.) 17.) 18.) 19.) 20.) c d d c a d d c 3 d 3 d) Part II 1.) The diagram below represents a periodic transverse wave traveling in a uniform medium. On the diagram, draw a wave having both a smaller amplitude and the same wavelength as the given wave. 2.) Base your answers on the diagram at right, which shows a light ray ( f = 5.09 1014 Hz) in air, incident on a boundary with fused quartz. At the boundary, part of the light is refracted and part of the light is reflected. a) Using a protractor, determine the angle of incidence of the light ray at the air-fused quartz boundary. __________________ b) Calculate the angle of refraction of the incident light ray. Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units. c) Using a protractor and straightedge, construct AND LABEL the refracted light ray in the fused quartz on the diagram. d) Using a protractor and straightedge, construct AND LABEL the reflected light ray on the diagram. 4 3.) A ray of light (f = 5.09 x1014 Hz) is incident on the boundary between air and an unknown material X at an angle of incidence of 55°, as shown. The absolute index refraction of material X is 1.66. of a) Identify a substance of which material X may be composed. _____________________________ b) Determine the speed of this ray of light in material X. c) Calculate the angle of refraction of the ray of light in material X. Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units. d) On the diagram, use a straightedge and protractor to draw the refracted ray of light in material X. 5 Part II ANSWER KEY 1.) 2.) a) Angle must be measured TO THE NORMAL LINE! Angle of incidence = 17° b) n1 = 1.0 (air) n2 = 1.46 (fused quartz) – see ref table θ1 = 17° θ2 = ? n1sinθ1 = n2sinθ2 1(sin 17) = 1.46(sinθ2) 0.292 / 1.46 = sinθ2 0.200 = sin θ2 sin-1(0.200) = θ2 12° = θ2 c) θ2 = refracted angle in the fused quartz – always MEASURED TO THE NORMAL!!!! d) reflected angle = incident angle always!! Ray will reflect (bounce) off a flat surface at the same angle it hit surface 6 3.) a) Material X has an index of refraction = n = 1.66 so if we look in our Reference Table we see that FLINT GLASS is the best choice for Material X’s composition. b) v = ? n = 1.66 c = speed of light in a vacuum = 3 x 108 m/sec (ref table) n=c/v v = 3 x 108 / 1.66 v = 1.81 x 108 m/sec c) n1 = 1.0 (air) n2 = 1.66 θ1 = 55° θ2 = ? n1sin θ1 = n2 sinθ2 1(sin55°) = 1.66 (sinθ2) 0.82 / 1.66 = sinθ2 0.494 = sinθ2 sin-1(0.494) = θ2 30° = θ2 d) = θ2, so just draw on diagram, measuring angle TO THE NORMAL 7