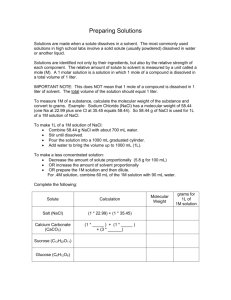
Chapter 15 Practice Problems Vocabulary Define the following
advertisement

Chapter 15 Practice Problems Vocabulary Define the following terms: 1.) Solution 2.) Solvent 3.) Solute 4.) Aqueous solutions 5.) Saturated 6.) Unsaturated 7.) Supersaturated 8.) Concentrated 9.) Dilute 10.) Mass percent 11.) Molarity 12.) Standard solution 13.) Dilution 14.) Neutralization reaction 15.) Normality 16.) Colligative property 17.) Equivalent weight 18.) Equivalent of an acid 19.) Equivalent of a base Answer the following using vocabulary terms: 1.) What does the solubility of a solute depend on? Problems 1.) What happens to the solubility of a gas when the temperature increases? 2.) The label “aqueous H2SO4” means that there is a relatively _____ amount of H2SO4 in the solution. 3.) If 59.5 g of NaCl is added to 250 g of water, calculate the mass percent of NaCl in the solution. 4.) If 625 g of NaOH is dissolved into a final total volume of 25.0 L, what is the molarity of the solution? 5.) Calculate the new molarity that results from the addition of 30 mL of water to 150mL of 0.251 M HCl. 6.) What is the volume (in L) of 0.25 M Na2SO4 solution is needed to precipitate all the barium, as BaSO4 from 12.5 mL of 0.15 M Ba(NO3)2 solution? 7.) What volume of 0.700 M NaOH solution is needed to neutralize 43 mL of 0.45 M HCl solution? 8.) Calculate the normality of .134 M HNO3. 9.) If 36.2 mL of 0.158 M CaCl2 solution is added to 37.5 mL of 0.149 M Na2CO3, what mass of NaCl will be precipitated? The balanced reatction is: CaCl2 + Na2CO3 CaCO3 + 2 NaCl 10.) If 10.0 mL of 0.1926 M HNO3 solution is needed to neutralize 0.035 M Ca(OH)2 solution of unknown volume, what is the volume of the calcium hydroxide? 11.) Solve problem number 10 using ionic and net ionic equations. 12.) Find the limiting reactant of Ba(NO3)2 + KCrO4 BaCrO4 + KNO3 13.) Using the same problem at question 12, find the mass of the product containing chromium (II) oxide. 14.) If 250mL of 0.125 M AgNO3 is added to 150 mL of 0.0125 M NaCl, find the mass of the aqueous product. 15.) Find the molarity of the two products resulting from 100mL of .1 M NaOH and 100 mL of .10 M HCl. Chapter 15 Answers Vocabulary Define: 1.) 2.) 3.) 4.) 5.) 6.) A homogeeous mixture The dissolving medium in a solution A substance dissolved in a solvent to form a solution A solution in which water is the dissolving medium, or solvent A solution that contains as much solute as can be dissolved in that solution A solution that has not reached the limit of solute that will dissolve in that solution 7.) A solution that contains more dissolved solid than a saturated solution will hold at that temperature. 8.) When a relatively large amount of solute is dissolved 9.) When a relatively small amount of solute is dissolved. 10.) Expresses the mass of solute present in a given mass of a solution 11.) The number of moles of solute per volume of solution in liters 12.) A solution whose concentration is accurately known 13.) The process of adding more solvent to a solution 14.) An acid-base reaction 15.) The number of equivalents of solute per liter of solution 16.) A solution property that depends on the number of solute particles present 17.) The mass in grams of 1 equivalent (equiv) of that acid or base 18.) The amount of that acid that can furnish 1 mol of H+ ions. 19.) The amount of base that can furnish 1 mol of OH- ions. Answer: 1.) It depends on the interactions between the solvent and solute particles. Problems 1.) 2.) 3.) 4.) 5.) 6.) 7.) 8.) 9.) It decreases Low 19.2% 0.5 M 0.206 M 0.075 L 27.6 mL .134 mol/L or .134 normal solution 138.3 g 10.) 11.) 12.) 13.) 14.) 15.) 27.5mL Ionic: Ca2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) +2H-(aq) + 2NO3- Ca2+ + 2NO3- +2H2O(l) a. Net ionic: 2OH-(aq) + 2H+ (aq) 2H2O(l) Ba(NO3)2 .88g .1598g .01 M NaCl and .01 M H2O