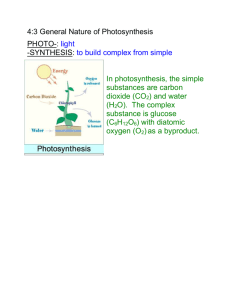
File - Mr. Schmitt Biology 12 AP
advertisement
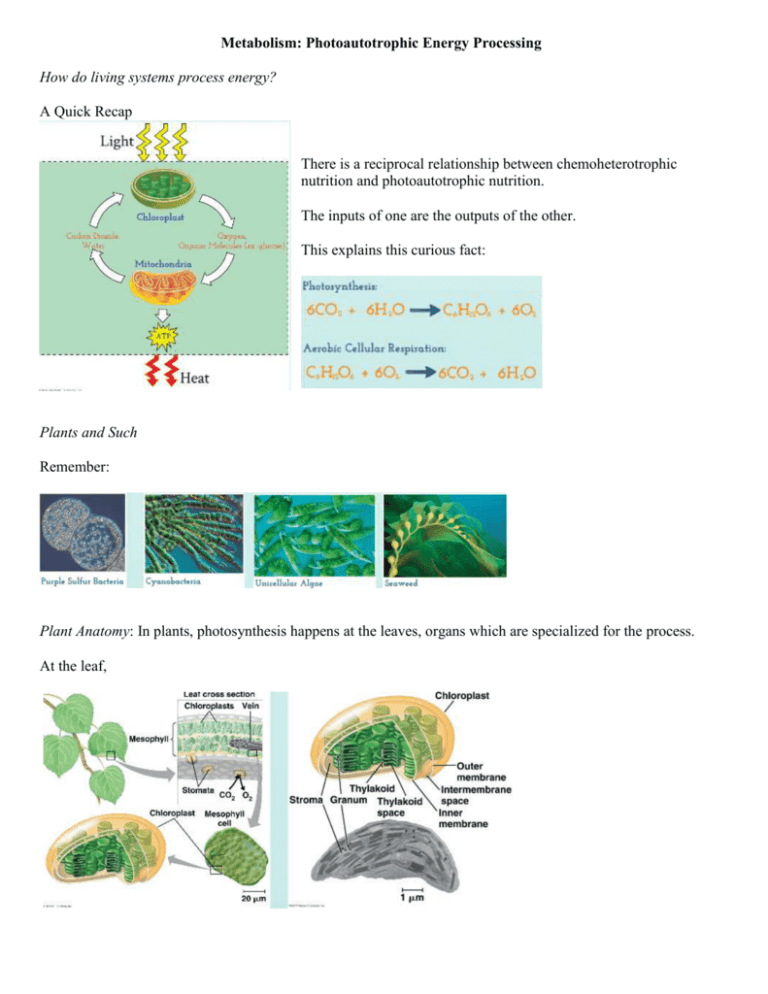
Metabolism: Photoautotrophic Energy Processing How do living systems process energy? A Quick Recap There is a reciprocal relationship between chemoheterotrophic nutrition and photoautotrophic nutrition. The inputs of one are the outputs of the other. This explains this curious fact: Plants and Such Remember: Plant Anatomy: In plants, photosynthesis happens at the leaves, organs which are specialized for the process. At the leaf, Light = Energy - Light is a form of - It is produced by - Visible light is just one tiny slice of the larger electromagnetic spectrum. Chlorophyll - Chlorophyll is a - Pigment: any - Chlorophyll comes in two varieties - While chlorophyll is the main photosynthetic pigment, it is not the only pigment found in chloroplasts. - _________________________________: other pigments that allow the chloroplast to Why are plants green? - Sunlight contains almost all wavelengths of visible light. - Chloroplasts do not - When plants are exposed to light, chloroplasts preferentially - Chlorophylls have an absorption spectrum that is highest in the blue and red portions of the visible light spectrum. - The accessory pigments expand the Photosynthesis An ______________________________ , _________________________________ process Overview Chloroplasts Chloroplasts consist of a series of - - - Photosynthetic prokaryotes use specialized cell membrane regions to accomplish photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is a two part process: 1. The light reactions: Occur in the thylakoid membranes. Light is used to drive the production of ATP and NADPH (an electron shuttle). Water provides the electrons needed and is converted to oxygen gas (a waste product). 2. The Calvin cycle: Occurs in the stroma. The ATP and NADPH produced in the light reactions are used to incorporate carbon dioxide into a 3-carbon sugar. The Light Reactions (Thylakoid) Light + Chlorophyll = Electrons! When This happens with ~1% of all the sunlight that strikes the surface of the earth. Isolated chlorophyll will fluoresce when exposed to light, as excited electrons return to the ground state. Photosystems Complexes of protein and pigment molecules that are embedded in the thylakoid membrane. Direct incoming photons into the Two types: - - Since chlorophyll is not going to have the electrons return to it, new electrons are needed. _______________ provides the replacement electrons (________________________). This creates 4 protons and 1 molecule of oxygen gas for every 2 water molecules consumed. The oxygen gas is released as waste product, becoming a major input for aerobic cellular respiration. Chemiosmosis As the electrons move through the ETC, they provide the energy for chemiosmosis, in a fashion almost identical to cellular respiration. A few notable differences: - In respiration, the energy comes from the oxidation of glucose, (oxidative phosphorylation). In photosynthesis, the energy come from protons (photophosphorylation). - In respiration, protons were pumped from the matrix into the intermembrane space by the ETC. In photosynthesis, electrons are pumped from the stroma into the thylakoid space. Electron Flow - Non-Cyclic Electron Flow - Cyclic Electron Flow Why? Inputs Calvin Cycle Three Phases 1. 2. 3. Outputs Every step of the Calvin Cycle is controlled by an enzyme (not shown). Where’s the Sugar? - In order to get 1 G3P as a product of the Calvin Cycle, 3 molecules of carbon dioxide have to be joined to three molecules of RuBP. - Inputs (per G3P) Outputs Versatility and Regulation An evolutionary quirk – Rubisco evolved in conditions of low oxygen and gas concentration. As a result, its active site has a high affinity for oxygen gas, which is a problem. Photorespiration – The metabolic pathway that occurs when rubisco incorporates oxygen instead of carbon dioxide into RuBP. A metabolic dead end, uses ATP but produces no sugar. As long as a plant C3 Leaves: No adaptations for minimizing photorespiration - Both stages of photosynthesis - Oxygen and carbon dioxide - Sugars are transported - But there are environments where keeping stomates open will lead to _____________________ - Closed stomates = = = 2 Major Adaptations C4 Leaves - Carbon fixation occurs in mesophyll cells. Carbon monoxide is incorporated into a - The 4C acid is then transported to - Since the bundle sheath cells are surrounded by mesophyll, CAM Plants – Carbon fixation occurs during The carbon dioxide is stored in an organic acid. During the day, Importance Make sure you can … … explain how photoautotrophic energy processing allows for the production of useful energy for organisms. … explain why and how photoautotrophic energy processing is controlled. … identify the oxidation and reduction reactions that occur in photosynthesis. … explain the processes and identify all inputs and outputs of all steps of photosynthesis, … relate the different steps of photosynthesis to their locations in the cell. … compare the adaptations that have been made to reduce photorespiration. … compare photosynthesis with cellular respiration. … explain how photosynthesis provides the energetic foundation for the vast majority of life on Earth.