Trigonometry
advertisement

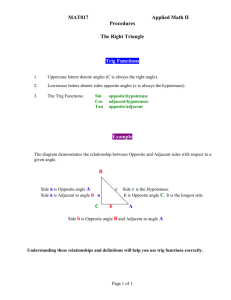
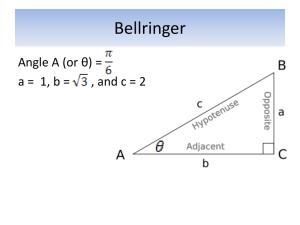
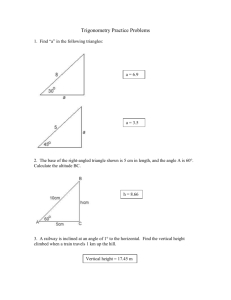
Trigonometry Trigonometry is the study of triangles; it connects the angles to the lengths of its sides. This chapter deals only with right-angled triangles, and first you need to know how to label the sides: First label the hypotenuse – it is always opposite the right angle. 𝑥 ℎ𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 The adjacent side is next to the angle you know or want to find. The opposite side is opposite the angle you know or want to find. 𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 A question might have the triangle a different way round, so be careful to follow these rules of labelling. SOH-CAH-TOA There are 3 formulae that connect an angle to two of the sides, you need to pick the correct formula based on what sides you know or are interested in: 𝑜𝑝𝑝 𝑎𝑑𝑗 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥 = ℎ𝑦𝑝 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑥 = ℎ𝑦𝑝 𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑥 = 𝑜𝑝𝑝 𝑎𝑑𝑗 The acronym SOHCAHTOA can be used to remember these formulae. 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥 is short for sine of the angle 𝑥, 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑥 is short for cosine of the angle 𝑥, and 𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑥 is short for tangent of the angle 𝑥. You calculator will give you these values for different angles, 𝑥. Example 1: Finding a side Find 𝑝. 12𝑐𝑚 is the hypotenuse, 𝑝 𝑝 is the adjacent, 32° so we need the 𝑐𝑜𝑠 formula 12𝑐𝑚 𝑎𝑑𝑗 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑥 = ℎ𝑦𝑝 𝑝 𝑐𝑜𝑠32 = 12 𝑝 = 12 × 𝑐𝑜𝑠32 = 10.2𝑐𝑚 (3𝑠𝑓) You should have sin, cos and tan buttons on your calculator Example 2 Find 𝑠 64° 𝑠 is the hypotenuse, 𝑠 9𝑐𝑚 is the opposite, so we need the 𝑠𝑖𝑛 formula 9𝑐𝑚 𝑜𝑝𝑝 9 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥 = ℎ𝑦𝑝 𝑠𝑖𝑛64 = 𝑠 𝑠 × 𝑠𝑖𝑛64 = 9 9 𝑠 = 𝑠𝑖𝑛64 = 10.0𝑐𝑚 (3𝑠𝑓) Example 3: Finding an angle Find 𝑥 𝑥 7𝑐𝑚 is the adjacent, 7𝑐𝑚 11𝑐𝑚 is the opposite, so we need the 𝑡𝑎𝑛 formula 11𝑐𝑚 𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑥 = 𝑜𝑝𝑝 𝑎𝑑𝑗 𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑥 = 11 7 11 𝑥 = 𝑡𝑎𝑛−1 ( 7 ) = 57.5° (3𝑠𝑓) Pressing shift, then tan, on your calculator, allows you use inverse tan to find an angle.