LC2 - King`s Leadership Academy
advertisement

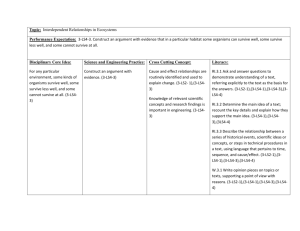
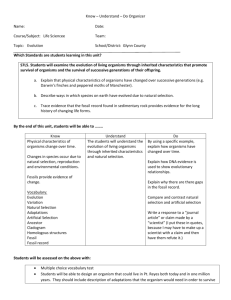
Year 10 Biology CORE Learning Cycle 2 Overview How do organisms become so well suited for their habitat? Learning Cycle Overview: Line of enquiry 1: Hypothesis 1 Hypothesis 2 Hypothesis 3 Hypothesis 4 Why does an ability to adapt mean your species is more likely to survive? Many organisms are adapted so that they can live to breed Most animals are adapted in the same way Both plants and animals face competition to survive A change in the environment may also alter the survival of an organism Line of enquiry 2: Hypothesis 5 Hypothesis 6 Hypothesis 7 Hypothesis 8 Why does a species change over time? Variation in animals is due to the genes they inherit There have been different theories of evolution Organisms evolve when members of their species die Different species do not share the same features Week 1 Week 1/2 Year 10 Biology CORE | Learning Cycle 2 | Medium Term Plan | Science 2015/16 How do organisms become so well suited for their habitat? Line of enquiry one: Why does an ability to adapt mean your species is more likely to survive? Intentions for learning AQA schemes of work/specification: ADAPTATION Explain the reason for adaptations in a range of organisms. Explain how organisms are adapted to survive in their habitat. Describe and explain adaptations for survival in the Arctic. Describe and explain adaptations for survival in a desert. Define the term extremophile and be able to give general examples. Be able to relate features seen in a diagram to the organism’s survival. Describe factors that affect the survival of organisms in their habitat. Describe resources that plants and animals compete for in a given habitat. Describe adaptations that some organisms have to avoid being eaten. Interpret population curves. ENVIRONMENTAL CHANGE Evaluate data on environmental change and the distribution and behaviour of living organisms. Describe with examples how an environment can change. Interpret data on lichen distribution and sulfur dioxide levels. Interpret data on invertebrates and water pollution. Home Learning Week 1: exam booklet part 1 to be used as revision tool (tutor marked to be handed back during week 2) Lesson 2: Most animals are adapted in the same way Lesson 3: Both plants and animals face competition to survive Key words: organism, Arctic, desert Learning Intentions: Students should develop an understanding that: plants and animals are adapted in different ways according to the habitat they live in and other external factors Key words: competition, advantage Learning Intentions: Students should develop an understanding that: there is competition for a variety of resources for many organisms Success Criteria: Be able to link features seen in a diagram to the organism’s survival Describe factors that affect the survival of organisms in their habitat Explain adaptations for survival in the Arctic/desert Success Criteria: Recall some of the resources that plants and animals compete for in a given habitat Describe adaptations that some organisms have to avoid being eaten Explain why the adaptations are such an advantage for the plant and/or animal Feedback Focus Knowledge input | Check | Development | REACH | Improvement Details: Self assessed multiple choice quiz given to pupils based on first two lessons work Feedback Focus Knowledge input | Check | Development | REACH | Improvement Details: Extended writing exam question provided and will be tutor marked Lesson 1: Many organisms are adapted so that they can live to breed Key words: adaptation, survival, breed Learning Intentions: Students should develop an understanding that: animals are adapted in order to survive so that they can breed Success Criteria: Recall reasons why organisms have adaptations Describe some simple adaptations in a range of animals Explain the reason for these adaptations Feedback Focus Knowledge input | Check | Development | REACH | Improvement Details: Peer marked exam question on slide with rubric provided for pupil-given formative feedback Lesson 4: A change in the environment may also alter the survival of an organism Key words: environment, distribution, behaviour, population Learning Intentions: Students should develop an understanding that: the environmental conditions can change over time this change may alter the behaviour or distribution of living things Success Criteria: Describe using examples how an environment can change over time Explain data on animal population in response to pollution Evaluate data on environmental change and how it affects living organisms Feedback Focus Knowledge input | Check | Development | REACH | Improvement Details: Act on feedback given by tutor and improve work Year 10 Biology CORE | Learning Cycle 2 | Medium Term Plan | Science 2015/16 How do organisms become so well suited for their habitat? Line of enquiry two: Why does a species change over time? Intentions for learning AQA schemes of work/specification: WHY ORGANISMS ARE DIFFERENT Classify characteristics as being due to genetic or environmental causes. Decide the best way to present information about variation in tables and charts. Describe the order of size of cell, nucleus, chromosome and gene. Interpret evidence relating to evolutionary theory. Classify organisms based on their similarities. Home Learning Week 2: exam booklet part 2 to be used as revision tool (tutor marked to be handed back during week 5 revision) EVOLUTION Describe Darwin’s theory of evolution. Describe different theories of evolution. Identify differences between Darwin’s theory of evolution and conflicting theories. Suggest reasons for the different theories. Explain the terms ‘inherited’ and ‘acquired’ characteristics. Describe the stages in natural selection. Define the term ‘mutation’. Explain why mutation may lead to more rapid change in a species. Explain why Darwin’s theory was only gradually accepted. Lesson 5: Variation in animals is due to the genes they inherit Key words: genetic, environmental, inherited, acquired Learning Intentions: Students should develop an understanding that: Adaptations that organisms have are a mixture of genetic (inherited) and environmental (acquired) Success Criteria: be able to group variation as either genetic or environmental explain the terms ‘inherited’ and ‘acquired’ characteristics describe the order of size of cell, nucleus, chromosome and gene explain how to present different types of variation information Lesson 6: There have been different theories of evolution Lesson 7: Organisms evolve when members of their species die Feedback Focus Knowledge input | Check | Development | REACH | Improvement Details: Peer marked exam question on slide with rubric provided for pupil-given formative feedback Lesson 8: Different species do not share the same features Key words: Darwin, theories, evolution Key words: mutation, natural selection, species Key words: classification, theory, similarities Learning Intentions: Students should develop an understanding that: there have been different theories for evolution with Darwin’s being the one that was gradually accepted Learning Intentions: Students should develop an understanding that: for a species to survive the weakest members should not be able to reach a breeding age and pass on their poor (less advantageous) genes Learning Intentions: Students should develop an understanding that: scientists group animals based on their similarities (both physical as well as genetically) and this helps explain evolutionary theory Success Criteria: define the term mutation describe the stages in natural selection explain why mutation may lead to more rapid change in a species Success Criteria: group organisms based on their similarities explain the similarities between certain organisms interpret evidence relating to evolutionary theory Success Criteria: describe different theories of evolution suggest reasons as to the different theories explain why Darwin’s theory was only gradually accepted Feedback Focus Knowledge input | Check | Development | REACH | Improvement Details: Self assessed multiple choice quiz given to pupils based on first two lessons work Feedback Focus Knowledge input | Check | Development | REACH | Improvement Details: Extended writing exam question provided and will be tutor marked Feedback Focus Knowledge input | Check | Development | REACH | Improvement Details: Act on feedback given by tutor and improve work