Study Guide for Cluster One
advertisement
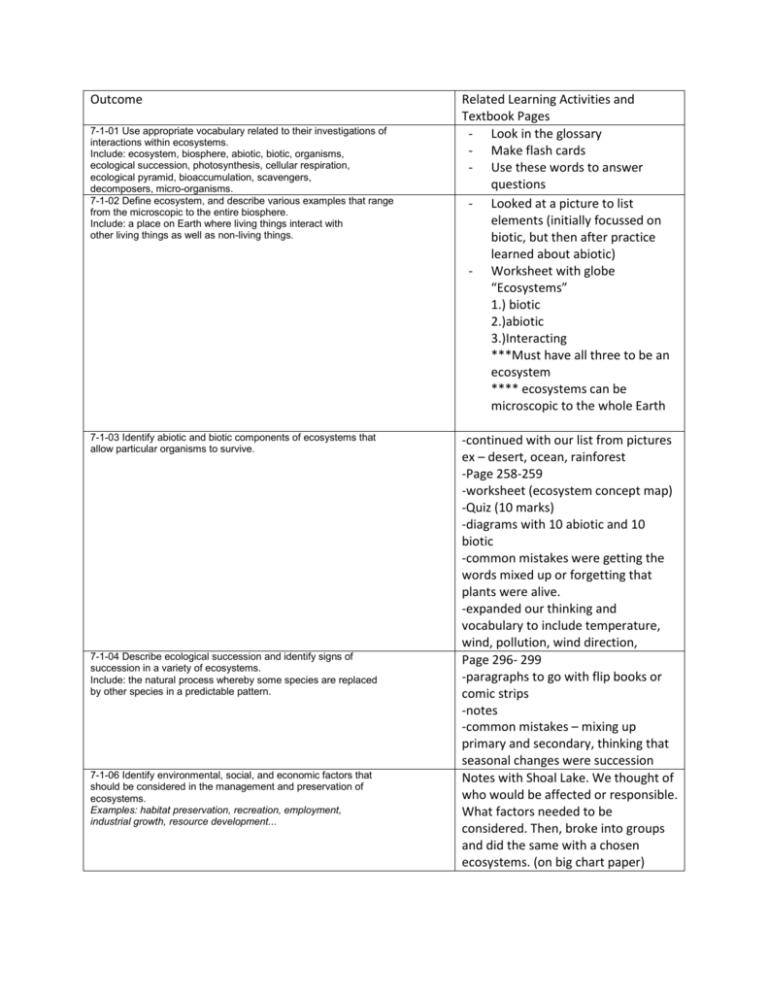
Outcome 7-1-01 Use appropriate vocabulary related to their investigations of interactions within ecosystems. Include: ecosystem, biosphere, abiotic, biotic, organisms, ecological succession, photosynthesis, cellular respiration, ecological pyramid, bioaccumulation, scavengers, decomposers, micro-organisms. 7-1-02 Define ecosystem, and describe various examples that range from the microscopic to the entire biosphere. Include: a place on Earth where living things interact with other living things as well as non-living things. 7-1-03 Identify abiotic and biotic components of ecosystems that allow particular organisms to survive. 7-1-04 Describe ecological succession and identify signs of succession in a variety of ecosystems. Include: the natural process whereby some species are replaced by other species in a predictable pattern. 7-1-06 Identify environmental, social, and economic factors that should be considered in the management and preservation of ecosystems. Examples: habitat preservation, recreation, employment, industrial growth, resource development... Related Learning Activities and Textbook Pages - Look in the glossary - Make flash cards - Use these words to answer questions - Looked at a picture to list elements (initially focussed on biotic, but then after practice learned about abiotic) - Worksheet with globe “Ecosystems” 1.) biotic 2.)abiotic 3.)Interacting ***Must have all three to be an ecosystem **** ecosystems can be microscopic to the whole Earth -continued with our list from pictures ex – desert, ocean, rainforest -Page 258-259 -worksheet (ecosystem concept map) -Quiz (10 marks) -diagrams with 10 abiotic and 10 biotic -common mistakes were getting the words mixed up or forgetting that plants were alive. -expanded our thinking and vocabulary to include temperature, wind, pollution, wind direction, Page 296- 299 -paragraphs to go with flip books or comic strips -notes -common mistakes – mixing up primary and secondary, thinking that seasonal changes were succession Notes with Shoal Lake. We thought of who would be affected or responsible. What factors needed to be considered. Then, broke into groups and did the same with a chosen ecosystems. (on big chart paper) 7-1-08 Compare photosynthesis to cellular respiration, and explain how both are part of the cycling of matter and the transfer of energy in ecosystems. Include: photosynthesis: water + carbon dioxide + light energy = sugar + oxygen in the presence of chlorophyll; cellular respiration: sugar + oxygen = water + carbon dioxide + energy. 7-1-09 Analyze food webs, using ecological pyramids, to show energy gained or lost at various consumer levels. Include: producers; primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers 7-1-10 Analyze, using ecological pyramids, the implications of the loss of producers and consumers to the transfer of energy within an ecosystem. 7-1-11 Explain, using ecological pyramids, the potential for bioaccumulation within an ecosystem. 7-1-12 Provide examples of scavengers and decomposers, and describe their role in cycling matter in an ecosystem. Include: micro-organisms. 7-1-14 Identify beneficial and harmful roles played by microorganisms. Examples: beneficial — aid in digestion, composting, food and vaccine production; harmful — cause disease, food spoilage... - Diagrams on the board (tree and ginger person) - List of questions 1-15 - Chemical equations - Related it to matter transfer (part of the carbon cycle) - Page 290-293 in text -page 274-275 -invasion of exotic species (zebra mussels) -notes (started with Mrs. C) used blocks to make a pyramid Page 275 has really good questions - “Deadly Links” game outside - Watched videos online DDT - Page 276-277 Page 268-269 -also included in notes about food chains/webs and pyramids Page 266-267 Page 268-269 T-chart on the board to be copied in notes. Study Stage 1: Turn each outcome into a question or questions. Review the material and activities covered and then write out a detailed answer to the questions. Study Stage 2: Predict what type of question Mrs. Shwaluk will ask. Try to make up a sample question and answer it. Study Stage 3: Make sure that you go over your material in many different ways so that the information is in your head instead of just in your binder/text Study Stage 4: You understand the material so much that you can apply it or relate it to new situations that were not specifically covered in class. Write Test Thursday, November 27, 2014