Properties_problems 3
advertisement
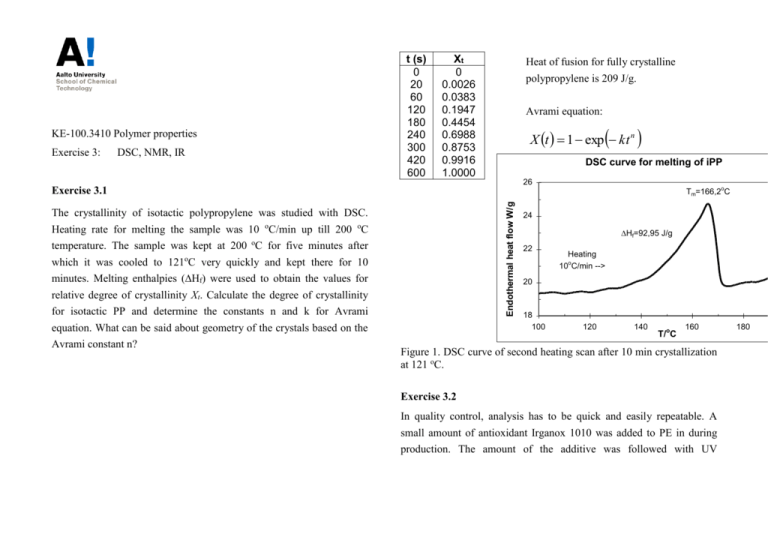
KE-100.3410 Polymer properties Exercise 3: DSC, NMR, IR t (s) 0 20 60 120 180 240 300 420 600 Xt 0 0.0026 0.0383 0.1947 0.4454 0.6988 0.8753 0.9916 1.0000 Heat of fusion for fully crystalline polypropylene is 209 J/g. Avrami equation: X t 1 exp kt n DSC curve for melting of iPP 26 Endothermal heat flow W/g Exercise 3.1 The crystallinity of isotactic polypropylene was studied with DSC. Heating rate for melting the sample was 10 oC/min up till 200 oC temperature. The sample was kept at 200 oC for five minutes after which it was cooled to 121oC very quickly and kept there for 10 minutes. Melting enthalpies (Hf) were used to obtain the values for relative degree of crystallinity Xt. Calculate the degree of crystallinity for isotactic PP and determine the constants n and k for Avrami equation. What can be said about geometry of the crystals based on the Avrami constant n? Tm=166,2oC 24 Hf=92,95 J/g 22 Heating 10oC/min --> 20 18 100 120 140 T/oC 160 Figure 1. DSC curve of second heating scan after 10 min crystallization at 121 oC. Exercise 3.2 In quality control, analysis has to be quick and easily repeatable. A small amount of antioxidant Irganox 1010 was added to PE in during production. The amount of the additive was followed with UV 180 spectroscopy. For the reference, a set of samples with the known amount of antioxidant (0-0.1 mol-%) was measured: t / cm 0.1 AO 0% A 0.042 AO 0.01% A 0.081 AO 0.05% A 0.29 AO 0.1% A 0.57 The proportion of - or -crystallinity (Xi) in syndiotactic polystyrene can be determined with the following equations: A851 a X A A A841 851 858 a a A858 a X A A A841 851 858 a a Use the measurements to formulate a correlation in the form A(c,t) = where Ai is the area of each absorbance peak and ai is the absorptivity (kc+a)t, according to Beer-Lambert law that can be used to determine the amount (c) of antioxidant (AO) in the PE sample. The thickness (t) of the sample as well as the UV absorbance (A) is measured. Use the equation then to determine the amount of antioxidant in a PE sample with a thickness of 0.4 cm and UV absorbance A = 0.61. ratio of each crystal form: a A851 A A841 * 841 a A858 A A841 * 841 A841* is the area of a fully amorphous sample, A841 is the area of the amorphous fraction of a partially -crystalline sample that corresponds Exercise 3.3 to 841 cm-1 absorbance peak and similarly A841 is the area of the Syndiotactic polystyrene (sPS) crystallizes in various crystal forms amorphous fraction of a partially -crystalline sample that corresponds () depending on crystallization conditions. The formation of - to 841 cm-1 absorbance peak. form is kinetically favorable whereas the formation of -form thermodynamically favorable. Fourier transform spectroscopy (FTIR) is used for analysis of polymer crystallinity. In the FTIR spectrum of syndiotactic polystyrene, characteristic absorbance peaks can be detected; for amorphous (841 cm-1), - (851 cm-1) and -form (858 cm1 ). Three syndiotactic PS samples were analysed by FTIR to determine absorptivity ratios. a) Based on the measurement data calculate the averages for each absorptivity ratio (a, a). b) Three samples of - and -forms were crystallized by using different isothermal crystallization times 2-240 min. Calculate the crystallinity degrees of each sample (Xor X) by using attained absorptivity ratios (a, a). c) Based on crystallinity degrees what can be said of the crystallization of syndiotactic PS? Sample 1 2 3 A841* 1.115 1.240 0.916 A841 0.706 0.842 0.642 A841 0.608 0.742 0.544 A851 0.072 0.071 0.050 A858 0.137 0.134 0.101 -crystalline samples: Sample t (min) 1 2 2 10 3 240 A841 1.123 1.086 0.311 A851 0.153 0.225 0.077 A841 0.439 0.448 0.377 A858 0.043 0.066 0.068 -crystalline samples: Sample t (min) 1 2 2 10 3 240