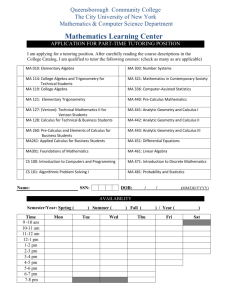
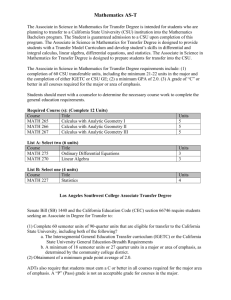
Arithmetic is the first branch of mathematics that you
advertisement

Mathematics Most high school students study several types of mathematics. In college, they complete additional math courses, some of which prepare them to study even more kinds of mathematics. You may think of math as one subject; in fact, there are many types of mathematics. This report describes seven kinds. Arithmetic Arithmetic is the first branch of mathematics that you studied in elementary and middle school. It deals with the study of numbers and the use of the four fundamental processes: Addition Subtraction Multiplication Division Arithmetic is everyday math. You use it daily in your personal affairs, and arithmetic is the basis for most other branches of mathematics. Algebra Algebra is used widely to solve problems in business, industry, and science by using symbols, such as x and y, to represent unknown values (Algebra). The power of algebra is that it enables us to create, write, and rewrite problem-solving formulas. Without algebra, we would not have many of the items we use on a daily basis: television, radio, telephone, microwave oven, etc. Geometry Geometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with shapes. More specifically, geometry is the study of relations, properties, and measurements of solids, surfaces, lines, and angles (Geometry). It is most useful in building or measuring things. Architects, astronomers, construction engineers, navigators, and surveyors are just a few professionals who rely on geometry. Trigonometry Trigonometry is mathematics that deals with triangular measurements. Plane trigonometry computes the relationships between the sides of triangles on level surfaces called planes. Spherical trigonometry studies the triangles on the surface of a sphere. Calculus Calculus is high-level mathematics dealing with rates of change (Calculus). It has many practical applications in engineering, physics, and other branches of science. Using calculus, we understand and explain how water flows, the sun shines, the wind blows, and the planets cycle through the heavens. Differential calculus determines the rate at which an object's speed changes. Integral calculus determines the object's speed when the rate of change is known. Probability Probability is the study of the likelihood of an event's occurrence. It is useful in predicting the outcomes of future events. Probability originated from the study of games of chance. It is now used for other purposes, including to (1) control the flow of traffic through a highway system; (2) predict the number of accidents people of various ages will have; (3) estimate the spread of rumors; (4) predict the outcome of elections; and (5) predict the rate of return in risky investments. Statistics Statistics is the branch of mathematics that helps mathematicians organize and find meaning in data. Anyone who listens to the radio, watches television, and reads books, newspapers, and magazines cannot help but be aware of statistics, which is the science of collecting, analyzing, presenting and interpret- ing data. Statistics appear in the claims of advertisers, . . . in cost-of-living indexes, and in reports of business trends and cycles. (Statistics) Works Cited “Algebra.” Encylopaedia Britannica. 2003. Encylopaedia Britannica Online. http://search.eb.com/eb/article?eu=120643 (accessed October 14, 2003). “Calculus.” Britannica Student Encyclopedia. 2003. Encylopaedia Britannica Online. http://search.eb.com/eb/article?eu=295242 (accessed October 14, 2003). “Geometry.” Britannica Student Encyclopedia. 2003. Encylopaedia Britannica Online. http://search.eb.com/eb/article?eu=296426 (accessed October 14, 2003). “Statistics.” Britannica Student Encyclopedia. 2003. Encylopaedia Britannica Online. http://search.eb.com/eb/article?eu=299352 (accessed October 14, 2003).