Dihybrid Cross Worksheet Use the table below to answer the
advertisement
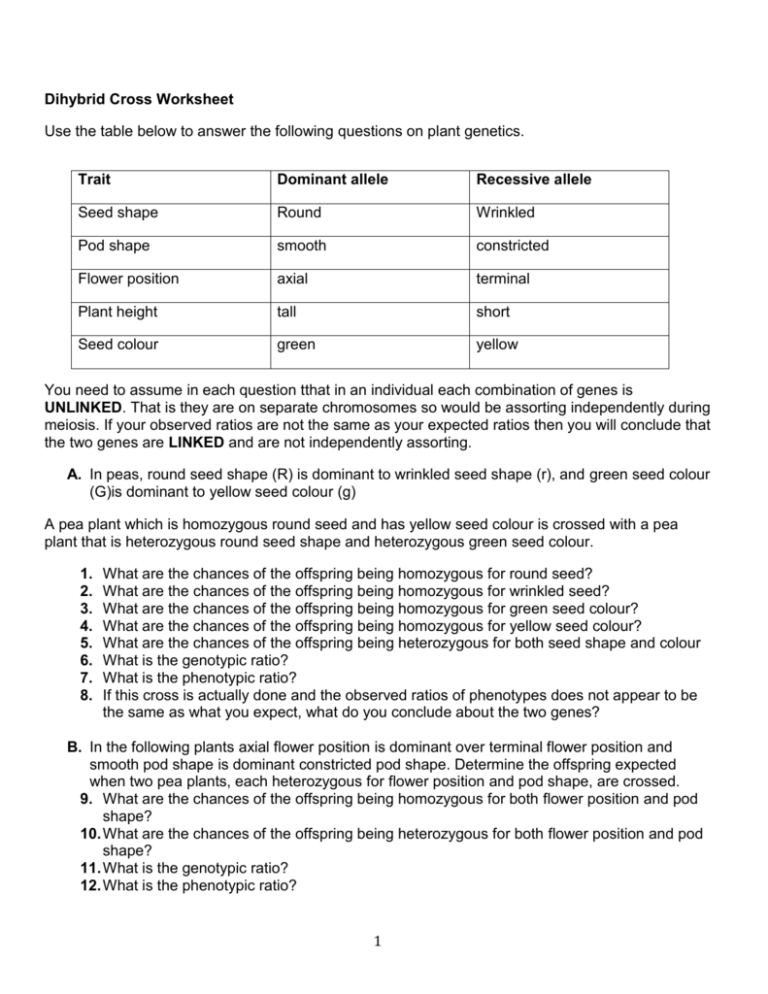
Dihybrid Cross Worksheet Use the table below to answer the following questions on plant genetics. Trait Dominant allele Recessive allele Seed shape Round Wrinkled Pod shape smooth constricted Flower position axial terminal Plant height tall short Seed colour green yellow You need to assume in each question tthat in an individual each combination of genes is UNLINKED. That is they are on separate chromosomes so would be assorting independently during meiosis. If your observed ratios are not the same as your expected ratios then you will conclude that the two genes are LINKED and are not independently assorting. A. In peas, round seed shape (R) is dominant to wrinkled seed shape (r), and green seed colour (G)is dominant to yellow seed colour (g) A pea plant which is homozygous round seed and has yellow seed colour is crossed with a pea plant that is heterozygous round seed shape and heterozygous green seed colour. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. What are the chances of the offspring being homozygous for round seed? What are the chances of the offspring being homozygous for wrinkled seed? What are the chances of the offspring being homozygous for green seed colour? What are the chances of the offspring being homozygous for yellow seed colour? What are the chances of the offspring being heterozygous for both seed shape and colour What is the genotypic ratio? What is the phenotypic ratio? If this cross is actually done and the observed ratios of phenotypes does not appear to be the same as what you expect, what do you conclude about the two genes? B. In the following plants axial flower position is dominant over terminal flower position and smooth pod shape is dominant constricted pod shape. Determine the offspring expected when two pea plants, each heterozygous for flower position and pod shape, are crossed. 9. What are the chances of the offspring being homozygous for both flower position and pod shape? 10. What are the chances of the offspring being heterozygous for both flower position and pod shape? 11. What is the genotypic ratio? 12. What is the phenotypic ratio? 1 13. If this cross is actually done and the observed ratios of phenotypes does not appear to be the same as what you expect, what do you conclude about the two genes? C. Cross a double heterozygous tall and smooth pod shape plant with a heterozygous tall with constricted pod shape. 14. What are the expected ratios of phenotypes? 15. If this cross is actually done and the observed ratios of phenotypes does not appear to be the same as what you expect, what do you conclude about the two genes? D. Cross a homozygous axial short plant with a terminal short plant. 16. What are the expected ratios of phenotypes? 17. If this cross is actually done and the observed ratios of phenotypes does not appear to be the same as what you expect, what do you conclude about the two genes? E. A purebred (homozygous) wingless red-eyed fruit fly is crossed with a purebred winged sepia-eyed fruit fly to produce F1 flies. A=wings a = wingless E = red-eyes e = sepia-eyes Two of the F1 flies are mated to produce an F2 generation of flies. 18. What is the phenotypic ratio of the F2 flies? 19. If this cross is actually done and the observed ratios of phenotypes does not appear to be the same as what you expect, what do you conclude about the two genes? F. In man, assume that spotted skin (S) is dominant over non-spotted skin (s) and that wooly hair (W) is dominant over non-wooly hair (w). Cross a heterozygous spotted, non-wooly man with a wooly-haired, non-spotted woman. 20. Give genotypic and phenotypic ratios of offspring. 21. If this cross is actually done and the observed ratios of phenotypes does not appear to be the same as what you expect, what do you conclude about the two genes? G. In horses, black is dependent upon a dominant allele, B, and chestnut upon its recessive allele, b. The trotting gait is due to a dominant allele, T, the pacing gait to its recessive allele, t. 22. If a homozygous black pacer is mated to a homozygous chestnut trotter, what will be the appearance of the F1 generation? 23. If this cross is actually done and the observed ratios of phenotypes does not appear to be the same as what you expect, what do you conclude about the two genes? 2 H. In snapdragon flowers, red colour is not completely dominant over white colour and tall plants are dominant over short plants. What would expect to get from a genetic cross of a homozygous tall red snapdragon with a short white plant? 24. Give genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the offspring. 25. If this cross is actually done and the observed ratios of phenotypes does not appear to be the same as what you expect, what do you conclude about the two genes? I. In mice, the ability to run normally is a dominant trait. Mice with this trait are called running mice (R). The recessive trait causes mice to run in circles only. Mice with this trait are called waltzing mice (r). Hair color is also inherited in mice. Black hair (B) is dominant over brown hair (b). For each of the following problems, determine the parent genotypes, possible gametes, then construct a Punnet square to solve. 26. Cross a heterozygous running, heterozygous black mouse with a homozygous running, homozygous black mouse Parental genotypes ______________ Possible gametes _____ _____ _____ _____ Offspring phenotypic ratio ________________ 27. Cross a homozygous running, homozygous black mouse with a heterozygous running, brown mouse Parental genotypes ______________ Possible gametes _____ _____ _____ _____ Offspring phenotypic ratio ________________ 28. Cross a waltzing brown mouse with a waltzing brown mouse Parental genotypes ______________ Possible gametes _____ _____ _____ _____ Offspring phenotypic ratio ________________ 29. Cross a homozygous running, heterozygous black mouse with a waltzing brown mouse Parental genotypes ______________ Possible gametes _____ _____ _____ _____ Offspring phenotypic ratio ________________ 30. Cross a heterozygous running, brown mouse with a heterozygous running, homozygous black mouse Parental genotypes ______________ Possible gametes _____ _____ _____ _____ Offspring phenotypic ratio ________________ 3 31. Cross a heterozygous running, heterozygous black mouse with a heterozygous running, heterozygous black mouse Parental genotypes ______________ Possible gametes _____ _____ _____ _____ Offspring phenotypic ratio ________________ Meiosis: Define meiosis. What separates during meiois I? What separates during meiois II? Draw SIMPLE sketches (2 pairs of chromosomes is enough) to show what is happening to the chromosomes in each stage of meiosis. Don’t forget to label. A cell has 20 chromosomes in Prophase I, how many chromosomes will each cell have in Prophase II. What stage of meiosis are the following cells in? A cell cycle review question. What is occurring in each stage of the cell cycle? Note that this diagram is showing mitosis not meiosis 4









