Topic 4 Lesson Objectives notes
advertisement

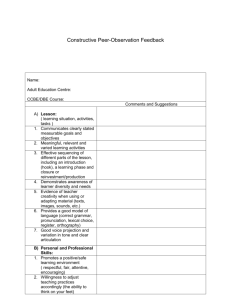
Lesson Objectives Putting together a lesson Regardless of the type of lesson, you need to put: • • • • • • Date Lesson Title Grade level/proficiency level Objective Materials needed Description • • • • Process – PPP; ESA; ERR; Hunter Closure Assessment Reflection Need a notebook for recording lessons Goals and objectives Look at the table. We have goals and objectives. Which word do you thinkgoeswhere? broad precise concrete can’t be validated narrow general abstract can be validated Goals Objectives Lesson Objectives • narrow – what learners will be able to do at the end of instruction – should describe the intended outcome of the instruction rather than the process of instruction itself – clear and precise – identifying concrete actions using concrete verbs • validated – proof or measurement – can and should be measured because it identifies what you are going to assess your students on Objective example Goal: To know vocabulary about clothing in English Objective: The learners will be able to label 14 articles of clothing on a picture of a person without referring to the textbook. ABCD model Briefly, the ABCD model stands for audience, behavior, conditions, and degree. A: Audience. Who will be doing the behavior? In other words, the learners. Objectives usually begin with one of these two phrases: “The learner will be able to …” (LWBAT) or “The student will be able to …” (SWBAT). B: Behavior. What should the learner be able to do? This is where concrete verbs come in. The behavior should be something that can be seen, heard, or measured in some way. For example: The learners will recite … The learners will compare … C: Conditions. Under what conditions do you want the learner to be able to do it? What can they use? What can’t they use? Who will they work with? For example: The learners will be able to recite the Gettysburg Address from memory … With a partner, the learners will be able to compare personality traits of the characters in the story … D: Degree. How well must it be done? Speed, accuracy, and quality are three common degrees that a teacher may measure. For example: The learners will be able to recite the Gettysburg Address from memory with 80 percent accuracy. With a partner, the learners will be able to compare at least six personality traits of the characters in the story. Objectives and assessment • Lesson objective – should focus on what students will learn from the lesson and be able to do. • English class – four language skills – grammar and vocabulary • Since the objective tells you what they will be able to do, it also tells you and the learners what you are going to assess – informal – formal Revised Bloom’s taxonomy Create Evaluate Analyze Apply Understand: Describe, explain Knowledge: Remember Bloom’s taxonomy - generally presented as a pyramid with the broadest and least in-depth type of learning at the bottom of the pyramid and the most focused at the top. Purpose - to help the learner move from knowledge acquisition to being able to use this knowledge critically and authentically. Associated with each level are verbs that help describe what the learner will be able to do to demonstrate that level of learning. When describing what the learners will be able to do use strong concrete verbs. Knowledge • • • To find or remember information Acquiring knowledge is fairly basic to any learning experience. Useful verbs for describing the learner’s behavior: – arrange, define, duplicate, match, label, list, name, recognize, relate, recall, repeat Write it down: Write an objective for a lesson about giving directions to some place using one of these verbs. They have a city map. – The LWBAT to Understanding • • • To describe or explain knowledge information Students should be able to describe or explain knowledge information, not just repeat it. Use verbs such as: – classify, describe, discuss, explain, identify, indicate, locate, recognize, report, restate, review, select, translate Write it down: Write an objective for a lesson about giving directions to some place using one of these verbs. They have a city map. – The LWBAT to Application • • • To apply knowledge Should be able to use the knowledge they have gained. The following verbs describe what learners can do: – apply, choose, compute, demonstrate, dramatize, employ, illustrate, interpret, operate, practice, schedule, sketch, solve, use Write it down: Write one objective for a lesson about giving directions to some place using one of these verbs They have a city map. – The LWBAT to Analysis • • • To take information or knowledge apart Moving from the ‘who’, ‘what’, ‘where’, and ‘how much’ levels to the ‘how’ and ‘why’ levels of complexity Verbs used at this level: – analyze, calculate, categorize, compare, contrast, criticize, distinguish, examine, experiment, question, test Analysis Objective Which of these two objectives is more complex and at the analysis level of Bloom’s taxonomy? Why? When given a list of vocabulary words, the learners will be able to categorize the words into at least three categories that they’ve identified themselves. When given a list of vocabulary words, the learners will be able to classify the words on the provided chart. Evaluation • • • To make judgments about knowledge Some verbs associated with evaluation are: – appraise, argue, assess, choose, compare, defend, estimate, evaluate, judge, predict, rate, select, value With many of these, a degree of judgment on the part of the learner is stated or implied Evaluation Objective Which of these two objectives is more complex and at the evaluation level of Bloom’s taxonomy? Why? When given two sets of directions from Point A and Point B, the learners will be able to compare the two routes and predict which is the shorter distance. When given two sets of directions from Point A and Point B, the learners will be able to describe the two routes. Creation • • • To make new ideas or things using one’s knowledge Many of the verbs are focused on the learner doing something new with their knowledge, not just repeating it or comparing with other knowledge. Some verbs are: – arrange, assemble, collect, compose, construct, create, design, develop, formulate, plan, prepare, propose, set up Write it down: Write one objective for a lesson about giving directions to some place using one of these verbs. – The LWBAT to Blooms and Objectives • • Lesson planning – similar to building a pyramid – solid foundation of knowledge about the necessary English grammar, vocabulary, and the four skills areas. – then ready to move up the pyramid to more complex, complicated, and authentic activities May move back and forth among the levels, giving your students a variety of experiences at different levels, as long as you prepare them for that next step A Word of Caution • A lesson should have at least one objective and can have two to three objectives. • If you find that you are writing more objectives than that, you may be writing about tasks rather than objectives. Your Turn In your groups use one of the lessons we have used in recent weeks and think about how you can write lesson objectives for the lesson. Think about skills, vocabulary, and/or grammar. Write 3 objectives using different levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy.