vocabulary_key
advertisement

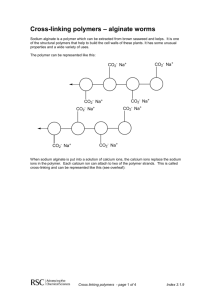
Vocabulary Vocabulary Word Polymer Cross-link (verb) Ionic Bond Gel (noun) Engineer (noun) Definition A long chain molecule made of repeating parts. To connect parallel chains of polymers together. A kind of chemical bond in which two atoms or groups of atoms are electrically attracted to one another. A semi-rigid, jelly-like material in which a liquid is dispersed in a solid. A person who designs, builds, or maintains engines or machines. Key Concepts and Interesting Facts Atoms are the building blocks of matter. Polymers are long, chain-like molecules made up of many (“poly”) repeating units of atoms (“mers”). Polymers are ubiquitous in nature, from rubber in trees to starch in potatoes to spider webs to DNA strands. Protein is a polymer, which is found in skin, organs, muscles, hair and fingernails, feathers and fur. The Golden Orb spider’s silk is stronger than the strongest synthetic polymer Kevlar. One of the materials used in this activity, Alginate, is a polymer that comes from seaweed. It is commonly used as a food thickener in foods from ice cream to Velveeta, and, when cross-linked, is found in pimento strips stuffed into green olives. It is also used for dental impressions, wound dressings, drug encapsulation and in the movie industry to make life masks. Synthetic polymers made by people include plastics, nylon, silicone, polyester, polyurethane, epoxy resins and the clear plastic polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). Kevlar was invented by chemist Stephanie Kwolek and is now used to make airplane parts, suspension bridge cables, sports gear and bullet-proof vests, among others. When polymers are put together they form an array of materials with different properties. Some are tough and hard; some are stretch and bend easily. The properties depend on the length of the polymer chains and how the polymers are mixed together. Polymers that are oriented parallel to one another can slip past one another and move. This is why you can push a skewer through a balloon without popping it and why you can stretch silly putty into a long string. Kevlar is also made this way. Jello is made of natural polymers that are entangled like a plate of spaghetti. The alginate worms of this activity are cross-linked (held together) through ionic bonding. A calcium ion has a plus two charge (two missing electrons), which is attracted to negative charges on the alginate. One calcium ion can cross link two different alginate chains, holding them together and making the worm-like gel. The alginate gel is mostly made of water, and it demonstrates alginate’s ability to absorb liquid 20 times its volume. That is why it has been used for decades as a wound dressing, particularly for wounds that produce a lot of “exudate” (puss etc.). Gel worms do not form in the sodium chloride solution because, unlike calcium, a sodium ion has only a plus one charge, so it can link to one alginate chain, but not to another. In fact, if a worm is put into the sodium chloride solution, it will eventually be “unlinked” and disappear. If an alginate bead colored with food coloring is left in the solution for a while, students should notice that the color has diffused out into the solution. Alginate gels can encapsulate medications or other substances that are slowly released over time, demonstrating their use in drug delivery. If the bead is colored with tempera paint instead of food coloring, there solution remains clear because the paint molecules are too big to diffuse through the pores of the gel. Polymers play a large part in biomedical engineering. Medical devices currently made of polymers include sutures, lens implants, contact lenses, and heart valves. At UNM researchers are making polymers that kill bacteria when exposed to light (for use as countertops and instruments in hospitals, for example); polymers that pop off sheets of cells that act like “biological sticky notes” to be stuck on damaged body tissue; and polymeric scaffolds for re-growing bone inside a patient’s body.