PP 04 Atoms_ molecules_ ions
advertisement

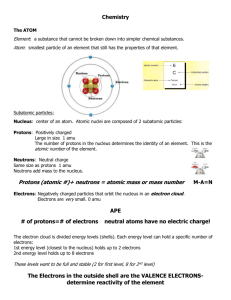
Power Point 4: Atoms, Molecules, & Ions Drill: Calculate the volume in mL of a 2.0 m by 500.0 mm by 4.00 x 105 mm container. (1 cm3 = 1 mL) Atomic Theory: Elements composed of atoms. Atoms can’t be changed. Compounds comtain multiples of atoms. John Dalton The Law of Conservation of Mass: In ordinary chemical reactions, matter can be neither created nor destroyed. The Law of Constant Composition: Compounds always have the same proportions of the elements within them. The Law of Multiple Proportions: The elements making up a compound will form whole number ratios. Atom: The smallest particle that an element can be broken down into and still maintain the properties of the element. • Nuclear Atom: Proved by Rutherford & Bohr in the famous gold foil experiments Atomic Composition: • Proton : in the nucleus (mass~ 1amu) (Charge = +1) • Neutron: in the nucleus (mass~ 1amu) (Charge = 0) • Electron: outside the nucleus (mass~ 1/1836amu) (Charge = -1) • Determined by Robert Milliken in the famous oil droplet experiment Atomic Number: The number of protons in an element (Z number) Mass Number: The number of protons and neutrons in an atom (A number) Nuclear Symbol: Z AX 4 2He Isotopes: Atoms that contain the same number of protons, but different number of neutrons (Z constant, A variable) Periodic Table: Graphic representation of all the elements indicating size, charge, electronic structure, & reactivity (Elements have symbols with 1 upper case letter & maybe a 2nd letter) • Periods: Rows which indicate energy level or shell or size of the atoms • Groups or Families: Columns which indicate the number of electrons in the outermost energy level determining charge & reactivity • Metals: Left three quarters of the chart. Lose electrons. Become positive. • Nonmetals: Upper right portion. Gain, lose, or share electrons when they react • Metalloids: Elements along the stair-stepped line from B to At. They share properties of metals & nonmetals. Compounds: A group of atoms that are chemically combined. Molecule: A covalent compound that can exist by itself. Drill: Convert: 1) 23 cm/ms to km/ns 2) 6 mg/nL to kg/ML Atomic Mass: The weighted average mass of all the isotopes of an element. (an average of relative abundance x mass number for each isotope) Ions: Charges particles. (Cl-1) (OH-1) Polyatomic Ion: A group of atoms chemically combined that together has a charge (SO4-2 ) (NO3-1) Chemical Formulas: Formulas that shows the number and kinds of atoms in a compound (CaCO3) Molecular Formula: A formula that shows the exact number and kinds of atoms in a molecule • C6H12O6 Binary Compound: A compound made up of two elements in any ratio. (NaCl) (Mg3P2) Diatomic Molecules: Molecules made up of wo atoms of the same element that are chemically combined. (Cl2, F2, O2) Atomic Structure Problem: List & describe the three subatomic particles. Atomic Structure Problem: Fill in the chart: • Isotope protons neutrons electrons • U-235 - - - • - 56 80 - • - - 14 13 Determine the number of atoms in each compound: C6H12O6 NaNO3 H3PO4 Al2(SO4)3 Problems: Calculate the atomic mass of the element made up of the following isotopes: (99.50 % H-1) (0.30 % H-2) (0.20 % H-3) Calculate the atomic mass of the element made up of the following isotopes: (5.00 % Pu-242) (5.00 % Pu-243) (80.00 % Pu-244) (10.00 % Pu-245)