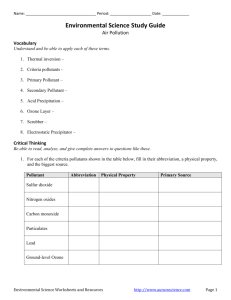
Study Guide: Air Pollution and Climate Change
advertisement
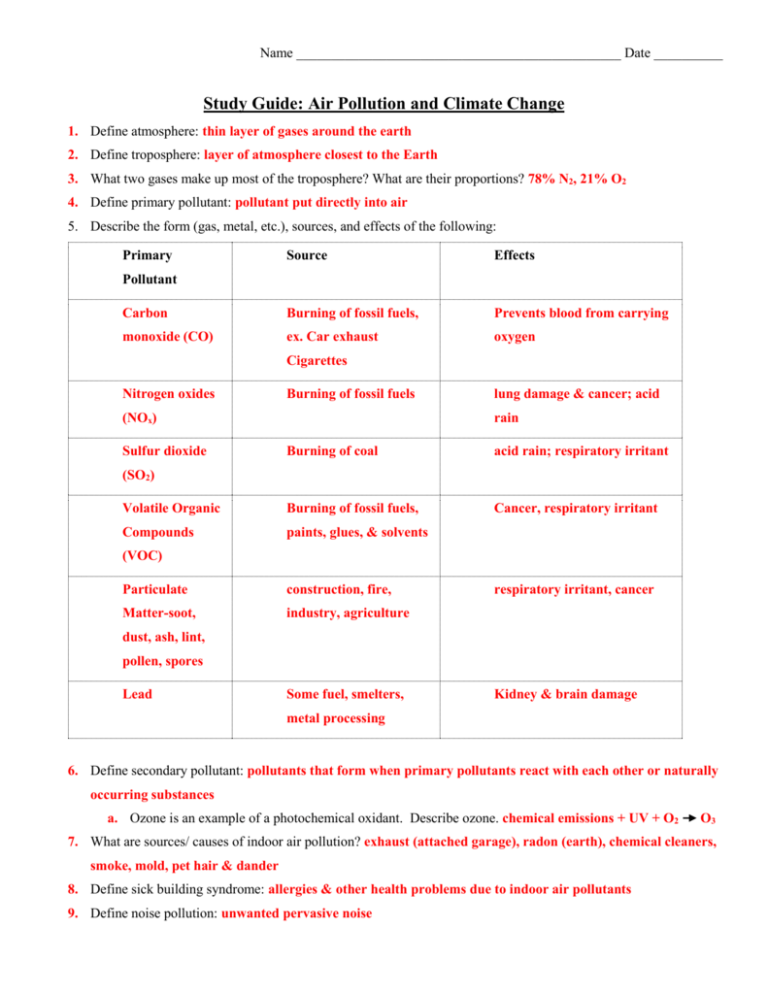
Name _______________________________________________ Date __________ Study Guide: Air Pollution and Climate Change 1. Define atmosphere: thin layer of gases around the earth 2. Define troposphere: layer of atmosphere closest to the Earth 3. What two gases make up most of the troposphere? What are their proportions? 78% N2, 21% O2 4. Define primary pollutant: pollutant put directly into air 5. Describe the form (gas, metal, etc.), sources, and effects of the following: Primary Source Effects Carbon Burning of fossil fuels, Prevents blood from carrying monoxide (CO) ex. Car exhaust oxygen Pollutant Cigarettes Nitrogen oxides Burning of fossil fuels (NOx) Sulfur dioxide lung damage & cancer; acid rain Burning of coal acid rain; respiratory irritant Volatile Organic Burning of fossil fuels, Cancer, respiratory irritant Compounds paints, glues, & solvents (SO2) (VOC) Particulate construction, fire, Matter-soot, industry, agriculture respiratory irritant, cancer dust, ash, lint, pollen, spores Lead Some fuel, smelters, Kidney & brain damage metal processing 6. Define secondary pollutant: pollutants that form when primary pollutants react with each other or naturally occurring substances a. Ozone is an example of a photochemical oxidant. Describe ozone. chemical emissions + UV + O2 O3 7. What are sources/ causes of indoor air pollution? exhaust (attached garage), radon (earth), chemical cleaners, smoke, mold, pet hair & dander 8. Define sick building syndrome: allergies & other health problems due to indoor air pollutants 9. Define noise pollution: unwanted pervasive noise 10. What are the effects of light pollution? inefficient energy use, diminished view of the night sky, disruption of animal migration and/or biological patterns 11. What are some health effects of air pollution? cancer, heart attack, asthma, respiratory irritation, immune suppression 12. How does air pollution affect plants? discoloration, death 13. Define acid precipitation: rain, sleet, or snow w/pH <5 14. What is the pH of normal rain? What acid is present in normal rain that makes it slightly acidic? normal rain tends to be 5-5.6, carbonic acid 15. What pH does acid rain have? pH <5 16. What environmental affects does acid rain cause? reduce crop yields, dissolves monuments (marble & limestone) 17. Define acidic shock? rapid influx of acid precipitation into body of water due to snow melting in spring causing a sudden drastic change in the pH 18. What is found in building materials that reacts with acid rain? calcium carbonate 19. Define Clean Air Act (1970): gave EPA authority to regulate car emissions & industry pollutants, eliminated lead in gas, required catalytic converters 20. Define/ describe catalytic converter: device used to clean exhaust gases before they exit tailpipe 21. Define scrubber: machine that moves gas through spray of water that dissolves pollutants 22. Define climate: prevailing weather patterns for an area including temperature & rainfall 23. Define ozone layer: protective shield in stratosphere made of O3 24. Why is the ozone layer important? it absorbs biologically harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation coming from the sun 25. What causes the ozone layer to start thinning? Why is this bad? CFC’s & other ODS’s react with ozone & destroy it, allows harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation to enter lower atmosphere 26. What meeting occurred where nations agreed to limit the use of CFCs? Montreal Protocol 27. Define greenhouse effect: occurs when greenhouse gases trap in heat (infrared radiation) from the sun 28. Define greenhouse gas & give examples: Gas that traps in infrared radiation, CO2, H20, CH4, CFC’s 29. Define global climate change: change in the world’s climate 30. What gas is mainly being blamed for causing global climate change? What causes excess amounts of this gas to be put in the atmosphere? CO2, burning of fossil fuels 31. Explain why atmosphere carbon dioxide goes up & down each year: In spring/summer, n. hemisphere is facing sun, plants are doing lots of photosynthesis = low atmospheric CO2 In fall/winter, n. hemisphere is facing away from sun, plants not doing photosynthesis, = high atmospheric CO2 32. What are some consequences of global climate change: stronger storms, warmer temperatures, drought & wildfires, rising sea level 33. Define Kyoto Protocol: The Kyoto Protocol) is an international treaty that sets binding obligations on industrialized countries to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases. 34. What are some actions you can take to reduce your contribution to air pollution & climate change: drive an energy efficient car, car pool, use public transportation, turn lights off, demand cleaner energy, fix leaky faucets, be water wise, reduce your waste- use reusable bags, spread the word http://www.epa.gov/climatestudents/solutions/actions/more.html