Chapter 8, Lesson 2: Notes
advertisement

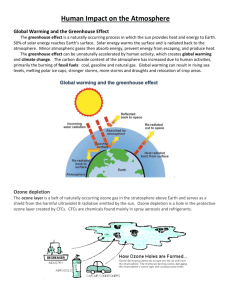
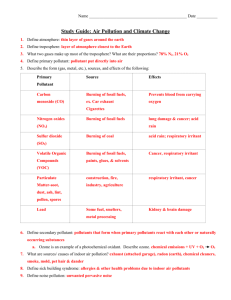
Chapter 8, Lesson 2: Air Pollution and Solutions EQ: What causes outdoor air pollution? A. Outdoor Air Pollution 1. Air is a mixture of gases that cycle between living things and the atmosphere. 2. Emissions are pollutants released into the air. 3. Today, a large source of emissions resulting in air pollution outdoors comes from motor vehicles such as cars and trucks. 4. In addition, factories, power plants, and natural sources cause air pollution. EQ: What causes outdoor and indoor air pollution? A. Photochemical smog is a thick, brownish haze formed when certain gases in the air react with sunlight. 1. It can cause breathing problems and eye and throat irritation. 2. The major sources of smog are the gases emitted by cars and trucks, which react in the sunlight and produce ozone, a toxic form of oxygen. Your Turn: Draw a picture of polluted air over a city. Make sure to label your drawing to include: polluted air, cool air, warm air. B. Weather conditions can cause a temperature inversion, in which a layer of warm air prevents rising air from escaping. 1. Polluted air is then held close to Earth’s surface. 2. Precipitation that is more acidic than normal because of air pollution is called acid rain. 3. Acid rain damages plants, waterways, and metals and stones. Your Turn: Draw a picture to show the damage acid rain can cause. C. Even indoor air can be polluted. 1. Some substances that cause indoor air pollution, such as dust and pet hair, bother only those people who are sensitive to them. 2. Other indoor air pollutants, such as toxic chemicals, can affect anyone. 3. Radon is a colorless, odorless gas that is radioactive. Your Turn: Draw a picture to show indoor air pollution. Label your drawing. EQ: What causes damage to the ozone layer? A. The ozone layer is a layer of the upper atmosphere about 30 kilometers above Earth’s surface. 1. It protects people from the effects of too much ultraviolet radiation. 2. Ozone is constantly being made and destroyed as part of the ozone cycle. 3. The amount of ozone in the ozone layer is decreasing, creating an ozone hole. 4. Scientists determined that the major cause of the ozone hole is a group of gases called CFCs. 5. CFCs were used in many household products. 6. Most uses of CFCs were banned in 2000. Ozone Layer CFCs