Midterm Project WS: Polarity and IMF
advertisement

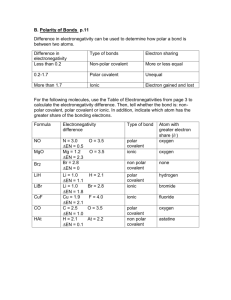
Polarity and Intermolecular Forces Electronegativity-ability of an atom to attract electrons *Electronegativity of Common Elements increases up a group and across a period* Electronegativity Difference Bond Type 0 to 0.3 Nonpolar Covalent 0.4 to 1.6 Polar Covalent ≥ 1.7 Ionic Nonpolar Covalent Bond- covalent bond with electrons shared equally between the two atoms Polar Covalent Bond- Covalent bond with greater electron density around one of the two atoms Ionic Bond-Bond with a positive ion and a negative ion Intermolecular Forces- attractive forces between molecules Dipole-Dipole Forces- attractive forces between polar molecules Hydrogen Bond- a special dipole-dipole interaction between hydrogen atoms in a polar N-H, O-H, or FH bond, and an electronegative N,O, or F atom Ion-Dipole Forces- attractive forces between an ion and a molecule polar Dispersion Forces- attractive forces that arise as a result of temporary dipoles induced in atoms or molecules (Ion-induced dipole interaction, Dipole-induced dipole interaction) Van Der Waals/ London Dispersion Forces- attractive forces between two nonpolar molecules (very weak) Polarizability- ease with which the electron distribution in the atom or molecule can be distributed Strongest Intermolecular Forces to Weakest Hydrogen Bond (H- N/O/F) Dipole-Dipole (D-D) (2 polar) Dipole-Induced Dipole (D-ID) London Dispersion Forces (LDF) *Note: Properties such as boiling point, viscosity, etc. increase with increasing strength of the bond.* Practice Problems Show all work! 1. Given the electronegativity of Li is 1.0 and F is 4, what type of bond Lithium fluoride have? What is the strongest intermolecular force on this compound? 2. Given the electronegativity of K is 0.8 and Cl is 3.0, what type of bond will potassium chloride have? What is the strongest intermolecular force on this compound? 3. Given the electronegativity of C is 2.5 and N is 3.0, what type of bond will cyanide have? What is the strongest intermolecular force on this compound? 4. Which of the following are capable of hydrogen bonding?(Circle One) HI BeH2 PF3 C3H8O3 5. Arrange the following in order of increasing boiling point: NaF, CO2, CH3OH, CH3Br 6.Which of the following molecules is(are) polar? Cl2, CH4, CH2O, CH3Cl Answer Key 1. Given the electronegativity of Li is 1.0 and F is 4, what type of bond Lithium fluoride have? What is the strongest intermolecular force on this compound? Ionic bond, Dipole-Dipole 2. Given the electronegativity of K is 0.8 and Cl is 3.0, what type of bond will potassium chloride have? What is the strongest intermolecular force on this compound? Ionic Bond, Dipole-Dipole 3. Given the electronegativity of C is 2.5 and N is 3.0, what type of bond will cyanide have? What is the strongest intermolecular force on this compound? Polar Covalent, Dipole-Dipole 4. Which of the following are capable of hydrogen bonding?(Circle One) HI BeH2 PF3 C3H8O3 5. Arrange the following in order of increasing boiling point: NaF, CO2, CH3OH, CH3Br CO2 < CH3Br < CH3OH< NaF 6. Which of the following molecules is(are) polar? CH3Cl, CH2O Cl2, CH4, CH2O, CH3Cl