assignment 2
advertisement

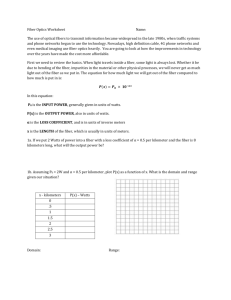
Optical Instrumentation [Year] ASSIGNMENT 2 A. SIGNAL DEGRADATION 1. The mean optical power launched into an optical fiber link is 1.5 mW and the fiber has an attenuation of 0.5 dB/km. Determine the maximum possible link length without repeaters (assuming lossless connectors) when the minimum mean optical power level required at the detector is 2 µW? 2. The numerical input/output mean optical power ratio in a 1 km length of optical fiber is found to be 2.5. Calculate the received mean optical power when a mean optical power of 1 mW is launched into a 5 km length of the fiber (assuming no joints or connectors)? 3. A 15 km optical fiber link uses fiber with a loss of 1.5 dB km. The fiber is jointed every kilometer with connectors which give an attenuation of 0.8 dB each. Determine the minimum mean optical power which must be launched into the fiber in order to maintain a mean optical power level of 0.3 µW at the detector? 4. A multimode, optimum, near-parabolic profile graded index fiber has a material dispersion parameter of 30 ps nm−1 km−1 when used with a good LED source of rms spectral width 25 nm. The fiber has a numerical aperture of 0.4 and a core axis refractive index of 1.48. Estimate the total rms pulse broadening per kilometer within the fiber assuming waveguide dispersion to be negligible. B. OPTICAL FIBER MANUFACTURING 1. Compare and contrast, using suitable diagrams, the outside vapor-phase oxidation (OVPO) process and the modified chemical vapor deposition (MCVD) technique for the preparation of low-loss optical fibers. 2. Briefly describe the salient features of vapor axial deposition (VAD) and the plasma-activated chemical vapor deposition (PCVD) when applied to the preparation of optical fibers. 3. Outline the phenomena that can affect the stability of the transmission characteristics in optical fiber cables and describe any techniques by which these problems may be avoided. C. OPTICAL SOURCES 1. An injection laser has a GaAs active region with a bandgap energy of 1.43 eV. Estimate the wavelength of optical emission from the device and determine its linewidth in hertz when the measured spectral width is 0.1 nm. 2. Briefly describe what is meant by the following terms when they are used in relation to injection lasers: (a) relaxation oscillations; (b) frequency chirp; (c) partition noise; (d) mode hopping. 3. Estimate the external power efficiency of a GaAs planar LED when the transmission factor of the GaAs–air Interface is 0.68 and the internally generated optical power is 30% of the electric power supplied. The refractive index of GaAs may be taken as 3.6.