Honors Science Grade - Huntsville City Schools
advertisement

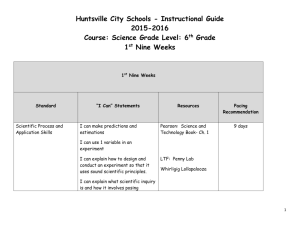
Huntsville City Schools - Instructional Guide 2015-2016 Course: Honors Science Grade: Sixth Grade 1st Nine Weeks 1st Nine Weeks Standard Scientific Process and Application Skills “I Can” Statements Resources I can make predictions and estimations Pearson: Science and Technology Book- Ch. 1 I can use one variable in an experiment LTF: Penny Lab and Whirligig Lollapalooza Pacing Recommendation 9 days I can create a working definition for the terms “independent” and “dependent” variables. I can explain how to design and conduct an experiment so that it uses sound scientific principles. I can explain what scientific inquiry is and how it involves posing 1 Al COS 1 Identify global patterns of atmospheric movement, including El Nino, the Gulf Stream, the jet stream, Coriolis effect, and global winds that influence local weather. predicting local weather and weather patterns Interpreting weather data through observations over time. Using lines of latitude and longitude to locate areas of specific weather events. Describing the function of instruments and technology used to investigate Earth’s weather, including barometers, thermometers, wind socks, weather vanes, satellites, radar, weather balloons, and rain gauges questions and developing hypothesis. I can independently and collaboratively record ideas and questions about earth’s weather and climate. I can create a working definition of the term “vortex”. I can compare and contrast storms, tornadoes, and hurricanes. I can use the Fujita Scale to determine the strength of a tornado. I can use the Saffir/Simpson Scale to determine the strength of a hurricane. Pearson: Chapter 12 2 days AMSTI Weather and Climate Lesson 1 Pearson: Chapter 12 5 days AMSTI Weather and Climate: Lesson 2, Lesson 7 *Honors Science will be working on an independent research project such as a science fair and/or a hurricane project. I can create a foldable to organize data from an AMSTI Weather and Climate Reading selection (page 3035). I can use lines of latitude and longitude to locate formation of hurricanes. 2 I can graph and analyze the heating and cooling rates of soil and water. I can describe the atmosphere and it’s layers. I can Compare land and water temperature at different times during a 24 hour period. Pearson: Chapter 12 6 days AMSTI Weather and Climate Lesson 3 I can investigate the effect of surface temperate on the temperature of air above the surface and its resulting movement. I can identify the major air masses that affect the weather in North America and describe how they move. I can name and explain the main types of fronts. I can identify the tools used to predict and forecast the weather. Pearson: Chapter 12 8 days AMSTI Weather and Climate Lesson 4 I can determine which weather instrument is used to calculate precipitation, temperature, and air pressure. 3 I can set up and investigation that demonstrates what happens to two air masses when they meet. I can develop a working definition for the term “convection current”. I can relate the movement of air within the convection model to the formation of land and sea breezes and tornadoes. I can explain how wind forms. I can describe the rotation of the Earth which causes surface currents and global winds to curve as the move across Earth’s surface. Pearson: Chapter 12 AMSTI Weather and Climate Lesson 5 LTF: Blowing in the Wind AMSTI weather and Climate Lesson 9 is a reinforcement of a convection model within the ocean instead of the atmosphere. 7 days Honors should begin making and using homemade barometers for the project listed in the next section Honors Science will be developing more 4 AL COS 3 Describe water cycle and its effect on earth I can explain the water cycle. I can model and describe how water evaporates and condenses and how these processes play a part in cloud formation. I can model and describe the air pressure under which clouds form. Benchmark Review and Assessment independent skills during labs. AMSTI Weather and Climate: Lesson 6 2 days LTF: Evaporation and Condensation Honors will make a homemade barometer, chart the data, and create a graph for 7 days. 2 days for Review 1 day for Assessment 5 Huntsville City Schools - Instructional Guide 2015-2016 Course: Honors Science Grade: Sixth Grade 2nd Nine Weeks 2nd Nine Weeks Standard AL COS 2 Describe factors that cause changes to Earth’s surface over time. Comparing constructive and destructive natural processes and their effects of land formation. Ex. Weather, Erosion, mining and reclamation “I Can” Statements I can use origin, texture, and mineral composition to identify the three types of rocks. I can describe the sequence of sedimentary rock formation. I can describe the 2 factors that cause change in metamorphic rock. Resources Pearson: Ch. 2, 6.1, and 7 Pacing Recommendation 5 days AMSTI Plate Tectonics: Lesson 13 LTF: Mineral Masters LTF: Rock-N- Roll LTF: We will Rock You I can illustrate the rock cycle. I can determine the factors that cause weathering. 6 AL COS 2 Describe factors that cause changes to Earth’s surface over time. AL COS 4 Explain the plate tectonic theory. Ex. Continental drift and seafloor spreading I can explain the process that wear down and build up Earth’s surfaces. I can illustrate the layers of the earth. I can determine the varying sizes, composition, temperature, and pressure of the layers of the Earth. I can explain the theory of plate tectonics and continental drift. I can illustrate the 3 types of plate boundaries. I can use a model to simulate the movement of lithospheric plate as they collide, separate, and slide past each other. Pearson: Chapter 1.2 2 days AMSTI Plate Tectonics: Lesson 8 Pearson: Chapter 3.3 3 days AMSTI Plate Tectonics: Lesson 5, Lesson 6 LTF: Dynamic Earth I can explain convection currents within the Earth’s mantle. I can identify the movement in the earth’s mantle as one cause of plate movement, earthquakes, and volcanoes. 7 AL COS 2 Describe factors that cause changes to Earth’s surface over time. Ex. Earthquakes COS 4 Explain the plate tectonic theory Determining energy release through seismographic data using data from the Mercalli scale and the Richter scale. Ex. Epicenter, focus, seismic wave, and subduction zone I can recognize that an understanding of the motion of seismic waves can help scientists formulate hypothesis about the earth’s interior. I can brainstorm about possible cause and effects of earthquakes and techniques for monitoring and predicting them. Pearson: Chapter 4 14 days AMSTI Plate Tectonics: Lesson 2, Lesson 3, Lesson 4, Lesson 7 I can use a spring to simulate pwaves, s-waves, and surface waves. LTF: Mapping an Epicenter I can design and build a model house that is resistant to shaking. I can locate the epicenter of an earthquake using data from S-P time method chart. I can plot on a world map the locations and magnitudes of some of the earthquakes that occurred during the 1990’s. I can use the Richter Scale to determine the magnitude of an earthquake. 8 AL COS 2 Describe factors that cause changes to Earth’s surface over time. Ex. Volcanoes AL COS 4 Explain the plate tectonic theory Ex. Lava, magma, eruption I can use the Mercalli scale to determine the intensity of an earthquake. I can classify the effects of volcanic eruptions as either destructive or constructive. I can devise a working definition for the words “magma” and “lava”. I can identify the cause and effect of volcanic eruptions. I can relate the viscosity of lava to the type of volcano formed. Pearson: Chapter 5 13 days AMSTI Plate Tectonics: Lesson 9, Lesson 11, Lesson 12, Lesson 14 Honors Science will complete AMSTI Plate Tectonics Exploration Activity Lesson 10. I can compare and contrast the 3 types of volcanoes. I can draw and label the inside of a volcano. I can develop a working definition for the word “pyroclastic material”. I can analyze the properties of volcanic ash sample and predict its potential effects on people, property and the environment. 9 Benchmark Review and Assessment 2 days for Review 1 day for Assessment 10 Huntsville City Schools - Instructional Guide 2015-2016 Course: Honors Science Grade: Sixth Grade 3rd Nine Weeks 3rd Nine Weeks Standard AL COS 8 Earth’s rotation, Earth’s axial tilt, and distance from the equator cause variations in the heating and cooling of various locations on Earth. Mapping seasonal changes in locations of constellations in the night sky “I Can” Statements Resources I can describe the apparent motions of the stars and planets throughout the year. Pearson:14.1 , 14.2, 14.6 I can identify objects and constellations visible without a telescope. Moon: Lessons 1-2, I can demonstrate how earth moves in space. I can record the length and angle of shadows cast by a shadow stick at different times during the day. Pacing Recommendation 12 days AMSTI Sun-EarthLesson 3 page 48-51 Honors Science will create a constellation / moon myth. I can model winter and summer shadows and compare the sun’s apparent position in the sky during each season. 11 AL COS 8 Earth’s rotation, Earth’s axial tilt, and distance from the equator cause variations in the heating and cooling of various locations on Earth. AL COS 9 Identify the moon’s phases. AL COS 9 Identify the Moon’s phases I can Explain what causes the cycle of seasons on earth. I can compare sunrise and sunset times at different latitudes at different times throughout the year. Pearson: 14.4 7 days AMSTI Sun- EarthMoon: Lesson 3 LTF: Reasons for the Seasons I can create a working definition for the terms “revolution” and “rotate”. I can explain what causes the phases of the moon. Pearson: Chapter 14.4 and 14.6 I can demonstrate the sun’s light as Earth revolves around the sun. AMSTI Sun- EarthMoon: Lesson 4 I can track, model, and illustrate the phases of the moon as seen from Earth. LTF: Moon Watch Honors Science will complete AMSTI SunI can analyze the moon to Earth- Moon Exploration determine if it is waxing or waning. Activity Lesson 5. (Individual research I can make predictions about the project). moon’s appearance on the basis of observed patterns. I can describe what causes a solar Pearson: 14.4 and lunar eclipse. 7 days 10 days 12 Describing lunar and solar eclipse. Relating effects of the moon’s positions on oceanic tides. I can analyze the conditions under which the lunar and solar eclipses occur. AMSTI Sun- EarthMoon: Lesson 6, Lesson 7 I can describe the phases during which lunar and solar eclipses occur. I can analyze solar and lunar eclipse data and compare it to phase data. I can develop working definitions for the terms “umbra” and “penumbra”. I can model the shadows cast by the moon and earth. I can graph and analyze patterns and the times in heights of tides, moonrise and moonsets times, and phases of the moon along Virginia Beach. I can explain the tidal process between the Earth and the moon. AL COS 10 I can investigate the effects of Describe components of the distance on the amount of energy universe and their received from a light source. Pearson: 16.1 6 days 13 relationship to each other including stars, planets and their moons, solar systems, and galaxies. Identify the impact of space exploration on innovations in technology. Ex. An MRI, microwave, satellite imagery, and GPS. I can use a radiometer to observe the effects of solar energy. AMSTI Sun- EarthMoon: Lesson 8, Lesson 9 I can describe the features that form on or above the sun’s surface. I can state the regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. I can explain how satellites use the electromagnetic spectrum to produce imagery. Benchmark Review and Assessment 2 days for Review 1 day for Assessment 14 Huntsville City Schools - Instructional Guide 2015-2016 Course: Honors Science Grade: Sixth Grade 4th Nine Weeks 4th Nine Weeks Standard AL COS 10 Describe components of the universe and their relationships to each other, including stars, planets and their moons, solar systems, and galaxies. Describing the life cycle of stars. Ex- H-R diagram AL COS 10 Describe components of the universe and their relationships to each other, including stars, planets and their moons, solar systems, and galaxies “I Can” Statements I can explain how stars are classified. I can explain the H-R diagram and how astronomers use it. I can summarize the life cycle of stars. I can describe what happens when a star runs out of fuel. Resources Pearson: 16.3 and 16.4 Pacing Recommendation 3 days Honors Science will be developing more independent skills during labs. Pearson: 16.3 and 16.4 5 days LTF: Beyond the Black Hole 15 AL COS 10 Describe components of the universe and their relationships to each other, including stars, planets and their moons, solar systems, and galaxies. AL COS 11 Describe units used to measure distance in space, including astronomical units and light years. I can define a star system. Pearson: 16.5 2 days Pearson: 15.1 and 15.2 5 days I can identify major types of galaxies. I can describe the order and sizes and the planets and their distances from each other. I can create a model of the solar system from a set of scaled items. I can use scale models to explore the relative diameters of and distances between the nine planets and the sun. AL COS 10 I can analyze patterns in planetary Describe components of the motion. universe and their relationships to each other, I can observe the motion of a including stars, planets and marble when acted upon by a their moons, solar systems, curved trajectory demonstrating and galaxies. gravitational pull from the sun. I can identify the main characteristics that distinguish each of the inner and outer planets. AMSTI Planetary Systems: Lesson 2 LTF: Not so Lost in Space Pearson: 14.3, 15.4, 15.5 5 days AMSTI Planetary Systems: Lesson 3, Lesson 7 Honors science will complete an independent planet research project for example a planet Prezi. 16 AL COS 2 Describe factors that cause changes to Earth’s surface over time. Distinguishing rock strata by geologic composition. Ex. Predicting relative age of strata by fossil depth. AL COS 3 Describe water and carbon biogeochemical cycles and their effects on Earth. AL COS 5 Describe layers of the oceanic hydrosphere, including the pelagic zone, benthic, abyssal, and intertidal zones. I can explain how fossils form. I can identify the different kinds of fossils. AL COS 6 Describe regions of the oceanic lithosphere, including the continental shelf, continental slope, and the abyssal plain. Benchmark Review and Assessment I can identify the ecological zone of the benthic and pelagic environments. I can explain what happens during radioactive decay. I can illustrate the carbon cycle. Pearson: 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4 5 days AMSTI Planetary Systems: Lesson 5, Lesson 8, Lesson 9 LTF: Relative Dating Sands of Time Pearson: 13.4 I can describe the features of the Pearson: Chapter 10 ocean floor. LTF: Sonar Seas Staying I can classify the subdivisions of out of Hot Water the two major regions of the ocean floor. 1 day 4 days 2 days for Review 17 AL COS 7 Describe Earth’s biome Identify geographic factors that cause diversity in flora and fauna including elevation, location, and climate. I can locate and describe the Pearson: Chapter 13 tropic, temperate, and polar zones. Honors science will I can describe the different complete an independent biomes found within the 3 zones. group biome project. 1 day for Assessment 7 days 18