expiry doctors
advertisement

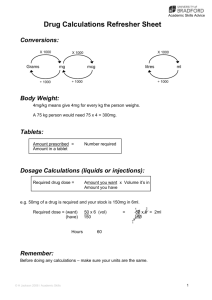
Intravenous Fluid Guideline Prescriber (Clinical officers or doctors) • Weight to calculate fluid requirement should be the most recent from the current admission • Refer to KPA handbook regarding type of fluid to prescribe • Pre-existing electrolytes should be considered prior to prescribing IV fluids • All patient demographic boxes to be filled • All boxes of prescription section MUST be filled before administration • For maintenance fluid in children, calculate correct daily maintenance volume and divide by 24 to get rate in ml/hr or refer to KPA handbook • For other fluid bolus or regimes in children, refer to KPA handbook or seek senior medical advice. • Children and neonates remaining on IV fluids for > 24 hours must have UEs checked (risk of electrolyte derangement esp. hyponatraemia) Administers (Trained nurses/COs/doctors) • Administers must be trained nurses/COs/doctors • Check fluid type to administer matches fluid prescribed • Check expiry date and batch number • A second trained staff nurse/CO/doctor must double check fluid type and correct drip rate • Ensure drip rate is calculated in relation to the giving set being used (i.e. 60 drops per ml paediatric giving set and 20 drops per ml using an adult giving set) • Drip rate to be checked over one minute • Both staff must complete all sections of administration chart IMMEDIATELY after setting up the infusion (except total volume given/pharmacy notes) • Nursing staff to review the drip rate each hour • Parents/patients should be advised to inform staff if drip rate runs faster than initially set • At end of administration, complete Total Volume Given box Dr Duke Razon March 2015 For review March 2016 • If IV fluids are required beyond 24 hours, a new fluid prescription must be made and administered Calculating Daily Maintenance Fluid Volume in Children • 100ml/kg for first 10 Kg • 50ml/kg for next 10kg (i.e. between 10-20kg) • 20ml/kg for remaining kg • This formula matches roughly the maintenance volumes in KPA handbook Drip Rate Formula • Drops per minute: Volume to be infused ml x drop factor (Time in minutes) • Adult giving set –20 drops = 1ml (drop factor is 20) • Paediatric giving set – 60 drops = 1ml (drop factor is 60) Example 1 - 27kg Child For example in a 27kg child the maintenance volume is: • 100ml x 10kg = 1000ml • 50ml x 10kg = 500ml • 20ml x 7kg = 140ml • Total maintenance volume is 1,640 • Hourly Rate is 1640ml/24 hours = 68 ml/hr • Drip rate in this child using a paediatric giving set is: 68ml x 60 60 minutes • Drip rate = 68 drops per minute Dr Duke Razon March 2015 For review March 2016 Example 2 – 11kg child • In a 11kg child, where you only have an adult giving set. • 100ml x 10kg = 1000ml • 50ml x 1kg = 50ml • Daily Maintenance volume is 1050ml • Hourly Rate is 1050ml/24 hours = 44ml per hour • Drip rate is: (44ml x 20) 60 minutes • Drip rate is 15 drops per minute Try these examples • Calculate maintence volume and drip rate • Using a paediatric giving set for: • – 8kg infant – 13kg child – 23kg child Calculate using an adult giving set for the above children ANSWERS • 8kg – maintenance volume = 800ml • Hourly rate is 33ml/hr • Drip rate – 33 drops/min (paediatric giving set) – 11 drop/min (adult giving set) • 12kg – maintenance volume = 1100ml • Hourly rate is 46ml/hr • Drip rate Dr Duke Razon March 2015 For review March 2016 – 46 drops/min (paediatric giving set) – 15 drops/min (adult giving set) • 23 kg - Maintenance volume is 1560ml • Hourly rate is 65ml/hr • Drip rate – 65 drops/min (paediatric giving set) – 22 drops/min (adult giving set) Dr Duke Razon March 2015 For review March 2016