Intern Basics- Part II
advertisement

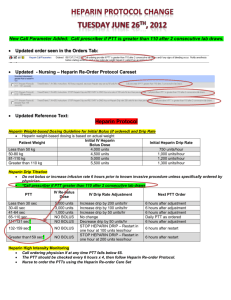
Intern Basics- Part II Jacobi medical Center Falls Assess the patient after the fall Witnessed or not Ask the patient about the fall and any injury Examine the patient with special attention to the area of injury; examine the head to rule out any injury to the head Imaging studies to rule out any fractures If any change in the mental status from the baseline is noted, get a head CT Complete the incident report Restrains as needed Altered Mental Status Confusion, delirium, drowsiness, stupor Look for the possible (and obvious) causes: -medications (opiates, benzodiazepines, other sedatives) -metabolic (hypoglycemia, hyponatremia, hypernatremia, uremia, hypercapnia, hypoxia) -trauma to the head -Stroke -Seizures -Infections -Others: hyperthyroidism, liver failure, Hypertensive encephalopathy AMS (contd.) Work up: -Any acute change in mental status (stupor), call an RRT (rapid response team), stabilize the patient first. Always check ABC. Make sure the patient has a working IV line -Check finger stick glucose to r/o hypoglycemia -If patient seems unable to protect his airway, then he probably needs intubation (call RRT if not already called; ask the nurse to call anesthesia and respiratory therapist) -labs: CBC, serum electrolytes, BUN/Cr, ABG -If any suspicion of infection, check UA and CXR -Head CT AMS (contd.) Management: -Delirium: Haldol 2-5mg IM can be given -Underlying cause should be treated. If patient has been intubated, then will need to be transferred to the ICU/CCU. Contact SMR for the transfer. Insomnia Antihistamines (benadryl): may cause daytime sleepiness the next day, avoid in patients with angina, cardiac arrythmias, BPH, COPD Benzodiazepine (restoril, ativan): daytime sleepiness, cause respiratory depression, avoid in COPD or any underlying lung problems Newer hypnotics (ambien): fewer side effects, better tolerated; consider trazodone Constipation Causes: functional (most common in the hospitals), obstruction, medications (most commonly opioids), neurogenic Abdominal x-ray if needed Treatment: colace, senna, dulcolax (bisacodyl), lactulose, enema (tap water, fleets), disimpaction of stool Diarrhea Acute onset: rule out infection Check fecal leucocytes, occult blood in stool, stool culture, C. diff toxin Check CBC for leucocytosis If any reason to suspect C. Diff infection and patient appears acutely sick, should start metronidazole empirically Heparin drip adjustments Initial dose PTT <35 PTT 35-45 PTT 46-70 PTT 70-90 PTT>90 80 U/Kg bolus, then 18U/Kg/hr 80 U/kg bolus, increase drip by 4 U/kg/hr 40 U/kg bolus, increase drip by 2 U/kg/hr No change in rate Decrease drip by 2 U/kg/hr Hold infusion for 1hr, decrease the rate of drip by 3 U/kg/hr Death notification Confirm death: pupils, heart, breathing Note the official time of death (when you pronounce the patient) Notify the family Call organ donation (If they reject the case, they will give a case number; also get the name of the person you speak to) Write a death note in the EMR and complete the discharge summary When the death certificate is ready, the admitting will call you to get your signature/ finger print (please do that promptly and do not sign that out) Sample death note Called to the bedside by the nurse. Patient found unresponsive, pupils unreactive, no spontaneous breathing, no heart sounds. Pt pronounced dead at 1100am on 07/24/2010. Pt’s son (name) notified. Called organ donation and spoke with Ms. X. The case was rejected and the case number is XXXXX. Questions??