Standard Operating Procedures
advertisement

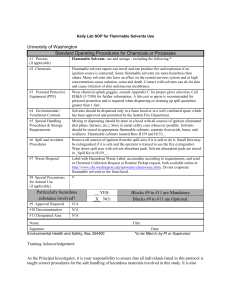
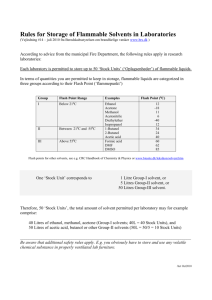
These safety training resources, prepared solely for the use of the Regents of the University of California, were provided by a variety of sources. It is your responsibility to customize the information to match your specific operations. Neither the University of California nor any of its employees, makes any warranty, express or implied, or assumes any legal liability or responsibility for the accuracy, completeness, or usefulness of any information, or represents that its use would not infringe privately owned rights. Reference herein to any specific commercial product, process, or service by trade name, trademark, manufacturer, or otherwise, does not necessarily constitute or imply its endorsement, recommendation, or favoring by the University of California. The views and opinions of authors expressed herein do not necessarily state or reflect those of the University of California, and shall not be used for advertising or product endorsement purposes. Standard Operating Procedure __________________________________________________ Print out the completed SOP and keep a readily accessible hard copy in the lab (also keeping an electronic copy is highly recommended). __________________________________________________ Date: SOP Title: Solvent Still usage Principal Investigator: Room and Building: Lab Phone Number: Section 1 – Process Solvent distillation/ purification Quenching of drying agents. Section 2 – Hazardous Chemicals Tetrahydrofuran, methylene chloride, acetonitrile, triethylamine, pyridine, organic solvents, calcium hydride. Section 3 – Potential Hazards Tetrahydrofuran is flammable, irritant, and can form peroxides. Methylene chloride is notflammable but is harmful, and probable human carcinogen. Pyridine is flammable and harmful. Acetonitrile is flammable and harmful. Triethylamine is flammable and corrosive. Calcium hydride is flammable and reacts with moist air (pyrophoric). Review MSDS if not familiar with hazards of these chemicals. Section 4 – Approvals Required New students as well as researchers who are not members of the lab are required to undergo training on how to operate the stills safely. Section 5 – Designated Area There is a fume hood dedicated to the solvent stills. Section 6 – Special Handling Procedures and Storage Requirements Running cold water and nitrogen flow are requirements. Temperature controls should not be turned beyond the indicated markings that are solvent specific. Never use alkali metals to dry chlorinated solvents. Make sure not to distill any flasks to dryness because peroxide can become concentrated and be explosive. Section 7 – Personal Protective Equipment Gloves, fire resistant lab coat, and safety glasses should be worn when using the solvent stills. Section 8 – Engineering/Ventilation Controls The solvent stills should always been kept within the fume hood and the sash drawn down when not in use. Section 9 – Spill and Accident Procedures If there is a spill into sanitary sewer, call the number posted on top of all the sink drains. For minor spills, spill kits can be. For exposure to solvents, use eye wash and safety shower are by the north door. Fire extinguisher can be found in the hallway. If injured by shattered glassware, contact the Tang center – telephone numbers are on the refrigerator in the group room. For large scale spills, evacuate the room and call EHS. Section 10 – Waste Disposal For chemical solvent disposal, follow general EHS disposal guidelines. Quenching of the stills must always take place in a fume hood. Remove any potentially flammable materials from the vicinity. First, cool the still pot to room temperature. Cool it further in an ice water bath. Begin the quenching procedure by slowly adding isopropanol to the still pot. Ensure proper ventilation since gas will slowly evolve. Let it sit for about 12 hrs., or until gas has stopped evolving. Progress ethanol, then methanol, and finally water. After each step, allow 12 hrs. between each step or until no more gas has stopped evolving. Dispose of the liquid in the hazardous waste disposal. Section 11 - Decontamination Use spill kit where necessary, and use safety shower. Section 12 – Process Steps This section is useful for particularly complex or multi-step processes. List each step of the process or procedure chronologically on the left side of the SOP Template page. On the right side of the page and directly across from the corresponding process steps, list precautionary safety measures to be taken, including the use of specific laboratory techniques and PPE. If possible, describe indicators (visual or otherwise) which show whether the reaction, equipment, etc. is working safely as intended or that a hazardous situation may be developing. Process Steps Turn on water. Turn on temperature control to the designated setting. Start collecting solvent in the upper bulb. Use needle to extract solvent. Turn off temperature control when done. Wait for solvent to cool down. Make sure to turn off water. Safety Measures Make sure water flow is just enough, without causing the water level to spill over. If still is dry, do not turn on the temperature. Make sure never to turn the temperature setting above the designated marking. Make sure valve isn’t leaking and solvent does not condense past condenser. Be careful with sharp needle. Keep needle capped when not in use. Use proper syringe technique to avoid overdrawing solvents. Training Documentation Name (Printed) Signature Date