UT Standards Academy Lesson Plan Template: Geological Columns
advertisement

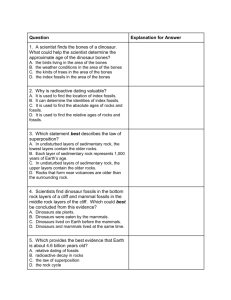
UT Standards Academy Lesson Plan Template: TITLE – With Grade Level and Topic Geological Columns of Fossils, Faulting, Folding, and Layers 8th Grade Science GENERAL: Summary – 3- 4 sentences Students are able to tie together many geological features and identification in this lesson. They will recognize and highlight the importance of index fossils in geological columns and how index fossils can help with relative dating of rock layers, even after folding and faulting. Working collaboratively as a class and groups, they will create two different geological time columns. Science Curriculum Standard Tie – Disciplinary Core Idea (K-12 Framework) UT SCIENCE CORE CURRICULUM Standard III Objective 3 b. Identify the assumptions scientists make to determine relative ages of relative ages of rock layers c. Explain why some sedimentary rock layers may not always appear with youngest rock on top and older rocks below (e.g., folding, faulting) d. Research how fossils show evidence of the changing surface of the Earth e. Propose why more recently deposited rock layers are more likely to contain fossils resembling existing species than older rock layers. NGSS MS-ESS 1-4 Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence from rock strata for how the geologic time scale is used to organize Earth’s 4.6 –billion-year-old history ILO – Science and Engineering Practice (K-12 Framework) UT SCIENCE CORE ILO 6.e. Understand that scientific conclusions are based on the assumption that natural laws operate today as they did in the past and that they will continue to do so in the future. NGSS Developing and Using Models Constructing Explanations and Designing Solutions Cross Cutting Concepts (K-12 Framework) Patterns Systems and Systems Models Math and/or ELA Curriculum Tie WHST.6-8.1 Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content Time Frame: Number of Class Periods – Number of Minutes 4- 45 minute periods Group Size 30-36 students Technology Tools Utilized Evernote App iTunes/AppleStore and Google Play Photobooth App Preinstalled on iTunes/AppleStore and Google Play Padlet Example-Reference ONLY and Make Your Own Review Game Computer or Device with Flash Bibliography Intro Video http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=tkxWmh-tFGs Videos on law of superposition and index fossils/geologic column http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oAJhGbs54zw http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YgE-dSx-fPc Layers of Time Review Game http://www.amnh.org/explore/ology/paleontology Faulting and Folding Website http://ees.as.uky.edu/sites/default/files/elearning/module10swf.swf Folding and Faulting Picture (SEE ATTATCHMENT NAMED: Folding and Faulting Padlet.jpg) http://www.troy.k12.ny.us/old%20sites/faculty/dibarij/earth%20science/answer 13_14.html Grand Canyon Picture http://4.bp.blogspot.com/kLBr72ROrAE/TVjJMJ5hGKI/AAAAAAAAEPQ/hGS55Yt4LtI/s1600/sed%2Brock.jpg Grand Canyon Information on Layers http://www.bobspixels.com/kaibab.org/geology/gc_layer.htm Key Words Fossils, index fossils, geological column, relative dating, folding and faulting, law of superposition, rock layers, unconformities, erosion, and weathering INSTRUCTIONAL: Materials – Quantity and Vendor if necessary White Butcher paper Crayons Colored Pencils Markers iPads or Android Tablets Teacher Computer Computer Lab Background for Teachers – Website It is important for students to understand that the Earth and the rock layers have been forming and reformed and changed over millions of years. Most of the time, the oldest layers are on the bottom of rock layers and the youngest lie on top. Often, changes from heat, pressure, and earthquakes change the order of layers. Determining rock ages and layers are from carbon or radioactive layers or relative dating based on layering and key fossils. Here is a helpful video for teachers and students to see how the Grand Canyon was formed and changed over the years: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YgE-dSxfPc Teacher Preparation Introduction/Attention Grabber 1. As a class starting activity, play this video 2. Use these questions as a starter or a discussion: a. How old is the Earth based on scientists and radioactive dating? b. Why was the Cambrian explosion important? c. Which explanation or analogy was easiest for you to understand the age of the Earth? Why? Geological Column Class Activity: Cut the worksheets found at: http://geology.utah.gov/online/pi/pi-93 (See attachment called Fossil Environments in Utah) into strips. 1. Split the class into 10 groups, depending on your size about 2-4 students a group. 2. Each of the ten groups will be given: a. A strip of butcher paper or poster paper to represent a rock layer of a specific time period b. A small information strip of their rock layer with fossil information, climate and geography of time, and age c. Colored pencils, markers, and crayons 3. Give the students about 10- 15 minutes to quickly draw and diagram the index fossils and time period on their strips as well as a sketch of what the land looked like at the time. 4. Then, as a class, they place their rock layer in the right order based on index fossils as they flow throughout the geological time column. The decision of the layer placement is first from the group and then approval from the class. Overview of the Law of Superposition and the Grand Canyon; Index Fossils 1. Watch Videos of law of superposition and index fossils/geologic column 2. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oAJhGbs54zw 3. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YgE-dSx-fPc 4. After showing either video or both, have students write a summary or discuss in small groups the law of superposition and the importance of index fossils in relative dating. Layers of Time Review Game 1. This is a fun game that can be played as a class or individually in class or a computer lab. It requires Flash so it cannot be played on an iPad. 2. Layers of Time Game Faulting and Folding Website 1. This website gives an animation and written explanation on how folding and faulting change established rock layers. This animation can be done as a class or individually. After doing the animation, students can discuss or write a summary of what they saw. 2. The website says it is unsafe when you click on the link but after it loads, it goes straight to the animation. http://ees.as.uky.edu/sites/default/files/elearning/module10swf.swf Photobooth Padlet Formative Assessment 1. Students are given a printed picture or download the photo from a class website. 2. Use picture printed (SEE ATTATCHMENT NAMED: Folding and Faulting Padlet.jpg) 3. Students manipulate the options of the photobooth app and the picture to create two pictures. One picture is of folding and the other is faulting. 4. As a teacher, prepare beforehand two Padlets websites to have students post their pictures online of Folding and Faulting and a written explanation of how and what events make these geological features occur. This is a simplified example of a Padlet wall. Please do not have your students post on the example. Example-Reference ONLY Performance Task A. Group Collaborative Assignment 1. (SEE ATTATCHMENTs NAMED: Geological Columns Student Sheet and Geological Columns Teacher ) 2. The students will be working together collaboratively to create and solve a new geological column where folding, faulting, intrusions, and erosion are present. There are four similar landmasses with similar index fossils and layers to help them solve it. However, not all the pages have the same information so they will work together as a group, each member has a different paper. 3. First students read their own card and discuss their research as the geologist specializing in that area of the Grand Canyon. Collaboratively, they use the smaller pieces of the layers to determine the relative dating and layers of the rocks from oldest to youngest and make a complete geological column together. 4. This is Formative Assessment to see if they can show how to make a geological column from the evidence of similar geological forms. B. Writing Prompt 1. After the Performance task, students will complete the writing task using the Evernote app. You are a famous geologist. A colleague from India sends you a photograph of rock layers that contain fossils. He claims that because he found a human fossil in a lower layer than a dinosaur fossils, that humans were alive before dinosaurs. Write him a letter giving other possible explanations as to why the human fossil was found below the dinosaur fossil. Possible words to include: folding, faulting, erosion, intrusion, extrusion, uplift Strategies for Diverse Learners ELL or SPED students can be paired with other students for the performance task. A guided outline of vocabulary with space to write the definition, example, sentence, and a picture can be helpful for all students to refer to during the performance and writing task. Extensions Students can create a presentation or video of their Performance task to share with the class. Students are given a similar picture to the one used for the Padlet activity and they write a history of the land and explain the changes that occurred in forming their geological column. Students create a video or presentation for a nearby elementary class to explain Earth’s surface and rock layers. The classes can connect via Skype or simply record their presentation and upload it to YouTube. ASSESSMENT: Assessment Plan Pre-Assessment: 1. Class Geological Columns: The teacher is able to identify their misconceptions and lack of understanding of rock layers, index fossils, and the law of superposition. Formative: 1. Performance Task: Students show how to make a geological column from the evidence of similar geological forms. Summative 1. Performance Task: Students show that they can use the principles of relative dating and the law of superposition to create a geological column. 2. Padlet: Students show the difference between folding and faulting. 3. Writing Task: Students explain all of the criteria, geological features, time scale, and fossilization of Earth’s surface rock layers. Assessment Rubric –