Cellular Respiration Skeleton Notes
advertisement

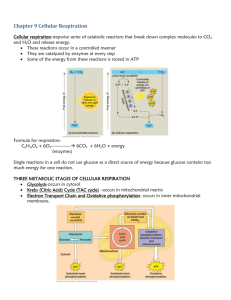
Name __________________________________________ Period _________ Date ________________ Chapter 7 -- Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration o Complex process that our cells make ____________ by breaking down ________________________ ________________________ o Organisms that use cellular respiration are known as ________________________ o Cellular Respiration is the process that releases energy by breaking down ___________________ molecules in the presence of ________________________ o C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP Same equation for photosynthesis JUST BACKWARDS! Glycolysis o Process where one molecule of ________________________ is broken in half, producing 3-carbon molecules of ________________________ ________________________ o Creates a small amount of ______________ and __________________ o Process is anaerobic Does not require oxygen Aerobic Respiration o If ________________________ is present in cell environment o Pyruvic acid is broken down to make a large amount of ____________ o If no oxygen is available for the pyruvic acid ____________________________ 1 Fermentation o Releases ________________________ from pyruvic acid ________________________ oxygen o Two types ________________________ _____________________ ________________________ Lactic Acid Fermentation o Lactic Acid is produced by ________________________ during ________________________ exercise when the body cannot supply enough ________________________ Alcoholic Fermentation o Alcoholic fermentation is done by ________________________ and some __________________________________ o Produces an ___________________ & ___________________ ___________________ Glycolysis o Glucose 2 pyruvic acid molecules o Step 1: Glucose molecule uses _________________ ATP molecule to make a 6-carbon molecule with two ___________________________ o Step 2: Glucose molecule breaks in ______________ to make two _______ molecules o Step 3: Each G3P molecule gets a __________________________ added and 2 NAD+ is reduced and gain an electron to become NADH o Step 4: Each 3-Carbon molecule loses their phosphates to make 4 molecules of ____________, 2 molecules of ______________________, and 2 molecules of ________________________ ____________________ 2 Fermentation o ________________________ process after glycolysis o Pyruvic acid is used to become either ________________________ ___________________ or ____________________ ________________________ o This process is important because it regenerates ______________ molecules for glycolysis to continue to work Lactic Acid Fermentation o Pyruvic acid lactic acid o NADH NAD+ o Important for making ________________________ products Produces certain ____________________ and ______________________ o Occurs naturally in your ______________________ when you work out Muscle soreness o Muscles use up all available ______________________ Switch to ______________________ respiration o Increases ________________ levels in muscles causing the fatigue Eventually gets processed in liver back to pyruvic acid Alcoholic Fermentation o Pyruvic acid ethyl alcohol o NADH NAD+ o Ethyl alcohol is a ____________________ molecule Pyruvic acid loses a carbon by releasing ____________ o Yeast needs to get food to survive such as ____________________ from fruit o Yeast breaks down to ____________________ the pyruvic acid into ____________________ ____________________ and ______________ If CO2 is released, you get ____________________ alcohol Ex: wine If CO2 is not released, you get ____________________ alcohol Ex: Champagne 3 Efficiency of Glycolysis o Glycolysis uses _______ ATP in order to create G3P molecules o Makes _______ ATP at the end of the process o As a process to make energy, the efficiency is about _______ Very __________ for necessary energy This is why we need ____________________ _______________________!! The Krebs Cycle o During the Krebs Cycle, pyruvic acid is broken down into ____________________ ____________________ in a series of energyextracting reactions o ____________________ ____________________ is created in this cycle thus giving it the nickname Citric Acid cycle o Net ATP Production is ________ ATP Electron Transport Chain o The electron transport chain uses the high-energy ____________________ from the Krebs Cycle to convert ADP to ATP o Total ATP ________ Aerobic Respiration o Only occur in the presence of ____________________ o Two stages ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ with chemiosmosis o Prokaryotes Occur in ____________________ o Eukaryotes Occur in ____________________ o After glycolysis, ____________________ ____________________ are produced o Pyruvic acid moves inside mitochondria into ________________________ ____________________ (space between two membranes) o Pyruvic acid + CoA Acetyl CoA + CO2 4 The Krebs Cycle o Acetyl CoA CO2 + H + ATP o The _______ produced reduce NAD+ NADH o ____________________ steps in the Krebs Cycle Occurs in mitochondrial matrix o Citric Acid is made in Step 1 therefore this is also called the ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ o Net ATP produced is ________ ATP Krebs Cycle o Step 1: Acetyl CoA + oxaloacetic acid Citric Acid This step releases ________________ back into the mitochondrial matrix for pyruvic acid to be fixed again o Step 2: Citric acid releases __________ and _______ Becomes a ____________________ compound The H released, reduces the NAD+ to ____________________ o Step 3: Five carbon compound releases another __________ and _______ Becomes a ____________________ compound Another NAD+ is reduced to ____________________ Produces an ____________________ o Step 4: 4 carbon compound releases _______ atom This time, FAD is reduced to ____________________ Similar molecule to NAD+ o Step 5: 4 carbon compound releases _______ atom Reduces NAD+ to ____________________ This reaction regenerates initial ____________________ ___________ 5 Electron Transport Chain o Uses the high-energy ______________________ from the Krebs Cycle to convert ADP to ____________ o Total net ATP produced is ___________!! o Prokaryotes Occurs on __________________ ______________________ of organism o Eukaryotes Occurs in the ____________________________ membrane called ______________________ ETC o Step 1: __________________ & __________________ are used to power this chain of reactions NADH & FADH2 are _____________________ (lose e-) to the electron transport chain Also donate H atoms NADH NAD+ FADH2 FAD+ o Step 2: _______________________ from NADH & FADH2 are passed down chain Lose some __________________ each time passed on o Step 3: Lost energy from electrons transferring down the chain __________________ protons (H+) This creates __________________ concentration of H+ between inner and outer membranes Creates a __________________________ __________________ & ___________________ __________________ since H+ are positive o Step 4: Concentration & electrical gradient in membranes produce _______________ molecules by __________________________ ATP ______________________ is protein embedded in membrane that pumps protons out and creates ATP 6 o Step 5: The electrons move to __________________ __________________ down the chain _____________________ is the final acceptor Oxygen also accepts _____________________ provided by NADH & FADH2 The protons, electrons, and oxygen all combine to produce __________________ Importance of Oxygen o The only way to produce ATP is by the movement of electrons in the _____________ _____________________ is the final acceptor o Without oxygen, the ETC would _____________________ Efficiency of Aerobic Respiration o Glycolysis = _________ ATP o Krebs Cycle = _________ ATP o ETC = _________ ATP o Total = _________ ATP!! Glycolysis Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chain Efficiency of Cellular Respiration o Depends on _____________________ of the cell o How _____________________ are transported o Cellular respiration is _____________________ times more efficient than _____________________ __________________________ 7 Summary o Cellular respiration Glycolysis Glucose _____________________ _______________ + ______________ + ________________ o Aerobic respiration Pyruvic acid ____________ + ______________ + ____________ Energy & Exercise Comparing Photosynthesis & Respiration Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O Function Location Reactants Products Equation 8