Ch 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
advertisement

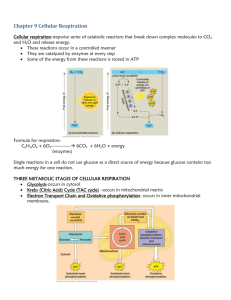
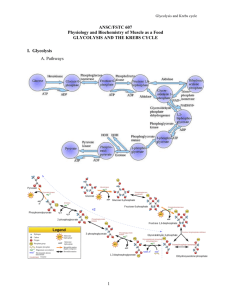
1 Review What happens to pyruvic acid in the Krebs cycle Interpret Visuals Look at the diagram of the Krebs cycle. List all the products that are made and include what happens to each one 2 Review How does the ETC use the high energy electrons from glycolysis and the Krebs cycle Relate Cause and Effect How does the cell use the charge differences that build up across the inner mitochondrial membrane during cellular respiration CH 9 CELLULAR RESPIRATION AND FERMENTATION 9.2 The Process of Cellular Respiration Glycolysis First stage of cellular respiration Glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of the 3-carbon molecule pyruvic acid ATP and NADH are produced. Glycolysis Cells “deposits” 2 ATP to start glycolysis. Glycolysis Produces 4 ATP molecules Net gain of 2 ATP for each glucose. Glycolysis NAD+ accepts a pair of high-energy electrons and becomes NADH Happens twice Goes to ETC. Glycolysis Produces ATP very fast Does not need oxygen. Krebs Cycle Pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide A.k.a. Citric Acid Cycle ATP is produced. Krebs Cycle 1 Pyruvic acid from glycolysis enters the matrix of the mitochondrion. Krebs Cycle 2 Enzymes split CO2 off from pyruvic acid Leaves 2 carbon molecule NADH is produced form NAD+. Krebs Cycle 3 2 carbon molecule joins a 4 carbon molecule to make citric acid. Krebs Cycle 4 Citric acid (6 carbon) becomes a 4 carbon molecule More NADH and CO2 are made. Krebs Cycle 5 More reactions capture energy as ATP, NADH, and FADH2. Krebs Cycle 6 4 carbon molecule goes through cycle again. Krebs Cycle Each glucose molecule will make two turns of the Krebs cycle Each glucose molecule will make 2 ATP molecules 8 NADH molecules 2 FADH2. Electron Transport NADH and FADH2 pass their electrons to ETC. Electron Transport Electrons combine with H+ ions and oxygen to form water at end of ETC. Electron Transport The high energy electrons move H+ ions against a concentration gradient across the inner mitochondrial. Electron Transport H+ ions pass back through the ATP synthase causing it to spin ATP synthase attaches a phosphate to ADP to produce ATP with each rotation. Energy Totals Complete breakdown of glucose through cellular respiration results in the production of 36 ATP molecules The rest of the energy is “lost” as heat (64%).