Hess`s Law
advertisement

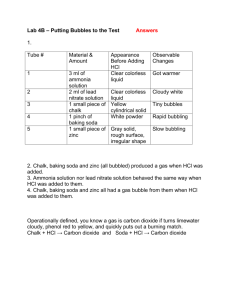
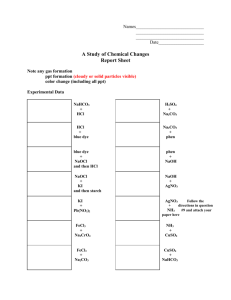
Hess's Law In this lab activity, you will calculate the enthalpy change for the thermal decomposition of sodium bicarbonate: Problem: What is the molar enthalpy of reaction for the thermal decomposition of sodium hydrogen carbonate at standard conditions? Materials weighing boats graduated cylinder 250 mL beaker styrofoam cups 2.00 g of solid sodium carbonate 2.00 g of sodium hydrogen carbonate (baking soda) 100 mL of 1.0 M hydrochloric acid temperature probe Pre lab: 1. Determine for each of the equations above. 2. Then determine the for the final reaction using Hess’s Law Part 1: 1. Measure out 2.00 g of NaHCO3 (baking soda) 2. Measure out 50 mL of HCl. 3. Add the HCl to the Styrofoam cup 4. Record initial temperature of the HCl 5. After 5-10 seconds, add the baking soda, stir 6. Click stop when the temperature has a reached a minimum and starts to increase again 7. Dump the liquid in the sink, rinse and dry the Styrofoam cup. 8. Repeat steps 1-7 using Na2CO3 instead of the baking soda Analysis: 1. 2. 3. 4. Calculate the change in temperature for the HCl with the baking soda Calculate the mass of the Styrofoam cup water (mass of solid and mass of HCl) Calculate q Repeat 1-3 with the Na2CO3 5. Determine the using Hess’s law using your actual lab values 6. Determine percent error of Hess’s law values from the pre-lab and your actual lab values. CP Hess Law lab Worksheet Pre-lab work: Data table Actual mass of baking soda (NaHCO3) Moles of baking soda (NaHCO3) Volume of HCl Initial temperature of HCl Final temperature of HCl and NaHCO3 Change in temperature Value of q (Cp=4.184J/gC) -q = value of ΔH ΔH / mol NaHCO3 Actual mass of Na2CO3 Moles of Na2CO3 Volume of HCl Initial temperature of HCl Final temperature of HCl Change in temperature Value of q (Cp=4.184J/gC) -q = value of ΔH ΔH / mole Na2CO3 Heat of formation using Hess’s law with lab values Percent Error Show all work for analysis calculations on back of this paper! Names