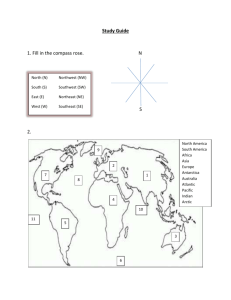
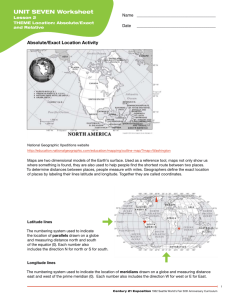
Unit Test 9/23 Study Guide Know maps 1A, 1B, 2, and 3 5 Themes of
advertisement

Unit Test 9/23 Study Guide Know maps 1A, 1B, 2, and 3 5 Themes of Geography Mr. Help M-Movement R- Region H-Human/ E-Environment Interaction L-Location P-Place *Remember location, place, and regions have two each *Remember how we connected each theme to pictures and places in class Location1.Absolute location- is the exact location Ex: street address (local location) Line where latitude and longitude cross- Paris, France-48°51’ North latitude and 2.20’East longitude 2.Relative location- landmarks, time, direction, or distance from one place to another Ex: Toms River is 20 minutes from Seaside Place 1.Physical- think nature Ex: mountains, rivers, soil, beaches, wildlife, soil 2.Human-ideas and actions of people that result in changes to the environment. Ex: buildings, roads, clothing, and food habits Movement The movement of people, import and export of goods, and mass communication. People interact through movement- travel, trade, E-mail *Also ideas, fashion, and fads move Regions 1.Formal Regions- defined by boundaries Ex: United States, Colts Neck 2.Vernacular Regions- defined by people’s perceptions Ex: The South, The Middle East Human Environmental Interaction *Humans change the environment There are 3 key concepts: Humans adapt on the environment Adapt to environment by wearing clothing that is suitable. Ex: Winter wear a jacket, rain use an umbrella Humans modify the environment Ex: Heating and cooling buildings Humans depend on the environment Depend on the Mississippi for water and transportation Artifacts & Archaeology (Think): 1.Where is the object located? 2.What is the object and how is it used? 3. What is the object made out of? 4.Historical Reference 5.Carbon Dating Artifact- Artifacts are defined as products of human skill. Ex: A piece of pottery, a tool, or a coin Archaeology- the study of artifacts in order to find out more about history or the people who lived years ago. *skeletons and bones are not artifacts-but we can use some of the same methods in order to understand more about them Carbon Dating- When an item made of carbon ages, little pieces of carbon-14 atoms fall off in the process. We can tell how old the object is by how much carbon the item still has. *Very popular method with scientists today *Look at picture in notebook Chronological Order – means placing events according to when these events occurred. (Be able to place dates in order) B.C. and B.C.E. are the same exact thing, only different terms! A.D. and C.E. are the same exact thing only with different terms! B.C.= Before Christ A.D.= Anno Domini (Year of the Lord) B.C.E.= Before Common Era C.E.= Common Era 1.Take all of the B.C. and B.C.E. terms and make the terms the same 2.Take all of the A.D. and C.E. terms and make the terms the same 3.Now, take all B.C./B.C.E. terms and list them from greatest to least 4.With the next number, take the lowest A.D./C.E. number and count to the highest number