Statutory Spoken Language, Reading and Writing for Year 3
advertisement
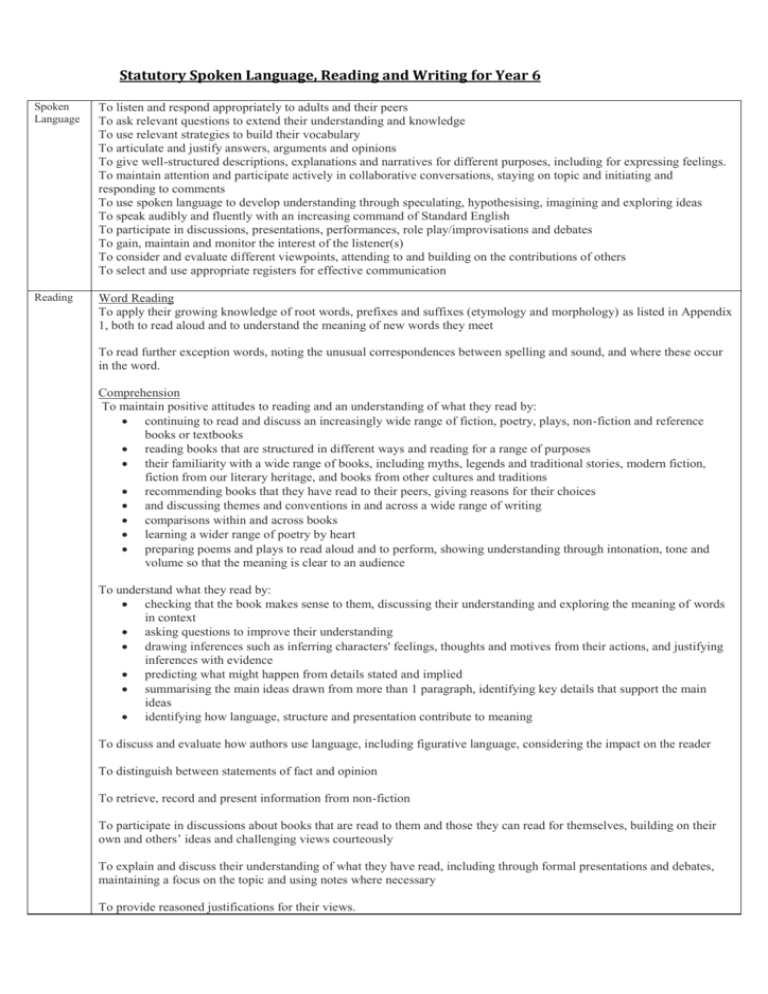
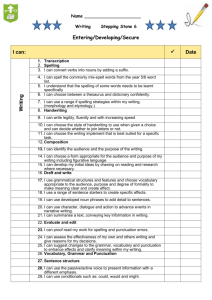
Statutory Spoken Language, Reading and Writing for Year 6 Spoken Language To listen and respond appropriately to adults and their peers To ask relevant questions to extend their understanding and knowledge To use relevant strategies to build their vocabulary To articulate and justify answers, arguments and opinions To give well-structured descriptions, explanations and narratives for different purposes, including for expressing feelings. To maintain attention and participate actively in collaborative conversations, staying on topic and initiating and responding to comments To use spoken language to develop understanding through speculating, hypothesising, imagining and exploring ideas To speak audibly and fluently with an increasing command of Standard English To participate in discussions, presentations, performances, role play/improvisations and debates To gain, maintain and monitor the interest of the listener(s) To consider and evaluate different viewpoints, attending to and building on the contributions of others To select and use appropriate registers for effective communication Reading Word Reading To apply their growing knowledge of root words, prefixes and suffixes (etymology and morphology) as listed in Appendix 1, both to read aloud and to understand the meaning of new words they meet To read further exception words, noting the unusual correspondences between spelling and sound, and where these occur in the word. Comprehension To maintain positive attitudes to reading and an understanding of what they read by: continuing to read and discuss an increasingly wide range of fiction, poetry, plays, non-fiction and reference books or textbooks reading books that are structured in different ways and reading for a range of purposes their familiarity with a wide range of books, including myths, legends and traditional stories, modern fiction, fiction from our literary heritage, and books from other cultures and traditions recommending books that they have read to their peers, giving reasons for their choices and discussing themes and conventions in and across a wide range of writing comparisons within and across books learning a wider range of poetry by heart preparing poems and plays to read aloud and to perform, showing understanding through intonation, tone and volume so that the meaning is clear to an audience To understand what they read by: checking that the book makes sense to them, discussing their understanding and exploring the meaning of words in context asking questions to improve their understanding drawing inferences such as inferring characters' feelings, thoughts and motives from their actions, and justifying inferences with evidence predicting what might happen from details stated and implied summarising the main ideas drawn from more than 1 paragraph, identifying key details that support the main ideas identifying how language, structure and presentation contribute to meaning To discuss and evaluate how authors use language, including figurative language, considering the impact on the reader To distinguish between statements of fact and opinion To retrieve, record and present information from non-fiction To participate in discussions about books that are read to them and those they can read for themselves, building on their own and others’ ideas and challenging views courteously To explain and discuss their understanding of what they have read, including through formal presentations and debates, maintaining a focus on the topic and using notes where necessary To provide reasoned justifications for their views. Writing Spelling use further prefixes and suffixes and understand the guidance for adding them spell some words with ‘silent’ letters continue to distinguish between homophones and other words which are often confused use knowledge of morphology and etymology in spelling and understand that the spelling of some words needs to be learnt specifically, as listed in Appendix 1 use dictionaries to check the spelling and meaning of words use the first 3 or 4 letters of a word to check spelling, meaning or both of these in a dictionary use a thesaurus Handwriting and Presentation Pupils should be taught to write legibly , fluently and with increasing speed by: choosing which shape of a letter to use when given choices and deciding whether or not to join specific letters choosing the writing implement that is best suited for a task Composition Plan their writing by: identifying the audience for and purpose of the writing, selecting the appropriate form and using other similar writing as models for their own noting and developing initial ideas, drawing on reading and research where necessary in writing narratives, considering how authors have developed characters and settings in what pupils have read, listened to or seen performed Draft and write by: selecting appropriate grammar and vocabulary, understanding how such choices can change and enhance meaning in narratives, describing settings, characters and atmosphere and integrating dialogue to convey character and advance the action précising longer passages using a wide range of devices to build cohesion within and across paragraphs using further organisational and presentational devices to structure text and to guide the reader Evaluate and edit by: assessing the effectiveness of their own and others’ writing proposing changes to vocabulary, grammar and punctuation to enhance effects and clarify meaning ensuring the consistent and correct use of tense throughout a piece of writing ensuring correct subject and verb agreement when using singular and plural, distinguishing between the language of speech and writing and choosing the appropriate register Proofread for spelling and punctuation errors Perform their own compositions, using appropriate intonation, volume, and movement so that meaning is clear. Vocabulary, grammar & punctuation Develop their understanding of the concepts by: recognising vocabulary and structures that are appropriate for formal speech and writing, including subjunctive forms using passive verbs to affect the presentation of information in a sentence using the perfect form of verbs to mark relationships of time and cause using expanded noun phrases to convey complicated information concisely using modal verbs or adverbs to indicate degrees of possibility using relative clauses beginning with who, which, where, when, whose, that or with an implied (ie omitted) relative pronoun learning the grammar for years 5 and 6 in Appendix 2 Indicate grammatical and other features by: using commas to clarify meaning or avoid ambiguity in writing using hyphens to avoid ambiguity using brackets, dashes or commas to indicate parenthesis using semicolons, colons or dashes to mark boundaries between independent clauses using a colon to introduce a list punctuating bullet points consistently Use and understand the grammatical terminology in Appendix 2 accurately and appropriately in discussing their writing and reading. Appendix 2