11 Photosynthesis Alternative Pathways to go with powerpoi

SBI4U Name: _____________________________ Date: _________________________________
Photosynthesis: Alternative Pathways
1.
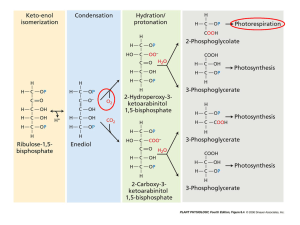
Is there any energy cost associated with carbon dioxide fixation in the C3 path?
_______
2.
When the oxygen levels are higher, photosynthesis decreases. Why?
3.
4.
What is the short form for Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase
______________
the enzyme that catalyzes the carbon fixation to RuBP.
the most abundant enzyme on Earth
is also the culprit of photorespiration since it cannot distinguish between CO
2
and O
2
This is the second enzyme to fix carbon dioxide in C4 and CAM plants!
5.
In PHOTORESPIRATION, oxygen replaces carbon dioxide. Is this productive?
6.
What substance undergoes subsequent metabolism, which releases CO
2
. This is a waste, both in terms of the energy required to carry out the process and the CO
2
lost.
__________________
7.
What is the name of the first enzyme in the C4 pathway?
8.
What is the name of the first enzyme in the C3 pathway?
9.
What does C4 refers to?
_________________
10.
Is there any energy cost associated with carbon dioxide fixation in the C4 path?
__________
11.
C4 Photosynthesis is a way to overcome photorespiration! Is this spatial or temporal separation?
C4 PLANTS
• PEP carboxylase functions in the mesophyll, during the day to fix CO2 into a 4 carbon molecule
• These 4C molecules are transferred to the bundle sheath, where they are decarboxylated to release
CO2, which enters the Calvin cycle – SPATIAL
SEPARATION
• During the Hottest part of the day, C4 plants have their Stomata Partially Closed.
• Such plants lose only about half as much water as C3 plants when producing the same amount of
Carbohydrate.
• C4 plants include corn, sugar cane and crabgrass.
12.
What do malate and pyruvate go through “cell-cell connection” to move from one cell to another?
___________________________
THE CAM PATHWAY
• Cactus, pineapples have different adaptations to Hot,
Dry Climates.
• Plants that use the CAM Pathway Open their Stomata at NIGHT and Close during the DAY, the opposite of what other plants do.
• At NIGHT, CAM Plants take in CO2 and fix into Organic Compounds.
• During the DAY, CO2 is released from these Compounds and enters the Calvin Cycle.
• TEMPORAL SEPARATION
• Because CAM Plants have their Stomata open at night, they grow very Slowly, But they lose LESS Water than C3 or C4 Plants.
13.
Do CAM and C4 plants have a C3 pathway within them? ________
14.
What is the product of the first carbon fixation reaction in C4 and CAM paths? _______________________
15.
Where is the site of the Calvin cycle for both? _____________________________
16.
Is the CAM pathway temporal or spatial separation? _______________________________
The light compensation point
• the point on a light-response curve at which the rate of photosynthetic carbon dioxide uptake exactly equals the rate of respiratory carbon dioxide evolution.
• In other words there is no net uptake or evolution of carbon dioxide at this light intensity even though both photosynthesis and cellular respiration are occurring.
17.
What happens at the light saturation point?
18.
How do the light response curves of C3 plants and C4 plants differ?
More Practice! Answers are on chat
1 a) Define photorespiration. b) What gas can compete with carbon dioxide for the binding site of the enzyme rubisco? c) Under normal conditions, what proportion of fixed carbon is affected by photorespiration in C3 plants? d) Compare the end products of photosynthesis and photorespiration.
2. How does temperature affect the relative amounts of photosynthesis and photorespiration that occur in C3 plants?
3. Label the following:
4 a) What is the main difference between the ideal environments of C4 plants and CAM plants? b) Name two C4 plants and two CAM plants.
5. What might have been responsible for the evolution of photorespiration?
6 a) At what time of the day would you expect to find the most malate in CAM plants? b) When would you find the least amount of malate in CAM plants? c) Why do plants that use CAM photosynthetic pathways close their stomata during the day?
D) During the cool of evening, CAM plants open their stomata. What gas is preferentially absorbed at this time?
E) Explain how this gas is stored for daytime use.
How do the light response curves of C3 plants and C4 plants differ? Identify A, B, 1, and 2.
How would an O
2
evolution curve appear if the stomata of a leaf closed during an experiment?
Which letter represents a plant with elevated carbon dioxide concentrations?
How would warming of the leaf affect the O2 evolution curve?
How does photosynthesis differ between “sun” or “shade” plants? Fill in the blanks below.
___________-leaves (curve B) often are more efficient in harvesting sunlight at low light levels
___________-leaves (curve A) display a higher _______________________ and maximum rate of photosynthesis
More Practice! ANSWERS
1.
Photorespiration refers to the addition of oxygen to ribulose bisphosphate to produce phosphoglyceraldehyde and glycolate, which subsequently releases carbon dioxide.
(b) Oxygen gas competes for the binding site of the enzyme rubisco.
(c) Under normal conditions in C3 plants, approximately 20% of the fixed carbon is lost to photorespiration.
(d) Photosynthesis produces glyceraldehydes 3-phosphate (G3P), while photorespiration produces phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGA) and glycolate.
2.
As temperature increases, the amount of photorespiration in C3 plants increases, as does the rate of photosynthesis. However, the optimum temperature for photorespiration is higher than that for
3.
A: oxaloacetate; B: carbon dioxide; C: pyruvate D: mesophyll cell; E: bundle-sheath cell
4. (a) C4 plants grow best in hot, wet environments whereas CAM plants grow best in hot, dry environments.
4.
photosynthesis, so photorespiration rates may still be increasing even though photosynthesis rates are decreasing. plants
(b) C4 plants: corn and sugar cane; CAM plants: pineapple, any succulent including cacti and jade
5.
The structural evolution of rubisco indicates that when rubisco was created, the atmosphere was probably rich in carbon dioxide and poor in oxygen
When photosynthesis evolved in early prokaryotes, rubisco was used to fix carbon dioxide
Oxygen began to accumulate in the atmosphere
This made the atmosphere hospitable for eukaryotic heterotrophic organisms
Rubisco was used to fix oxygen once the atmosphere became rich in it, but some plants evolved alternative methods of carbon fixation that concentrate carbon dioxide at the site where carbon dioxide is found, thereby suppressing photorespiration
6.
6. (a) The most malate in a CAM plant would be found late at night.
(b) The least malate in a CAM plant would be found at the end of the day.
(C) CAM plants close their stomata during the day to prevent water loss, as they live in dry environments.
(D) The gas that is preferentially absorbed during the cool evening is CO2.
(E) During the dark, CAM plants take in CO2 and incorporate it into C4 organic acids using PEP caboxylase.
These are stored in vacuoles until morning.
SBI4U Name: _____________________________ Date: _________________________________
Photosynthesis: Alternative Pathways
1.
Is there any energy cost associated with carbon dioxide fixation in the C3 path?
No
2.
When the oxygen levels are higher, photosynthesis decreases. Why?
This is due to
PHOTORESPIRATION! (the competition between oxygen and carbon dioxide on the
Rubisco enzyme in the Calvin cycle!)
3.
What is the short form for Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase
(Rubisco)
the enzyme that catalyzes the carbon fixation to RuBP.
the most abundant enzyme on Earth
is also the culprit of photorespiration since it cannot distinguish between CO
This is the second enzyme to fix carbon dioxide in C4 and CAM plants!
2
and O
2
4.
In PHOTORESPIRATION, oxygen replaces carbon dioxide. Is this productive?
non-productive, wasteful reaction!
5.
What substance undergoes subsequent metabolism, which releases CO
2
. This is a waste, both in terms of the energy required to carry out the process and the CO
2
lost.
Glycolate
6.
What is the name of the first enzyme in the C4 pathway?
PEP carboxylase
7.
What is the name of the first enzyme in the C3 pathway?
8.
What does C4 refers to?
rubisco
The number of carbons in the first product of the calvin cycle.
(phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase)
9.
Is there any energy cost associated with carbon dioxide fixation in the C4 path?
Yes
10.
C4 Photosynthesis is a way to overcome photorespiration! Is this spatial or temporal separation?
This
is SPATIAL SEPARATION!
C4 PLANTS
• PEP carboxylase functions in the mesophyll, during the day to fix CO2 into a 4 carbon molecule
• These 4C molecules are transferred to the bundle sheath, where they are decarboxylated to release
CO2, which enters the Calvin cycle – SPATIAL
SEPARATION
• During the Hottest part of the day, C4 plants have their Stomata Partially Closed.
• Such plants lose only about half as much water as C3 plants when producing the same amount of
Carbohydrate.
• C4 plants include corn, sugar cane and crabgrass.
11.
What do malate and pyruvate go through “cell-cell connection” to move from one cell to another?
Plasmodesmata
THE CAM PATHWAY
• Cactus, pineapples have different adaptations to Hot,
Dry Climates.
• Plants that use the CAM Pathway Open their Stomata at NIGHT and Close during the DAY, the opposite of what other plants do.
• At NIGHT, CAM Plants take in CO2 and fix into Organic Compounds.
• During the DAY, CO2 is released from these Compounds and enters the Calvin Cycle.
• TEMPORAL SEPARATION
• Because CAM Plants have their Stomata open at night, they grow very Slowly, But they lose LESS Water than C3 or C4 Plants.
12.
Do CAM and C4 plants have a C3 pathway within them? Yes
13.
What is the product of the first carbon fixation reaction in C4 and CAM paths? oxaloacetate
14.
Where is the site of the Calvin cycle for both? Bundle sheath cells
15.
Is the CAM pathway temporal or spatial separation? TEMPORAL separation!
The light compensation point
• the point on a light-response curve at which the rate of photosynthetic carbon dioxide uptake exactly equals the rate of respiratory carbon dioxide evolution.
• In other words there is no net uptake or evolution of carbon dioxide at this light intensity even though both photosynthesis and cellular respiration are occurring.
16.
What happens at the light saturation point?
The dark reactions can not handle any more
ATP/NADPH produced by the light reactions for carbon fixation!
17.
How do the light response curves of C3 plants and C4 plants differ?