CH 235-2F Worksheet 6-Exam 2 September 29, 2014
advertisement
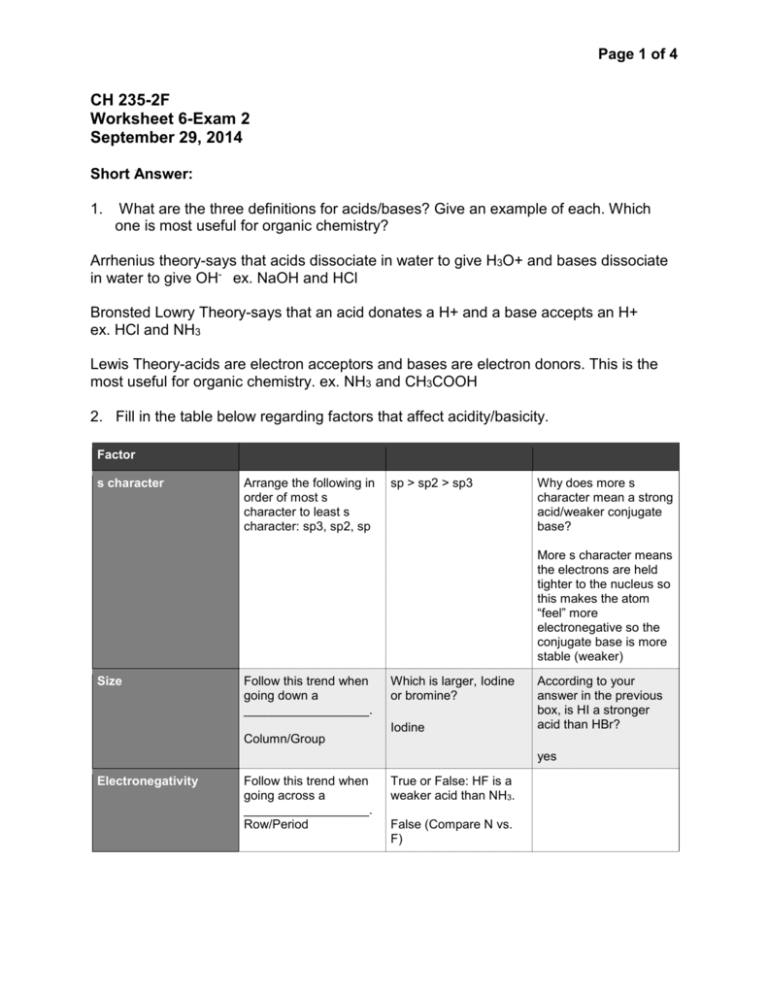
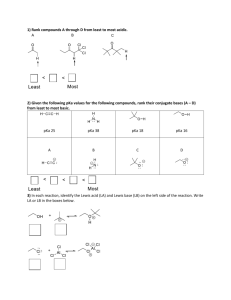
Page 1 of 4 CH 235-2F Worksheet 6-Exam 2 September 29, 2014 Short Answer: 1. What are the three definitions for acids/bases? Give an example of each. Which one is most useful for organic chemistry? Arrhenius theory-says that acids dissociate in water to give H3O+ and bases dissociate in water to give OH- ex. NaOH and HCl Bronsted Lowry Theory-says that an acid donates a H+ and a base accepts an H+ ex. HCl and NH3 Lewis Theory-acids are electron acceptors and bases are electron donors. This is the most useful for organic chemistry. ex. NH3 and CH3COOH 2. Fill in the table below regarding factors that affect acidity/basicity. Factor s character Arrange the following in order of most s character to least s character: sp3, sp2, sp sp > sp2 > sp3 Why does more s character mean a strong acid/weaker conjugate base? More s character means the electrons are held tighter to the nucleus so this makes the atom “feel” more electronegative so the conjugate base is more stable (weaker) Size Follow this trend when going down a __________________. Column/Group Which is larger, Iodine or bromine? Iodine According to your answer in the previous box, is HI a stronger acid than HBr? yes Electronegativity Follow this trend when going across a __________________. Row/Period True or False: HF is a weaker acid than NH3. False (Compare N vs. F) Page 2 of 4 Factor Inductive Effect This involves the pulling of electron density through _____________ How does distance affect this? More distance means less of an effect true ____________. bonds Resonance This trend allows for __________________ of charge. True or false: more electronegative atoms will result in more of an inductive effect. Draw the resonance structure for the conjugate base of CH3COOH Delocalization General Question: Does equilibrium favor the strong acid/strong base or the weak acid/weak base? Weak acid/weak base 3. What is a nucleophile? What is an electrophile? Give examples of each. How do you determine which species is a nucleophile/electrophile given a reaction? Nucleophile- the “base” in the reaction, “nucleus loving”, usually has a lone pair of electrons or a source of electrons that can be used to attack the electrophile. Ex. NH3 Electrophile-the “acid” of the reaction, “electron loving”, usually electron deficient. Ex. HBr 4. For each reaction below, determine which species is the nucleophile and which species is the electrophile. H20 + NH3 CH3COOH + H2O HPO42- + NH4+ NH4+ + OH- ________________ H2O is the Elec. NH3 is the Nuc. CH3COO- + H3O+ CH3COOH is the Elec. H2O is the Nuc. NH3 + H2PO4- ___ HPO42- is the Nuc. and NH4+ is the elec. For this type of problem, look at what happens in the reaction. Something that has an added proton in the product was a nucleophile in the reactants. Something that lost a proton or gained an electron pair in the products was an electrophile in the reactants. Matching A. Low pKa B. High pKa A, E 1. Strong Acid C, G 2. Strong Base Page 3 of 4 C. D. E. F. G. H. Low pKb High pKb High Ka Low Ka High Kb Low Kb B, F 3. Weak Acid D, H 4. Weak Base Remember, Ka/Kb is the equilibrium equation for the reaction. It is equal to products over reactants. A strong acid will have a lot of product because it readily dissociates; so, it will have a higher Ka. pKa is the (-)log of the Ka. A high Ka means a small pKa. This same trend works for Kb/pKb. 5. Arrange the following in order of increasing acidity: HS, HF, HCl, HSe. What trend did you use? HF < HCl < HS < HSe Use the size trend. Remember when going from left to right, atoms get smaller. When going from top to bottom, atoms get bigger. 6. Arrange the following from weakest to strongest conjugate base (I have shown the acid): 2 3 1 To get the conjugate base, simply remove the proton from the OH group. The first molecule has resonance, but the middle molecule does not. The last structure has resonance AND electronegative atoms, which allows for the inductive effect. Remember: strong conjugate bases come from weak acids. Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following statements is true? A. HCl is a stronger acid than HI. B. A molecule that can delocalize charge due to resonance is a more stable conjugate base than one with no resonance structures. C. A carbon with sp2 hybridization has more s character than a carbon with sp hybridization. D. HF is a weaker acid than H2O. Page 4 of 4 E. Both B and D. 2. Which of the hydrogens indicated below is most likely to be removed in an acid/base reaction? A. B. C. D. Green Arrow Blue Arrow Yellow Arrow Red Arrow Think about the resonance structures you can draw when this proton is taken off. This means you can delocalize that charge instead of it “sitting” on one atom.