Water Cycle Warm-Ups
advertisement

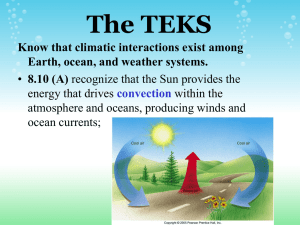
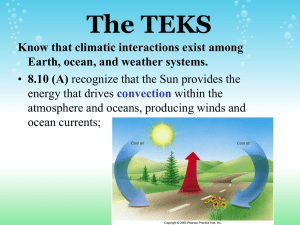
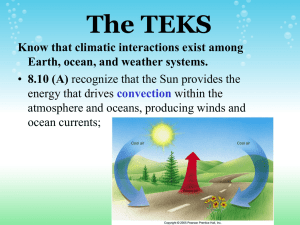
Warm Up January 7, 2016 Convection Currents Discussion: Have you heard the word current before? 1. Look up the definitions of Convection and Current. 2. Define in your own words what you think Convection Currents are and how they are involved with tectonic plate movement. January 8, 2016 1. What is the plastic-like layer that lays below the lithosphere? 2. What type of plate is the San Andreas Fault part of? Why volcanoes do not form along this plate?EXPLAIN! a. Divergent b. Subduction c. Convergent d. Transform 3. Concerning Plates that move together, if crust is being added at one location, why doesn’t the Earth’s surface keep expanding? Give details in three to five sentences. January 11, 2016 Concept Map: Make an events-chain concept map that describes seafloor spreading along a divergent plate boundary. Choose from the following phrases: magma cools to form new seafloor, convection currents circulate hot material along divergent boundary, and older seafloor is forced apart. January 12, 2016 Warm-Up 1. 2. This was a large ancient landmass that consist of all the continents on the Earth. a. Plate b. Plate tectonic c. Seafloor spreading d. Pangea This explains the locations of mountains, trenches, and volcanoes. a. Continental Drift b. Seafloor Spreading c. Plate Tectonic d. Convection Current Explain: Why the fossil of an ocean fish found on two different continents would not be good evidence of continental drift. Write 2 to 3 sentences. January 13, 2016 Warm-Up 1. Fill in the blank. Movement along any plate boundary means that ___________ happens at another boundary. a. Seafloor spreading b. Volcano formation c. Changes d. Earth quakes 2. When plates move together, crust is added in one place and then _________ in another place. a. Changes in another place b. Builds up in another place c. Spreads in another place d. Disappears in another place 3. In which order of events would you say takes place when two moving plates collide? a. Sinks, becomes denser, and cools. b. Becomes denser, cools, sinks. c. Cools, becomes denser, and sinks. d. Cools, rises, spreads and then sinks. Warm-Up January 19, 2016 1. How do differences in density cause deep ocean currents? Explain what density has to do with ocean currents. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FuOX23yXhZ8 January 20, 2016 1. Density currents are created by a. Temperature differences b. Wind c. salinity differences d. Both temperature and salinity differences. 2. As the amount of salt in the water increases, the salinity of the water ______________. a. increases b. decreases c. stays the same d. increases and decreases 3. What do you think the Coriolis Effect has to do with surface currents in the ocean? First you have to know what the Coriolis Effect is. Can you explain? Hint: Deflection and circulation. Ocean Currents: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_fcXL61NZS0 Coriolis Effect: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i2mec3vgeaI Coriolis Effect: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rdGtcZSFRLk Warm Up January 21, 2016 Coriolis Effect: Draw a Globe demonstrating Coriolis Effect. Use line arrows showing the direction in which ocean currents are effected by the Coriolis affect. Make sure you include the Equator, North Pole, and the South Pole. Also demonstrate the direction of the Earth’s rotation. Use a pencil. Question: If a hurricane is spinning counter clock wise, which direction is the wind and currents blowing? Explain: 1. What is the Coriolis Effect? 2. How does the Coriolis Effect cause ocean surface currents? 3. How does Current Density relate to the Coriolis Effect that produces Ocean Currents? Warm-Up January 22, 2016 Vocabulary: Please use science book to define these words: Pages 516-521 1. Surface current 2. Coriolis Effect 3. Upwelling 4. Density Current 5. Salinity Ocean tides and waves: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5ohDG7RqQ9I January 25, 2016 1. Which of the following describes upwelling? a. Horizontal ocean circulation that brings deep, cold water to the surface. b. Vertical ocean circulation that brings deep, warm water to the surface. c. Horizontal ocean circulation that brings deep, warm water to the surface. d. Vertical circulation that brings deep, cold water to the surface. January 26, 2016 1. Which type of tide occurs when the sun, the moon, and the Earth are aligned? a. Low tide b. High tideh c. Neap tide d. Spring tide 2. When are spring tides higher or lower than neap tides? Explain in two to three sentences. January 27, 2016 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZzY5-NZSzVw Water Cycle https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gY9HG8zUgOE January 29, 2016 USA Test Prep 1. What are the progresses water moves through, in order, as it moves from the surface of a lake to a cloud in the sky? A. Evaporation then Condensation B. Condensation then Evaporation C. Precipitation then condensation D. Condensation then Precipitation 2. During the water cycle, the sun’s energy evaporates water from the surface of Earth. This water returns to Earth as some form of a.Condensation b. Ground water c. Transpiration d. Precipitation February 1, 2016 1. A hurricane is most likely to occur in an area____ a. Near warm water. b. Near cool water. c. With strong winds d. With little moister 2. Adrienne noticed a puddle in her driveway after a rain storm before the Sun came out. Later that afternoon, she noticed the puddle was much smaller. What made the puddle become smaller? a. The rain stop falling b. The puddle drained into the grass c. The sun heated the water and it evaporated d. The water was sucked into the driveway. 3. #6 Based on the weather map seen here, what weather conditions would we expect in El Paso? a. Cold Temperature and sunny skies. b. Cold temperature and cloudy skies. c. Warm temperatures very cloudy and heavy rain. d. Warm temperatures, increasing clouds and showers.