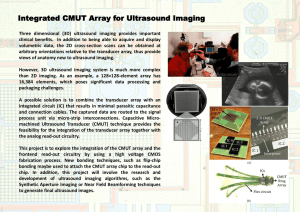
Lecture #44 – Ultrasound Notes what is sound? The transfer of
advertisement

Lecture #44 – Ultrasound what is sound? The transfer of motion The human ear can hear sound waves that vibrate 16-20,000 times/second Above this rate is 750,000 to 3 million times/second (Mega Hertz = MHz) therapeutic ultrasound Acoustical energy (sound waves) above the range of human hearing Therapeutic range: 0.75 to 3.3 MHz Effects: Thermal Nonthermal ( ) ultrasound frequencies anatomy of an ultrasound machine Generator Crystal Transducer - Converts electrical energy into acoustic energy Houses the crystal Applicator soundhead Part of the ultrasound unit that contains the crystal Also called transducer or transducer faceplate Ultrasound machines can have dual soundheads of different sizes how does it work? Generator produces a high-frequency at 0.75–3 million cycles per second (MHz). Current travels through the coaxial cable to the transducer. Transducer converts mechanical vibration by a reversal of the effect. Crystal in the transducer converts electrical energy to sound energy. Notes Reverse piezoelectric effect - modes of application Continuous Ultrasonic energy is Can produce thermal effects based on: Output intensity Treatment duration Pulsed Ultrasonic output is Produces non-thermal effects pulsed output Ultrasonic output is cycled “On” and “Off” On = Pulse length Off = Pulse interval Expressed as a ON/(ON+OFF) * 100 20mSec/(20mSec+10mSec) * 100 20/30 * 100 67% output frequency Measured in (MHz) 1 MHz = 1,000,000 waves per second Determines the of effects 1 MHz output Penetrates Thermal effects last longer More beam 3 MHz output Penetrates More collimated beam power & intensity Power The total amount of ultrasound energy produced by the generator ( ) Intensity Strength of the sound waves over the given area ( ) The higher the , the faster the If intensity is increased, treatment time should be and vice versa size of treatment area Should be limited to no more than If the area is too large, ultrasound won’t heat the tissues. Lecture #44 – Ultrasound transducer movement Use slow movement covering about Back and forth or circular strokes Keep the soundhead Keep the soundhead flat on the surface being treated coupling Ultrasonic energy cannot pass through A coupling medium is required Medium should be water-based coupling methods Direct coupling – use of a to deliver US energy Immersion coupling – use of to deliver US energy Best for body parts Bladder coupling – use of a commercial bladder pad to deliver US energy thermal effects Increased sensory nerve conduction velocity motor nerve conduction velocity of collagen-rich tissue vascular permeability structures collagen deposition blood flow Reduction of muscle spasm Effects are based on heating classifications heating rate Heating rate and magnitude are based on: Duty cycle Output frequency ( 1MHz vs. 3MHz) (W/cm2) Target tissue (muscle, ligament, tendon, etc.) Size of the treatment area non-thermal effects Increased cell membrane Altered rates of diffusion across the cell membrane Increased vascular permeability Increased Notes Reduction of edema Diffusion of ions Tissue regeneration Formation of stronger connective tissue non-thermal application Pulsed output % duty cycle Non-thermal output intensity Continuous output 100% duty cycle Low output intensity (less than 0.3 W/cm2) how does it work? As ultrasound wave exerts pressure against the cell wall, the membrane deforms slightly (referred to as micromassage) Acoustical Streaming (Microstreaming) acoustical streaming Ultrasound causes fluid between cells to flow Fluids strike cell membranes Produce Eddy currents displace ions and molecules Alter: Cell membrane permeability Cellular function stable cavitation Compression and expansion of in the blood and tissue Cellular effects ○ Increase in cell membrane diffusion ○ Increase cellular activity indications Bursitis Inflammatory conditions ( ) Joint stiffness Pain Muscle Spasm Acute injuries (non-thermal US) contraindications Acute injuries ( ) Areas of impaired circulation Anesthetic areas Over Over sites of active infection Over the spinal cord or large nerves in high doses Exposed metal that penetrates the skin (e.g., external fixation devices) Areas around the eyes, heart, skull, or genitals Lecture #44 – Ultrasound Over the thorax in the presence of an implanted pacemaker Pregnancy when used over the pelvic or lumbar areas Stress fracture sites or sites of osteoporosis Over the pelvic or lumbar area in menstruating female patients precautions Symptoms may after the initial treatment Use caution when applying ultrasound around the spinal cord The use of ultrasound over metal implants is not contraindicated Keep the sound head moving Use caution when applying ultrasound over epiphyseal plates of growing bone patient preparation Establish that no are present Determine the method and mode of ultrasound application to be used Clean the area to be treated Determine the type of coupling method to be used Identify a treatment area that is For direct coupling: spread the gel over the area to be treated Explain the sensations to be expected during the treatment: Mild to moderate warmth (but not pain or burning) for treatments for pulsed ultrasound Advise the patient to report any adverse, unusual, or painful sensations during the treatment. Notes initiation of the treatment Reduce the intensity to zero before turning on the power. Select the appropriate mode for the output (CONTINUOUS or PULSED) Set the timer to the appropriate treatment duration Begin slowly moving the sound head over the medium Press the START button to begin the treatment session Slowly increase the intensity Move the head at a slow pace ( ) Use firm, overlapping strokes If pain is experienced: Move the sound head at a rate Use a duty cycle Use a lower If the gel begins to wear away or if the sound head begins sticking on the skin, press the PAUSE button and termination of the treatment If the treatment is being terminated prematurely: Reduce the intensity before removing the transducer Clean the remaining gel from the patient’s skin Immediately initiate any post-treatment To ensure continuity of treatment sessions: Record the treatment parameters ○ Output ○ Intensity ○ Duration ○ ○ Running count of ultrasound treatments given for this condition
![Jiye Jin-2014[1].3.17](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005485437_1-38483f116d2f44a767f9ba4fa894c894-300x300.png)