frame the lesson
advertisement

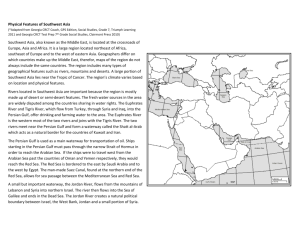
FRAME THE LESSON Student Expectations Bundled in Lesson Noun=Underline Verb=Italicize 4F: identify the location of major world countries such as Canada, Mexico, France, Germany, the United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, Norway, Sweden, Russia, South Africa, Nigeria, Iraq, Afghanistan, Israel, Iran, India, Pakistan, the People's Republic of China, the Republic of China (Taiwan), Japan, North and South Korea, Indonesia, and Australia 6B: identify the location of renewable and nonrenewable natural resources such as fresh water, fossil fuels, fertile soils, and timber Objective/Key Understanding: Describe the physical features and natural resources of Arabia and Iraq, and explain the importance of oil to the region. Explain the population patterns of Arabia and Iraq, identify the location of fresh water in the region. Closing Product/ Question/ Informal Assessment: CLASS: 6th Social Studies TEACHER: How is Yemen’s climate different from that of other countries on the Arabian Peninsula? How does this affect population in the region? What is one positive effect of oil on the region? What is one negative effect? Why farming difficult throughout much of the region? How would you describe population patterns in the region? Where do most people live? What is unique about the ethnic makeup of Kuwait, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates? What causes these countries in the region? LESSON DATE: January 25-26 M T W TH F Topic 6, Lesson 4: Geography of Arabia and Iraq Resources/Materials: Teaching Points & Activities: The mostly desert landscape of the region is rich in oil and poor in freshwater. Many residents live near freshwater supplies. Many of those who do no are supplied with water by pipelines connected to desalination plants. The region is mostly Arab Muslim, with large non-Arab minorities and small nonMuslim minorities. Pearson Contemporary World Cultures TE, pgs. 349-356 Pearson Contemporary World Cultures Digital Resources: Small Group Purposeful Talk Question Stems: Physical Features and Resources of Arabia and Iraq (p.350-352) Identify the location of Iraq, a major world country. Analyze information by identifying the cause-and effect relationships. Look at the information on the maps in this text and identify cause-and-effect relationship in settlement patterns. Where do you think most people in Iraq live? Climate, Water, and People in Arabia and Iraq (p.352-353) How does the region support its large urban populations? Is Arabia and Iraq a culturally unites region? Why or why not? Vocabulary: Plate fossil fuel desalination urbanized Majority Tigris Arabian Peninsula Euphrates Editable Presentation Start-Up Activity Interactive Flipped Video Analyzing Maps Analyze Charts Analyze Information Language Lesson: Arabic from Saudi Arabia Digital Activity: Oil & Water Digital Lesson Quiz Rigor & Relevance: (Real World Connection) Critical Writing Prompt: Why are oil and gas called fossil fuels? How are oil resources related to water supplies in dry countries like Saudi Arabia? We live in a global society. It’s important that students grasp the geographical and societal peculiarities to a particular region so that they can relate to the people around them. Engage Explore Explain Elaborate *Have students preview the lesson objectives and the list of key terms (p.349). Use the Editable Presentation found on the digital course to present the main ideas of the lesson (p. 349). Start Up Activity (p. 349) Project the Start Up Activity (p. 349). Have students look briefly at the Arabia and Iraq: Climate and Water Resources map. Have them locate the desalination plants on the map, and explain that these are plants that turn saltwater into freshwater. What would be required to build desalination plants and pipelines to carry the freshwater to different locations where it is needed? Why would the countries of the region need to turn saltwater into freshwater? *Tell students that in this lesson they will learn about the geography of Arabia and Iraq. *Divide the class in to groups. Each group is to read a section and be prepared to discuss and share findings with the class. Physical Features and Resources of Arabia and Iraq (p.350-352) Climate, Water, and People in Arabia and Iraq (p.352-353) *Students are to read assigned sections and use the Note Taking Study Guide to help them take notes and understand the text as they read. *Tell students that in this lesson they will learn about the geography of Arabia and Iraq. Physical Features and Resources of Arabia and Iraq (p.350-352) Iraq is located north of the Arabian Peninsula. It is west of Iran and south of Turkey. Arabia and Iraq are part of the continent of Asia. Climate, Water, and People in Arabia and Iraq (p.352-353) Most of Arabia and Iraq is desert, or an area that receives very little rainfall or snowfall. Most of the region lies within a worldwide belt in the subtropical latitude that contains many major deserts. *Guided Reading and Discussion Questions See Small Group Purposeful Talk Question Stems from the previous page for this portion of the lesson. *Analyzing Maps and Charts & Digital Activity See Online Resources from the previous page for this portion of the lesson. *Active Classroom Use the Sticky Note strategy to have students write three important ideas from the Flyover video. *Topic of Inquiry Students work in teams to examine different perspectives on this issue by analyzing several sources, arguing both sides of a Yes/No questions, then developing and discussing their own point of view on the question: Should the high Aswan Dam have been built? FRAME THE LESSON CLASS: 6th Social Studies TEACHER: Student Expectations Bundled in Lesson Noun=Underline Verb=Italicize 1B: analyze the historical background of various contemporary societies to evaluate relationships between past conflicts and current conditions 12A: identify and give examples of governments with rule by one, few, or many 19B: explain the significance of religious holidays and observances such as Christmas, Easter, Ramadan, the annual hajj, Yom Kippur, Rosh Hashanah, Diwali, and Vaisakhi in various contemporary societies LESSON DATE: January 27-28 Topic 6, Lesson 5: History of Arabia and Iraq Teaching Points & Activities: Resources/Materials: Iraq has a history as a birthplace of civilization and Arabia’s history as the birthplace of Islam. Both Arabia and Iraq played important roles in the growth and success of Muslim empires until their conquest by the Ottoman Turks. More recently, Iraq has been involved in a series of wars, first with Iran and then with the U.S. and its allies. Describe the civilizations of ancient Mesopotamia. Explain the origins and beliefs of Islam, including the significance of Ramadan and the annual haji, and trace the spread of Islam. Identify important events in modern Arabia and Iraq, including the creation of Iraq, the discovery of oil, and the Persian Gulf conflicts. Closing Product/ Question/ Informal Assessment: What major change to the way people lived occurred in Mesopotamia around 10,000 years ago? What disagreement between today’s Muslims originated in the 600s? How are Ramadan and the annual haji significant religious observances for Muslims? How did trade advance Islamic learning? What event caused the U.S. to send troops to Arabia and Iraq in 1991? Pearson Contemporary World Cultures TE, pgs. 357-365 Pearson Contemporary World Cultures Digital Resources: Objective/Key Understanding: M T W TH F Small Group Purposeful Talk Question Stems: Early Civilizations and Empires in Arabia and Iraq (p.358-359) How might Iraq’s past as Mesopotamia influence current conditions in the country? Historians sometimes call Mesopotamia “the cradle of civilization.” What do you think that means? When historians call Mesopotamia “the cradle of civilization,” are they stating a fact, expressing an opinion, or making a reasoned judgement? Islam and Islamic Civilizations (p. 360-363) How might the Muslim empire of the past affect current conditions in Arabia, Iraq, and beyond today? What impact does observing Ramadan have on people in different Muslim countries? Arabia and Iraq in Modern Times (p. 363-365) Analyze the historical background of various contemporary societies in this region. Evaluate the relationship between the past conflict of World War I and current conditions in Iraq. Vocabulary: civilization mosques Mesopotamia monotheism minority Ramadan Quran dictator haji caliph Mecca Critical Writing Prompt: Why was cuneiform a significant development in world history? What issue divided Muslims into Sunnis and Shias? Describe the government of Iraq under Saddam Hussein. Editable Presentation Start-Up Activity Interactive Flipped Video Sequence Events Interactive Maps: Assyrian and Muslim Interactive Timeline: History of Arabia and Iraq Since A.D. 610 Analyze Maps Analyze Information Digital Activity: The Origins and Impacts of Islam Digital Lesson Quiz Rigor & Relevance: (Real World Connection) We live in a global society. It’s important that students grasp the geographical and societal peculiarities to a particular region so that they can relate to the people around them. Engage Explore Explain Elaborate *Have students preview the lesson objectives and the list of key terms (p.357). Use the Editable Presentation found on the digital course to present the main ideas of the lesson (p. 357). Start Up Activity (p. 357) Project the Start Up Activity (p. 357). Tell students that many people in Arabia and Iraq observe Ramadan, a holy month when Muslims fast from sunrise to sunset. One celebration during Ramadan is iftar, when people gather at sun down to break their fast. Ask students to explain why religious holidays and observances are important in cultures around the world. Have students think of holidays and observances that are held in their community. *Tell students that in this lesson they will learn about the history of Arabia and Iraq, including how Islam and its holidays developed. *Divide the class in to groups. Each group is to read a section and be prepared to discuss and share findings with the class. Early Civilizations and Empires in Arabia and Iraq (p.358-359) Islam and Islamic Civilizations (p. 360-363) Arabia and Iraq in Modern Times (p. 363-365) *Students are to read assigned sections and use the Note Taking Study Guide to help them take notes and understand the text as they read. *Tell students that in this lesson they will learn about the history of Arabia and Iraq, including how Islam and its holidays developed. Early Civilizations and Empires in Arabia and Iraq (p.358-359) Mesopotamia refers to the valley of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. This region is mainly in present-day Iraq. Historians sometimes refer to Mesopotamia as being part of a Fertile Crescent, a crescent-shaped region stretching from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean coast. Islam and Islamic Civilizations (p. 360-363) In early Arabia, one important place was the city of Mecca. It was a trading and religious center, built at an oasis. People throughout the Arabian Peninsula traveled to Mecca. They went to worship at a shrine called the Kaaba. Many worshiped more than one god. In the A.D. 600s, however, this changed. Arabia and Iraq in Modern Times (p. 363-365) World War I brought much of the region under European control. The region’s countries gained independence later in the 1900s. Still foreign powers continued to play a role. *Guided Reading and Discussion Questions See Small Group Purposeful Talk Question Stems from the previous page for this portion of the lesson. *Analyzing Maps and Charts & Digital Activity See Online Resources from the previous page for this portion of the lesson. *Active Classroom Use the See-Think-Wonder activity with the Spread of the Muslim Empire layer of the Interactive Map. Have students work with a partner to answer the questions: What do you see? What does that make you think? What are you wondering about? Ask volunteers to share what they wonder about and discuss as a class possible answers. *Topic of Inquiry Students work in teams to examine different perspectives on this issue by analyzing several sources, arguing both sides of a Yes/No questions, then developing and discussing their own point of view on the question: Should the high Aswan Dam have been built? FRAME THE LESSON TEACHER: CLASS: 6th Social Studies LESSON DATE: January 29 M T W TH F Topic 6, Lesson 3: Arabia and Iraq Today Student Expectations Bundled in Lesson Noun=Underline Verb=Italicize 5C: explain the impact of geographic factors on economic development and the domestic and foreign policies of societies 12A: identify and give examples of governments with rule by one, few, or many Objective/Key Understanding: Describe the different kinds of governments the region has had, including monarchies and the dictatorship of Saddam Hussein. Explain political changes in the region, including regime change in Iraq and protests across the region. Compare and contrast Arabia and Iraq’s different religious and cultural traditions, including the changing role of women. Assess the role of oil in the economies and identify cultural issues in contemporary Arabia and Iraq. Closing Product/ Question/ Informal Assessment: What kind of government does Saudi Arabia have? Is it an example of rule by few, rule by many, or rule by one? How was political unrest in Bahrain influenced by its religious divisions? How are these divisions seen in Bahrain’s neighbors? Why is Wahhabism a significant influence in the region? How does the geographic factor of the presence of oil affect the domestic policies of countries in this region? What does it mean to diversify an economy? Resources/Materials: Teaching Points & Activities: The region is a mix of traditional and modern cultures Singleperson rules and new deomcracies Oil wealth and dependence Recent Conflicts Pearson Contemporary World Cultures TE, pgs. 366-375 Pearson Contemporary World Cultures Digital Resources: Small Group Purposeful Talk Question Stems: Governments in Arabia and Iraq (p.367-368) How is the government of Iraq different now from what it was like under Saddam Hussein? How has Kuwait become more democratic in recent years? Conflict and Change in Arabia and Iraq (p. 368-370) Do you think there might be people in Iraq who want to return to a dictatorship like Saddam Hussein’s? Why or why not? Which governments do you think is more stable: Bahrain’s or Yemen’s? Why? Arabia and Iraq’s Religion and Culture (p. 371-373) How has the region’s oil resources affected these countries’ domestic policies? Some women in Saudi Arabia defy the law and drive anyway. Why do you think being able to drive is so important to these women? Oil and the Economies of Arabia and Iraq (p. 373-375) Ask students to explain the impact of geographic factors on the domestic policies of societies in this region. How are Yemen, Bahrain, and Dubai different from other countries in the region? Vocabulary: Islamism absolute monarchies Saddam Hussein terrorism entrepreneurship hijab Baath Party constitutional monarchies Critical Writing Prompt: What is an absolute monarchy? Give an example of one in the region. What was the result of Bahrain’s protest movement? How has oil led to changes in the region’s culture? Despite great wealth, why has the region seen incomplete economic growth? Editable Presentation Start-Up Activity Reading and Note Taking Guide Interactive Flipped Video Interactive Chart: Contemporary Governments of Arabia and Iraq Analyze Graphs Digital Activity: Oil Economics Digital Lesson Quiz Rigor & Relevance: (Real World Connection) We live in a global society. It’s important that students grasp the geographical and societal peculiarities to a particular region so that they can relate to the people around them. Engage Explore Explain Elaborate *Have students preview the lesson objectives and the list of key terms (p.366). Use the Editable Presentation found on the digital course to present the main ideas of the lesson (p. 366). Start Up Activity (p. 366) Project the Start Up Activity (p. 366). Tell students that many countries in Arabia and Iraq are rich with fossil fuels. These resources are in great demand worldwide, and the region has become rich by selling oil and gas. How do you think the presences of oil and gas has affected your life? Give students a list of modern conveniences, such as ovens, cars, toasters, furnaces, and microwaves. Have them identify which ones use oil or gas. *Tell students that in this lesson they will learn about Arabia and Iraq today, including how oil and gas affect the lives of people there. *Divide the class in to groups. Each group is to read a section and be prepared to discuss and share findings with the class. Governments in Arabia and Iraq (p.367-368) Conflict and Change in Arabia and Iraq (p. 368-370) Arabia and Iraq’s Religion and Culture (p. 371-373) Oil and the Economies of Arabia and Iraq (p. 373-375) *Students are to read assigned sections and use the Note Taking Study Guide to help them take notes and understand the text as they read. *Tell students that in this lesson they will learn about Arabia and Iraq today, including how oil and gas affect the lives of people there. Governments in Arabia and Iraq (p.367-368) Monarchies govern most of Arabia today. Some are called kings, while others have a title of emir, or sultan. Saudi Arabia and some other states have absolute monarchies. The people have little or no say in politics. There are no legal limits to the ruler’s power. Absolute monarchy is an example of rule by one. Conflict and Change in Arabia and Iraq (p. 368-370) Since 2000, much change has come to Arabia and Iraq. As you have read, a U.S.-led invasion of Iraq toppled the regime of Saddam Hussein in 2003. It led to a decade of civil war and a new democracy. In 2011, the protest movement known as the Arab Spring spread to Bahrain and Yemen. Reformers in these countries called for more democratic governments. Arabia and Iraq’s Religion and Culture (p. 371-373) Islam and other traditions have shaped the cultures of Arabia and Iraq. So have the rich oil and natural gas reserves that come with the region’s geography. Oil has brought wealth and contact with outside cultures. The region’s people have worked to balance tradition and modern culture. Oil and the Economies of Arabia and Iraq (p. 373-375) The world today depends on oil to power cars, trucks, and other vehicles. Oil is a fuel for industries and for heating homes. Oil is also a raw material for plastics and other products. Oil in one of the world’s most important products. It is also vital source of income for this oil-rich region. *Guided Reading and Discussion Questions See Small Group Purposeful Talk Question Stems from the previous page for this portion of the lesson. *Analyzing Maps and Charts & Digital Activity See Online Resources from the previous page for this portion of the lesson. *Active Classroom After completing the tile sort, use the Quick Draw strategy to have students create illustrations that represent the three types of government found in Arabia and Iraq: democracy, constitutional monarchy, and absolute monarchy. *Topic of Inquiry Students work in teams to examine different perspectives on this issue by analyzing several sources, arguing both sides of a Yes/No questions, then developing and discussing their own point of view on the question: Should the high Aswan Dam have been built?