RANGER COLLEGE Syllabus COURSE NUMBER AND TITLE
advertisement

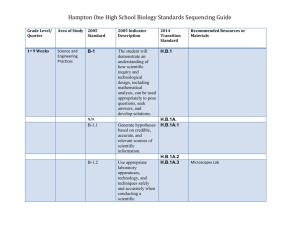
RANGER COLLEGE Syllabus COURSE NUMBER AND TITLE: Biology 1406 - General Biology I (online) CREDIT HOURS : 4 HRS/WK LEC 3 HRS/WK LAB: 3 Name of Instructor (Title): Gretchin Geye Office Location:Ranger College Brown County Center Office Hours: below Office Phone:325-641-5726 E-Mail: mailto:ggeye@rangercollege.edu Cell Number: (call or text between 9AM & 9PM) 325-642-7028 I. CATALOG DESCRIPTION Fundamental principles of living organisms, including physical and chemical properties of life, organization, function, evolutionary adaptation and classification. Detailed study of a typical cell, cell phenomena, mitosis, meiosis, nucleic acids, protein synthesis, basic principles of genetics and genetic expression, evolution and speciation. The history of early life, with representative examples studied in the laboratory. ***II. REQUIRED BACKGROUND / PREREQUISITES Passing score on TSI Reading section or equivalent alternate test is recommended. III. TEXTBOOK (S) ; READINGS; MATERIALS 1259335976 9781259335976 MHHE Hoefnagels: Connect and LearnSmart Labs Access Card for Biology: Concepts and Investigations © 2015 IV. METHODS OF INSTRUCTION Reading/lectures/notes Online practice, homework LearnSmart with Connect Lab Access Labs in which major biological principles will be demonstrated by examination of specimens, conducting experiments and viewing videos virtually. OFFICE SCHEDULE MONDAY: 3:45 - 5:00 PM TUESDAY: 3:45 - 5:00 PM WEDNESDAY: 3:45 - 5:00 PM THURSDAY & FRIDAY 9-10 AM The above schedule and procedures in this course are subject to change in the event of extenuating circumstances V. EXEMPLARY EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES NATURAL SCIENCES (N) N-1 to understand and apply methods and appropriate technology to the study of natural sciences; N-2 to recognize scientific and quantitative methods and the differences between these approaches and other methods of inquiry and to communicate findings, analyses, and interpretation both orally and in writing; N-3 to identify and recognize the differences among competing scientific theories; N-4 to demonstrate knowledge of the major issues and problems facing modern science, including issues that touch upon ethics, values, and public policies; N-5 to demonstrate knowledge of the interdependence of science and technology and their influence on, and contribution to, modern culture. VI. BASIC INTELLECTUAL COMPETENCIES B-1 Reading -the ability to analyze and interpret a variety of printed material. B-2 Writing - the ability to produce clear, correct and coherent prose adapted to purpose, occasion and audience. B-3 Speaking - the ability to communicate orally in clear, coherent and persuasive language appropriate to purpose, occasion and audience. B-4 Listening - the ability to analyze and interpret various forms of spoken communication. B-5 Critical Thinking - the ability to apply both qualitative and quantitative skills analytically and creatively to subject matter to evaluate arguments and construct alternative strategies. B-6 Computer Literacy - the ability to understand our technological society, use computer based technology in communication, solving problems and acquiring information. VII. COURSE OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the process of science as a way to understand the natural world. ( N-1, N-2, N-4, N-5) (B-1, B-4, B-5) 2. Describe the cell as the basic unit of life. (N-4) (B-1, B-4, B-5) 3. Describe the structure and expression of the genetic material in living organisms (N-1, N-4, N-5) (B-1, B-4, B-5) 4. Describe the process of cellular division. (B-1, B-4, B-5) 5. Describe the mechanics of passing characteristics from parent to offspring. (N-2, N-4) (B-1, B-4, B-5) 6. Describe the mechanism of organic evolution and adaptation. (N-3, N-4) (B-1, B-4, B-5) 7. Describe the major events that occurred on early Earth, and the origin of life (B-1, B-4, B-5) In order to evaluate the progress in achieving the course objectives each student will respond on written exams to questions in the following areas: - Distinguish between inductive and deductive reasoning. - List the steps in the scientific method. - List the assumptions of the scientific process. - List the characteristics of living organisms. - Describe the properties of water and carbon that make them essential for life. - List the four major groups of biological molecules. - List the components of typical cells and describe the function of each. - Describe the mechanisms for movement of materials into and out of cell. - List the three components of nucleotides. - Distinguish between deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid. - List the five nitrogen bases that occur in the genetic material and describe how these molecules form the basis of genetic information. - Define DNA transcription and DNA translation. - Describe the structure of proteins and the relationship between DNA and protein structure. - Describe the role of proteins in cellular physiology. - Distinguish between mitosis and meiosis. - Define the term homologous chromosomes. - List in sequence the stages in the mitotic cell cycle and describe the events that occur within the cell during each stage. - List in sequence the stages in the meiotic cell cycle and describe the events that occur within the cell during each stage. - Describe the three events that occur within the cell that bring about genetic variation of organisms. - Define allele, genotype and phenotype. - Describe Gregor Mendel’s two laws of inheritance. - Predict genetics of offspring from crosses of genetically known parents. - Define evolution in terms of population genetics and describe the primary factors that cause evolution. - Describe the conditions and outcomes of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. - Describe the mechanisms of natural selection and how this leads to adaptation. - Explain exaptation and the evolution of complex structures. - List and define the conditions that lead to speciation. - List the major steps in the origin of life. - Describe the conditions that scientist think occurred on early Earth - Explain the role of prokaryotes in the history of Earth environments VIII. COURSE CALENDAR (see attachments) IX. COURSE / CLASSROOM POLICIES 1) THE FINAL EXAM MUST BE PROCTORED!!!! This means that you will either need to come to one of the Ranger College campuses to take the exam OR have a Pre-approved proctor at another university that is closer in proximity to you. ALL proctored exams must be pre-approved by ME! 2) It is important that you understand there is both a LECTURE COMPONENT (75%) and a LAB COMPONENT (25%), however, your grade will be ONE grade as a combination of both. You will need to be very diligent in staying on top of both parts. Please check the calendar weekly to keep up with assignments and their due dates. 3) You must purchase the electronic textbook so that you will have access to the CONNECT site (with LABS), if you have trouble connecting to this please email me. Instructions for connecting are ON BLACKBOARD! ADA Statement: Ranger College provides a variety of services for students with learning and/or physical disabilities. The student is responsible for making the initial contact with the Ranger College Counselor. It is advisable to make this contact before or immediately after the semester begins. X. ASSESSMENT (Grading Procedures) Exams will consist of multiple choice and short answer questions and will cover all material discussed in class or in reading assignments. Each question will be graded as correct or incorrect in accordance with information in the text, lectures and readings. Exam grades will be taken as the points correct. Students missing lectures are responsible for getting notes from the instructor or classmates. Make-up exams, for exams missed due to an excused absence, will be given later in the semester. Students are strongly urged to not miss exams. The course grade will be computed as follows: Average of lecture exams = 3/4 (Lecture Ave. * 3) + Lab Ave Lab average = 1/4 4 Letter grades will be assigned as follows: 90-100 = A, 80-89 = B, 70-79 = C, 60-69 = D, below 60 = F XI. ADMISSIONS, EMPLOYMENT, AND PROGRAM POLICIES OF RANGER COLLEGE ARE NONDISCRIMINATORY IN REGARD TO RACE, CREED, COLOR, SEX, AGE, DISABILITY, AND NATIONAL ORIGIN. XII. RECEIPT OF SYLLABUS (see attachments)