Hashing Worksheet
advertisement

Hashing using Examples
Hashing is a method of creating a quick lookup of data in a table. The simple rule for hashing
data is to convert the data into its ASCII equilvilent, add this together then calculate the
following where d is the sum total of ASCII characters in the string:
d MOD table size = hash
For the purposes of this exercise, navigate to www.ideone.com and select the Pascal(FPC)
language.
Annotate the code below with its functionality, then copy it into the IDE.
program ideone;
Uses sysutils, strutils;
var
hashed : integer;
name : string;
table_size : integer;
function hash(Mystr : string; table_size : Integer) : Integer;
var result,count : Integer;
hash_char : char;
test_string : string;
begin
result := 0;
for count := 1 to Length(Mystr) do
begin
test_string := MidStr(Mystr,count,1);
hash_char := test_string[1];
write(ord(hash_char));
if count <> Length(Mystr) THEN
begin
write('+');
end;
result:= result + ord(hash_char);
end;
write('= ', result);
writeln(' ');
hash := result MOD table_size;
write(result, ' MOD ',table_size,' = ', hash);
writeln(' ');
end;
begin
table_size := 12;
hash('Holly',table_size);
end.
Run your hashing program and for each of the following questions, paste a screen capture
of your results:
1. What is the meaning of
hash(‘Mr Bush’,table_size);
2. Run the program calling the function for your own name & complete the table below:
Hash_ID
3. What is the meaning of
Name
ASCII Value
ord(hash_char);
4. Run the program calling the function for ‘Fred Flintstone’ and ‘Barney Rubble’ & complete
the table below:
Hash_ID
5. What is the meaning of
Name
Fred Flintstone
Barney Rubble
ASCII Value
hash_char := test_string[1];
6. Run the program calling the function for both Mr Bush & Mrs Billinghurst. Why do your
teachers cause an error in a hash table?
Hash_ID
Name
Mr Bush
Mrs Billinghurst
ASCII Value
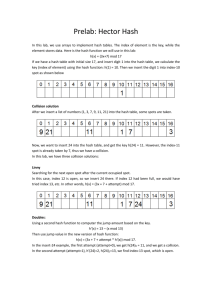
When collisions occur, there are two methods of dealing with this in a hash table.
Collision Option 1: locate the next available location
This is known as Open Hashing. Further resources on Hashing methods can be found here:
http://filestore.aqa.org.uk/subjects/AQA-2510-W-TRB-COMP3HASH.PDF
1. Describe Open Hashing in your own words.
2. Use the algorithm below to adjust the program to identify and deal with collisions.
create hash value
store value at hash location
IF data exists at location
THEN hash hash +1
LOOP until space found
OUTPUT original hash value
OUTPUT new hash value
3. Run the program calling the function for the first names of all members of the class
(where names duplicate, add an initial)
Collision Option 2: create a linked list using pointers.
This is known as Closed Hashing. Further resources on Hashing methods can be found here:
http://filestore.aqa.org.uk/subjects/AQA-2510-W-TRB-COMP3HASH.PDF
1. Describe Closed Hashing in your own words.
2. Use the algorithm below to adjust the program to identify and deal with collisions.
create has value
store value at hash location
IF data exists at location
THEN store value in linked list of hash location
pointer ID of linked list of hash location
OUTPUT original hash value
OUTPUT new hash value
3. Run the program calling the function for the first names of all members of the class
(where names duplicate, add an initial)
4. Draw out a visual example of how your data has been stored.