BCLN_Chem_11_U7P1_Ty..
advertisement
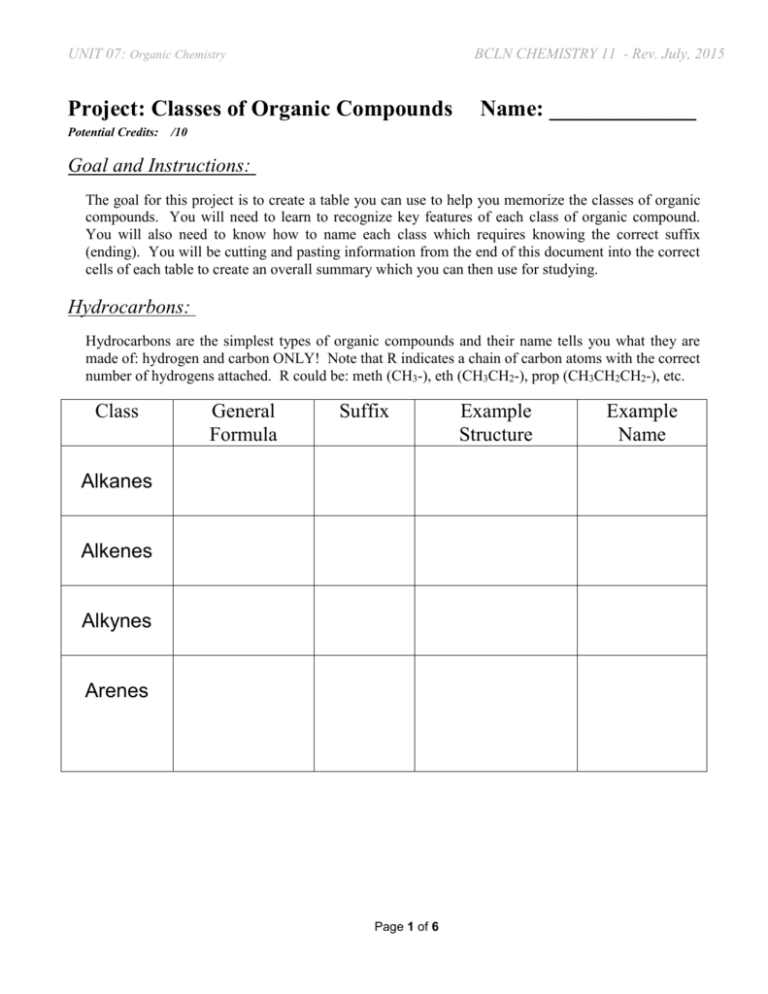
UNIT 07: Organic Chemistry BCLN CHEMISTRY 11 - Rev. July, 2015 Project: Classes of Organic Compounds Potential Credits: Name: _____________ /10 Goal and Instructions: The goal for this project is to create a table you can use to help you memorize the classes of organic compounds. You will need to learn to recognize key features of each class of organic compound. You will also need to know how to name each class which requires knowing the correct suffix (ending). You will be cutting and pasting information from the end of this document into the correct cells of each table to create an overall summary which you can then use for studying. Hydrocarbons: Hydrocarbons are the simplest types of organic compounds and their name tells you what they are made of: hydrogen and carbon ONLY! Note that R indicates a chain of carbon atoms with the correct number of hydrogens attached. R could be: meth (CH3-), eth (CH3CH2-), prop (CH3CH2CH2-), etc. Class General Formula Suffix Alkanes Alkenes Alkynes Arenes Page 1 of 6 Example Structure Example Name UNIT 07: Organic Chemistry BCLN CHEMISTRY 11 - Rev. July, 2015 Halogen Compounds: In a halogen compound, one or more of the hydrogen atoms from a hydrocarbon is replaced by a halogen. The halogens are fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine and astatine. The general letter used for a halogen is X. In general a halogen is considered to be a substituent so, in the name, they go at the start (prefix) rather than the end (suffix) Class General Formula Prefix Example Structure Example Name Alkylhalides Arylhalides Oxygen: These three classes of compounds contain oxygen but NOT a C=O double bond. Class General Formula Suffix Alcohols Phenols Ethers Page 2 of 6 Example Structure Example Name UNIT 07: Organic Chemistry BCLN CHEMISTRY 11 - Rev. July, 2015 Carbonyls: These four classes all contain a carbon-oxygen double bond (C=O). It's important you recognize the differences between them and learn how to tell them apart from each other. Class General Formula Suffix Example Structure Example Name Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic Acids Esters Nitrogen: These two classes contain nitrogen atoms. One of them also contains a carbonyl (C=O) Class General Formula Suffix Example Structure Amines Amides Page 3 of 6 Example Name UNIT 07: Organic Chemistry BCLN CHEMISTRY 11 - Rev. July, 2015 Goal and Instructions: In this section you should type out something that stands out for each class. A few are done for you! Class Distinguishing Feature Alkanes Has only C and H. No double or triple bonds. Alkenes Alkynes Arenes Alkylhalides Arylhalides Alcohols Has a halogen and a benzene group Has a hydroxyl (OH) group. Phenols Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic Acids Has a carbonyl (C=O) and an OH Esters Amines Amides Page 4 of 6 UNIT 07: Organic Chemistry BCLN CHEMISTRY 11 - Rev. July, 2015 General Formulas: Suffixes and Prefixes: -oxy -ane Halo- -ol -amide -al -ene -phenol -one -yne -amine -benzene -oic acid Halo- -yl -oate -ane Page 5 of 6 UNIT 07: Organic Chemistry BCLN CHEMISTRY 11 - Rev. July, 2015 Example Structures: Example Names: Methyl Ethanoate Chloropropane Ethanamide Methylbenzene 2-Butene Propanal Butanone Bromobenzene Propyne Ethylamine 2- Propanol 2-Methylphenol Methoxyethane Propanoic Acid Propane Page 6 of 6