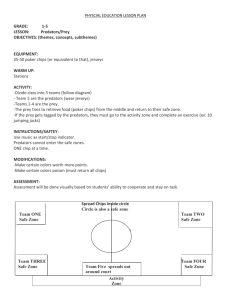
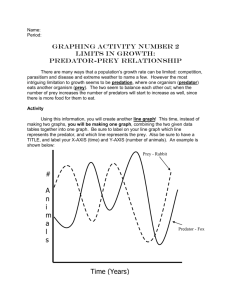
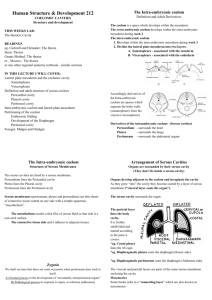
Zoology Study Guide
advertisement

Zoology - Comprehensive Final Exam Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. The species of tortoises that Darwin found on the Galápagos Islands displayed different structural adaptations. One of the adaptations that Darwin noted was the a. similarity in the tortoises’ embryos. b. difference in shell markings of the tortoises. c. variation in length of the tortoises’ necks. d. difference in number of eggs in each tortoise’s nest. 2. Lamarck’s theory of evolution includes the concept that new organs in a species appear as a result of a. continual increases in population size. b. the actions of organisms as they use or fail to use body structures. c. an unchanging local environment. d. the natural variations already present within the population of organisms. 3. When lions prey on a herd of antelope, some antelope are killed and some escape. Which part of Darwin’s concept of natural selection might be used to describe this situation? a. acquired characteristics c. survival of the fittest b. reproductive isolation d. descent with modification 4. According to Darwin’s theory of natural selection, the individuals that tend to survive are those that have a. characteristics their parents acquired by use and disuse. b. characteristics that plant and animal breeders value. c. the greatest number of offspring. d. variations best suited to the environment. 5. Darwin’s concept of evolution was NOT influenced by a. the work of Lyell. b. knowledge of the structure of DNA. c. his collection of specimens. d. his trip on the H.M.S. Beagle. 6. The number and location of bones of many fossil vertebrates are similar to those in living vertebrates. Most biologists would probably explain this fact on the basis of a. the needs of the organisms. c. the struggle for existence. b. a common ancestor. d. the inheritance of acquired traits. 7. Darwin’s theory of evolution is based on the idea(s) of a. natural variation and natural selection. b. use and disuse. c. a tendency toward perfect, unchanging species. d. the transmission of acquired characteristics. 8. Scientists assign each kind of organism a universally accepted name in the system known as a. traditional classification. c. binomial nomenclature. b. the three domains. d. cladistics. 9. For many species, there are often regional differences in their a. common names. c. taxa. b. scientific names. d. binomial nomenclature. 10. The second part of a scientific name is unique to each a. order in its class. c. genus in its family. b. family in its order. d. species in its genus. ____ 11. Several different classes make up a a. kingdom. c. family. b. phylum. d. genus. ____ 12. Which two kingdoms did Linnaeus recognize? a. bacteria and animals c. plants and animals b. plants and fungi d. protists and animals ____ 13. Traditional classifications tended to take into account primarily a. extinct organisms. c. DNA similarities. b. RNA similarities. d. general similarities in appearance. ____ 14. Sometimes organisms that are not closely related look similar because of a. convergent evolution. c. mutations. b. molecular clocks. d. reclassification. ____ 15. In an evolutionary classification scheme, species within one genus should a. be more similar to each other than they are to other species. b. not be similar in appearance. c. be limited to species that can interbreed. d. have identical genes. ____ 16. An analysis of derived characters is used to generate a a. family tree based on external appearance. b. family tree based on DNA structure. c. cladogram. d. traditional classification system. ____ 17. What is true about dissimilar organisms such as a cow and a yeast? a. They are not related at all. b. Their degree of relatedness cannot be evaluated. c. Their degree of relatedness can be determined from their genes. d. They can interbreed and thus are the same species. ____ 18. Which of the kingdoms in the six-kingdom system of classification was once grouped with plants? a. Animalia c. Fungi b. Carnivores d. Protista ____ 19. Organisms in the kingdoms Eubacteria and Archaebacteria were previously grouped in a kingdom called a. Animalia. c. Monera. b. Fungi. d. Eukarya. ____ 20. An animal is each of the following EXCEPT a. multicellular. c. heterotrophic. b. autotrophic. d. eukaryotic. ____ 21. Animals that have no backbone, or vertebral column, are called a. vertebrates. c. deuterostomes. b. ectoderms. d. invertebrates. ____ 22. When an animal’s environment changes, sexual reproduction improves a species’ ability to a. react. b. increase its numbers rapidly. c. evolve. d. produce genetically identical offspring. ____ 23. A blastula is a stage in the development of an embryo that consists of a a. solid ball of cells. c. flat sheet of cells. b. hollow ball of cells. d. folded sheet of cells. ____ 24. Which term is NOT associated with sponges? ____ 25. ____ 26. ____ 27. ____ 28. ____ 29. ____ 30. ____ 31. ____ 32. ____ 33. ____ 34. ____ 35. ____ 36. ____ 37. ____ 38. a. choanocytes c. spicules b. medusa d. gemmules Which of the following best describes the feeding habits of sponges? a. predators c. parasites b. filter feeders d. detritivores The benefit of a sponge’s producing gemmules is that the gemmules a. are a form of sexual reproduction. b. defend the sponge against predators. c. help to filter food for the sponge. d. allow the sponge to survive difficult environmental conditions. Which of the following animals has an asymmetrical body plan? a. jellyfish c. sponge b. coral d. none of the above Sponges benefit some marine animals by a. providing a habitat. c. poisoning their predators. b. eating diseased coral. d. supplying them with oxygen. Cnidocytes help a cnidarian survive by a. storing food. c. paralyzing prey. b. forming colonies. d. providing movement. The body symmetry of a cnidarian is a. radial in the medusa stage and bilateral in the polyp stage. b. radial in both the medusa and polyp stages. c. bilateral in both the medusa and polyp stages. d. bilateral in the medusa stage and radial in the polyp stage. Cnidarians in the class Anthozoa are distinguished by a. having only colonial species. c. reproducing only sexually. b. having only a polyp stage. d. obtaining food only from symbionts. The Portuguese man-of-war is a member of what class of cnidarian? a. Hydrozoa c. Anthozoa b. Scyphozoa d. Porifera Which of the following is NOT true about flatworms? a. They have a fluid-filled body cavity called a coelom. b. They are the simplest animals to have three embryonic germ layers. c. They are acoelomates. d. They are bilaterally symmetrical. In free-living flatworms, what organ pumps food into the digestive cavity? a. coelom c. pharynx b. ganglia d. flame cells Many flatworms can detect changes in the amount of light in their environment using groups of cells called a. flame cells. c. ganglia. b. nerve cords. d. eyespots. In the tapeworm, both male and female reproductive organs are contained in each mature a. scolex. c. cyst. b. proglottid. d. egg. In a pseudocoelom, mesoderm partially lines the a. germ layer. c. blood vessels. b. body cavity. d. pharynx. Which of the following is NOT true about roundworms? ____ 39. ____ 40. ____ 41. ____ 42. ____ 43. ____ 44. ____ 45. ____ 46. ____ 47. ____ 48. ____ 49. ____ 50. a. They have a digestive system with two openings. b. They have specialized tissues and organ systems. c. They are segmented worms. d. They have pseudocoeloms. Which of these animals has a true coelom? a. filarial worm c. planarian b. tapeworm d. leech In annelids, nitrogen-containing wastes are eliminated by a. clitella. c. nephridia. b. parapodia. d. gills. The muscular extension of a leech that penetrates the tissue of its host is the a. septum. c. proboscis. b. radula. d. ganglion. The larvae of many marine annelids are ecologically important because they a. poison coral reefs. b. are eaten by fishes and other marine animals. c. feed on earthworms. d. none of the above Which of the following is NOT true about mollusks? a. They usually have an external or internal shell. b. They are all filter feeders. c. They are soft-bodied animals. d. They have tube-shaped nephridia to remove ammonia from blood. The tubelike structure through which water enters and leaves a mollusk’s body is the a. sinus. c. coelom. b. siphon. d. mantle cavity. The most active mollusks are the a. gastropods. c. bivalves. b. cephalopods. d. nudibranchs. Which cephalopods have external shells? a. nautiluses c. octopi b. squid d. cuttlefish The appendages of arthropods are a. found only on the head. b. hard and immovable. c. jointed and extend from the body wall. d. divided into six branches. All of the following are true about arthropods EXCEPT that a. they have a closed circulatory system. b. they have an exoskeleton made of chitin. c. they include herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores. d. they move using muscles controlled by the nervous system. An arthropod is vulnerable to predators during the molting period because a. it must come out of hiding to molt. b. its new exoskeleton is soft. c. molting cannot occur without the assistance of predators. d. predators are more numerous during this period. The function of mandibles is to a. bite and grind food. c. propel an arthropod when it swims. ____ 51. ____ 52. ____ 53. ____ 54. ____ 55. ____ 56. ____ 57. ____ 58. ____ 59. ____ 60. ____ 61. ____ 62. ____ 63. b. sense the environment. d. support an arthropod when it walks. An example of a chelicerate is a a. lobster. c. crayfish. b. centipede. d. spider. Spiders feed by a. swallowing their prey whole. b. biting off and swallowing pieces of their prey. c. sucking up prey tissues that have been liquefied by enzymes. d. sipping nectar through a tubelike mouthpart. An insect can detect minute movements in its environment by using its compound eyes and its a. Malpighian tubules. c. chelicerae. b. tracheal tubes. d. sensory hairs. Which of the following explains why flying has been beneficial to insects? a. Nymphs can escape most predators. b. Insects can disperse long distances and colonize a variety of habitats. c. Insect societies can communicate without using pheromones. d. The insect body plan can function with only two sections. An example of an insect that undergoes incomplete metamorphosis is the a. moth. c. beetle. b. bee. d. chinch bug. In most species of echinoderms, respiration occurs mainly in the a. tube feet. c. ring canal. b. madreporite. d. radial canals. The skeleton of an echinoderm is an a. exoskeleton made of calcium carbonate. b. exoskeleton made of chitin. c. endoskeleton made of calcium carbonate. d. endoskeleton made of chitin. The water vascular system of echinoderms is involved with each of the following body functions EXCEPT a. respiration. c. movement. b. circulation. d. reproduction. One characteristic that made early animals different from all animals of today was their a. habitat. c. body plan. b. body segmentation. d. bilateral symmetry. The classification of an animal as a deuterostome or a protostome is based on a. its body symmetry. b. whether or not it has a coelom. c. what happens to the blastopore. d. the number of germ layers it has. An acoelomate is an animal that has a. a body cavity lined with endoderm and ectoderm. b. a body cavity partially lined with mesoderm. c. a body cavity completely lined with mesoderm. d. no body cavity between the germ layers. Which invertebrates exhibit radial symmetry? a. cnidarians and echinoderms c. roundworms and annelids b. sponges and flatworms d. mollusks and arthropods Cephalization refers to the ____ 64. ____ 65. ____ 66. ____ 67. ____ 68. ____ 69. ____ 70. ____ 71. ____ 72. ____ 73. ____ 74. a. division of the body into upper and lower sides. b. concentration of sense organs and nerve cells in the front of the body. c. joining together of specialized cells to form tissues. d. formation of a body cavity between the germ layers. The distinguishing feature of a closed circulatory system is that a. it does not include a heart. b. blood is contained within vessels that extend throughout the body. c. blood is kept at low pressure. d. blood is circulated less efficiently than in an open circulatory system. An example of an invertebrate with a hydrostatic skeleton is a(an) a. spider. c. sea star. b. sponge. d. earthworm. An endoskeleton is a a. shell of a mollusk. b. fluid-filled body cavity that supports the muscles. c. structural support located inside the body. d. hard body covering made of chitin. Which statement refers to sexual reproduction? a. All offspring are genetically identical to the parent. b. Offspring are produced from the fusion of male and female gametes. c. An organism breaks into pieces that grow into new individuals. d. New individuals are produced from outgrowths of the parent’s body wall. Which of these chordate characteristics exists as paired structures? a. tail c. pharyngeal pouch b. notochord d. nerve cord Which of the following statements about a vertebrate’s skeleton is INCORRECT? a. It supports and protects the body. b. It is an endoskeleton. c. It grows as the animal grows. d. It is made entirely of nonliving material. Lancelets belong to the phylum a. Urochordata. c. Vertebrata. b. Cephalochordata. d. Chordata. In most fishes, the structures that are most important for obtaining oxygen from water are the a. scales. c. lungs. b. gills. d. vertebrae. Fishes that lived during the late Cambrian Period a. lacked paired fins. b. had powerful jaws. c. had limbs. d. had soft bodies with little or no armor. All fishes in the class Chondrichthyes are alike in the a. foods that they eat. c. shape of their bodies. b. size and form of their teeth. d. composition of their skeletons. Which feature distinguishes most fishes from most amphibians? a. a vertebral column b. scales c. breathing with gills during at least part of the life cycle d. living in water during at least part of the life cycle ____ 75. A frog’s tympanic membranes would be most useful for a. enabling the frog to jump long distances. b. filtering wastes from the frog’s blood. c. listening to the mating calls of other frogs. d. keeping the frog’s eyes from drying out on land. ____ 76. Which of the following is NOT an adaptation for a completely terrestrial life? a. limb girdles c. scaly skin b. lungs d. amniotic egg ____ 77. Compared with the limbs of most amphibians, the limbs of reptiles tend to be a. smaller and weaker. b. capable of carrying less weight. c. located farther under the body. d. less specialized in form and function. ____ 78. A four-chambered heart is found in a. tuataras. c. turtles. b. snakes. d. alligators. ____ 79. Which of the following statements about temperature regulation in birds is NOT correct? a. Birds are endotherms. b. A bird’s body temperature depends on the temperature of the outside environment. c. Bird’s can generate their own body heat. d. Feathers help birds conserve body heat. ____ 80. The structure of a bird’s heart ensures that a. oxygen-rich blood never mixes with oxygen-poor blood. b. oxygen-rich blood is always pumped to the lungs. c. oxygen-poor blood is always pumped to the body. d. oxygen-poor blood never enters the heart. ____ 81. If a bird has a hooked bill and sharp talons, it might be a(an) a. water bird. c. bird of prey. b. ostrich. d. perching bird. ____ 82. Which organ is used by a cow to feed her newborn calf? a. mammary gland c. marsupium b. placenta d. rumen ____ 83. The first true mammals appeared a. about the same time dinosaurs became dominant. b. long after dinosaurs became extinct. c. about the same time amphibians became extinct. d. long after birds appeared. ____ 84. Which trait is NOT characteristic of mammals? a. external fertilization b. nourishing young with milk c. providing care for young after birth d. generating body heat ____ 85. In which of the following mammals does an embryo spend the most time developing inside the mother? a. echidna c. kangaroo b. elephant d. koala ____ 86. Proboscideans are mammals that a. have sharp teeth and claws. b. have trunks. c. spend most of their time underwater. ____ 87. ____ 88. ____ 89. ____ 90. ____ 91. ____ 92. ____ 93. ____ 94. ____ 95. ____ 96. ____ 97. d. have a single pair of long, curved incisors. The similarities in body structure between an anteater and an aardvark are the result of a. climate changes. c. convergent evolution. b. habitat destruction. d. adaptive radiation. Having a thumb that can move against the other fingers makes it possible for a primate to a. hold objects firmly. b. merge visual images. c. display elaborate social behaviors. d. judge the locations of tree branches. Hominids differ from other primates on the basis of all of the following EXCEPT a. brain size. c. method of locomotion. b. method of reproduction. d. shape of the hip bones. For a behavior to evolve under the influence of natural selection, that behavior must a. improve survival and reproduction. b. influence physical characteristics. c. be acquired through learning. d. be related to predator avoidance. Animals that have very simple nervous systems cannot a. detect external stimuli. b. process information from their senses. c. respond to stimuli. d. exhibit complex behaviors. Complex inborn behaviors include each of the following EXCEPT a. web-building in spiders. b. nest-building in birds. c. potato-washing in macaques. d. suckling of newborn mammals. Insight learning is a form of behavior that a. is characterized by decreased responsiveness to unimportant stimuli. b. involves random responses that lead to either reward or punishment. c. involves applying something already learned to a new situation. d. is performed correctly without any previous experience. In Pavlov’s experiments on classical conditioning, dogs a. learned to associate food with salivation. b. learned to ring a bell whenever they were hungry. c. associated a new stimulus with a reward. d. were conditioned to produce an innate behavior in response to food. Imprinting is a form of behavior that a. is restricted to birds. b. is often used in the training of adult animals. c. occurs during a specific time in young animals. d. always involves the sense of sight. An animal is most likely to enter into dormancy when a. it is advantageous to be active. c. food is very plentiful. b. resources are most difficult to find. d. the weather is very mild. Animals are LEAST likely to migrate out of an area where a. there is little or no seasonal change in weather. b. food becomes scarce during part of the year. c. competition for resources increases during part of the year. d. winters are very cold and snowy. ____ 98. It is advantageous for grazing mammals to gather in groups because groups a. can make the available food resources last longer. b. can migrate more easily than individuals can. c. are more difficult for predators to locate than individuals are. d. offer greater protection from predation. ____ 99. In some species of balloon flies, males spin balloons of silk and carry them while flying. If a female approaches one of the males and accepts his balloon, the two will fly off to mate. This type of behavior is an example of a. aggression. c. courtship. b. territorial defense. d. language. ____ 100. Nocturnal animals that have a poorly developed sense of smell are most likely to communicate by a. sound signals. c. pheromones. b. visual displays. d. chemical signals.